Discover the basics of cloud efficiency as well as six advanced data-driven strategies you can use to make your cloud environment more efficient.
With incredibly complex cloud architecture — that may even include Kubernetes and multi-tenant infrastructure — organizations are finding it hard to measure and monitor the performance and cost of their cloud environments.
To stay competitive, organizations should aim to be as efficient as possible, which can help companies to lower costs, increase margins, and improve cloud efficiency.
In this guide, we cover the basics of cloud efficiency and six advanced, data-driven strategies to make your cloud environment more efficient.
What Is Cloud Efficiency — And Why Does It Matter For Your Budget In 2026?
To some cloud users, cloud efficiency entails attaining remote connectivity to their business infrastructure. Others use it to describe resource utilization in their data centers, while many understandably link it to performance and robustness.
Although all these definitions are admissible, cloud efficiency is best described by combining them. Think of it as a holistic concept that relies on multiple dynamic factors.
Simply put, you could say that cloud efficiency refers to your capacity to utilize cloud resources in the best possible way and at the lowest possible cost while, at the same time, minimizing cloud wastage.
Achieving cloud efficiency has become particularly critical in recent times, as organizations continue to consume more resources than they actually need. Over the past few years, businesses have developed a tendency to expand their cloud deployments as they grow blindly.
This is how they ultimately end up with complex cloud architectures marred by idle resources, leading to wasted cloud spend.
In 2020, for instance, early research by Gartner established that while the market for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) would grow to $50 billion by the end of the year, companies were set to lose over $17 billion in wasted cloud spending due to idle resources.
What Are The Cost Challenges Of The Cloud?
Some of the principal issues that make it particularly difficult for organizations to achieve cost efficiency are:
- Lack of cloud spend insight. While total usage costs are obvious, many companies cannot break down the figures to reveal the precise cost metrics for each resource. This lack of visibility leads to what is popularly known as cloud sprawl — where organizations haphazardly scale up their cloud resources without proper management.
- Billing complexity. For users hoping to generate cloud spend insights from their bills, it turns out cloud platforms are never that forthcoming. You’ll receive your monthly cloud bill, but it’ll come with incomprehensible details about your cloud spending.
AWS is one example of a platform that’s infamous for this. Although its default cost and usage reports appear exhaustive, users often struggle to make sense of the complex technical specifications. So far-reaching is the problem that, from a survey of 7,500 AWS users, 95% admitted that bills are the most confusing part of the Amazon Cloud platform.
- Misaligned cost optimization strategies across teams. Some organizations mistakenly assume that cloud cost management is exclusively meant for IT teams. As such, they introduce one-sided cost-reduction strategies, with other departments taking a back seat.
- Manual cost management and optimization. Until recently, it was common for DevOps teams to manually analyze their cloud usage trends and calculate costs before adjusting resource allocations for each application.
This whole approach is not only time-consuming and burdensome but also error-prone, making it impossible to guarantee cloud efficiency.
6 FinOps-Ready Ways To Boost Cloud Efficiency
Now that we’ve ruled out traditional approaches, here are six proven strategies that the most advanced enterprises are using to improve their cloud efficiency. These are the steps you should follow to boost performance, reduce cloud costs, and increase your overall output:
1. Minimize the movement of data
With hybrid being one of the most preferred cloud setups across organizations, vast volumes of data are regularly transferred between public and on-premises environments.
This whole to-and-from process requires both time and resources. So, the more data you choose to transfer between environments, the more resources you stand to consume, and the longer it’ll take to relay everything.
For optimal system performance, you should minimize data movement between your cloud servers and the company’s on-premises environment. You could start by carefully classifying your data, then selecting the optimal environment for each category.
Mission-critical data, for instance, ought to be stored on on-premises servers, with remote data centers reserved for non-mission-critical data and applications.
2. Select the most appropriate instances
Leading IaaS providers offer a range of computing instances to cater to different workloads.
On AWS, you’ll find EC2 instances that provide varying combinations of networking, storage, CPU, and memory capacities. Some instances are optimized for general computing, while others are meant for storage, accelerated computing, etc.
To retain the best resources at the lowest possible cost, you should take the time to select the most suitable instances aligned with your cloud computing objectives.
If the instance is too small, you may save money but then end up impeding performance. And if it happens to be too big, your workload will benefit from increased performance, but you’ll be drowning in wasted cloud spend.
3. Take advantage of autoscaling
You don’t have to restrict your computing to the default capacities provided by instances. To cater to dynamically changing needs, cloud platforms can automatically scale user resources on demand. Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, and AWS are all known to add or remove instances and related resources as workloads shift.
For example, you can capitalize on their load balancers to avoid overloading your instances during workload spikes. Once you set appropriate autoscaling rules based on expected utilization trends, the load balancer will monitor and distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances.
4. Track performance
Autoscaling helps, but it’s not enough. To truly optimize cloud efficiency, you need deep visibility into real-time cloud monitoring metrics that show how your workloads behave.
Track key metrics like:
- CPU and GPU use
- Memory utilization
- Disk I/O and throughput
- Network latency and bandwidth
- Request rates (RPS)
- Error rates and failed requests
- Pod/container restart frequency
- Queue depth and processing time
- Cost per request / per workload
- Idle resource hours and orphaned volumes
This is where you leverage not only built-in analytical tools but also third-party services that can track performance in real time. You should be able to keep tabs on everything that’s going on in your cloud environment.
5. Supplement the cloud network with caches
While storing data on cloud servers is a good way to conveniently enable remote access, transferring it to and from your local network is another problem altogether. Moving the data takes time, which could hamper your applications’ responsiveness.
One way to speed up the transfer process is to use cache services compatible with your cloud platform. This will mirror your cloud data across a content delivery network with multiple cache servers — minimizing the relative data transfer distance.
Instead of loading files from the original cloud server, your applications will quickly retrieve data from the nearest cache server.
And most importantly…
6. Implement cloud cost intelligence
Since cloud efficiency cannot be achieved without minimizing costs, cloud performance optimization should always go hand in hand with cloud cost management.
What Is AI’s Impact On Cloud Efficiency?
AI has introduced a new layer of complexity and opportunity in cloud efficiency. Modern workloads increasingly include model training, inference, vector databases, and GPU-accelerated compute.
See the state of AI costs in 2025 here.
These deliver speed and intelligence, but also introduce new efficiency challenges:
- GPU demand and use. GPUs, TPUs, and custom accelerators (such as AWS Trainium) deliver outsized performance gains but are expensive to run idle. Efficiency now depends on scheduling, use, and workload routing — not just instance rightsizing.
- Model lifecycle costs. Training and fine-tuning are only part of the cost story. Serving, re-training, and monitoring model drift all carry cost footprints that need visibility and control.
- Data movement and egress. AI systems frequently move large datasets across storage layers, pipelines, and inference services. Excessive data transfer and egress fees can quietly erode efficiency.
- New cost units. AI introduces real-time cost drivers such as:
- Cost per inference or per 1,000 tokens
- Cost per embedding/vector search
- GPU cost per training hour
- Cost per AI user or workflow
For more insights into how companies are measuring and improving cloud use, see our article on Cloud Efficiency Rate. To dig even deeper into the implications of modern AI workloads on efficiency, check out our guide on GenAI Efficiency.
How Can You Ensure That Your Cloud Spending Is Efficient?
CloudZero isn’t just a better way to slice and dice your bill. By enriching your cost with services metadata, telemetry, and more, the CloudZero cost intelligence platform lets you see your costs from any angle.
You can unlock previously impossible unit-cost metrics (like cost per feature, cost per customer, etc.), and drill down and zoom out on cost — with way less effort than legacy cost-reporting tools.
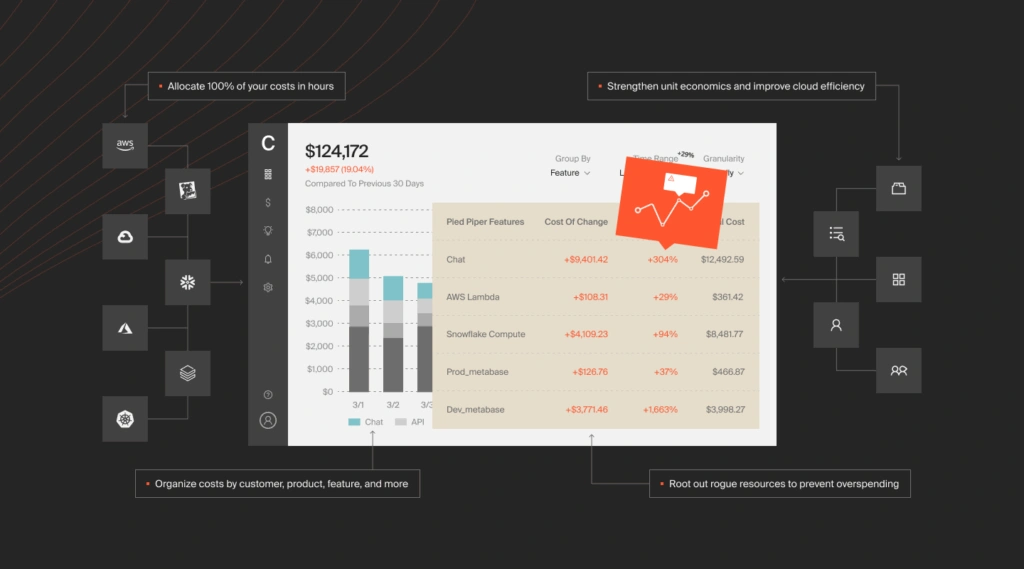
CloudZero gives you the what, why, and where of your AWS investment. Engineering can self-serve and explore the cost of their architecture and apps — enabling them to make cost-aware engineering decisions that ensure your company’s profitability. Finance can measure the ROI of your technical investments — and differentiate between an out-of-control cloud bill and economies of scale.
Schedule a demo today to see how CloudZero can empower your organization with cloud cost intelligence so you can ensure your cloud environment is cost-efficient.
Cloud Efficiency FAQs
Why does cloud efficiency
It protects margins, improves performance, and reduces unnecessary cloud spend as you scale. Read: Cloud Cost Optimization Examples
How can I ensure that my cloud spending is efficient?
Track unit costs, right-size, monitor usage, automate scaling, and eliminate idle resources.
How does AI affect cloud efficiency?
AI adds GPU, model training, and inference costs. Efficiency now depends on workload routing and cost-per-token or per-inference tracking.
What tools improve cloud efficiency?
Use performance monitoring + cloud cost intelligence to see resource use and cost impact in real time.








