AWS Lambda is an event-driven compute service, which means it executes tasks automatically when triggered by a compute event. This automation also means that your Lambda costs can quickly exceed your budget. That is especially true when you’re not familiar with AWS Lambda pricing.
In this guide, we’ll discuss the AWS Lambda pricing model, including how billing works and how to optimize Lambda costs.
What Does AWS Lambda Do?
Amazon’s Lambda service enables you to run code for nearly any type of app or backend system without the need to provision or manage servers yourself. You only need to upload your code. AWS Lambda will handle everything your code requires to run and scale with high availability.
Because it is event-driven, AWS Lambda leverages the concept of Functions. A Lambda function is a piece of Python code (no name when defining it) that performs a specific task. The lambda (function) assesses an expression based on a given argument. You provide the lambda a value (an argument) and then supply the operation (the expression).
That code executes when specific events occur in related AWS services, for example, when an object is added to an Amazon S3 bucket.
Some call this Function-as-a-Service (FaaS). Many refer to this approach as serverless computing.
Every function, or lambda, runs in an isolated environment, complete with its own file system view and resources.
Lambda is useful for a wide range of tasks, such as:
- Running inconsistent workloads with long pauses between executions over the course of a day
- Performing real-time data process
- Supporting social media streaming together with Amazon Kinesis
- Operating serverless websites
- Quickly converting documents into different formats, particularly when their content changes frequently
If choosing the right resources for your serverless compute requirements is important to you, check out CloudZero Advisor for customized recommendations based on factors such as AWS service, resource type, instance type, region, pricing, and more.
So, how does AWS Lambda charge for its capabilities?
AWS Lambda Pricing Explained
AWS Lambda charges you for the serverless compute time you use, the total time it takes your code to execute and the number of requests for your functions. There are no charges when your code is not running.
Once you package your code into Lambda functions, the service will run the function only when triggered. It then scales automatically to meet the compute demand that your workload requires. AWS Lambda can scale from handling a few requests daily to thousands per second.
Here’s how that works during operations.
Primary Factors That Affect Lambda Pricing
AWS Lambda pricing depends on seven major factors:
Number of requests
Lambda charges based on the number of requests your functions receive. A request begins as soon as Lambda starts executing your code, whether triggered by an event or an invoke call. There’s no charge for the first 1 million requests each month, after which the cost is $0.20 per 1 million requests.
Code execution duration
Duration is measured from when your code begins executing until it terminates, rounded to the nearest millisecond. AWS Lambda calculates this based on the memory allocated to your function. The cost per duration will depend on the memory size and CPU architecture.
Memory allocation
AWS Lambda pricing varies based on the memory (RAM) you allocate to your function, ranging from 128 MB to 10,240 MB. Higher memory allocations offer more CPU power, and costs increase with higher memory settings.
CPU architecture
Lambda supports both x86 and ARM architectures (Graviton2), with Graviton2 offering potentially lower costs for certain workloads due to its optimized pricing.
Compute savings plans
If you are eligible for Savings Plans, you can receive up to a 17% discount on AWS Lambda costs by committing to a certain amount of usage over one or three years. This applies to both Provisioned Concurrency and Duration charges.
Ephemeral storage
Lambda functions come with 512 MB of ephemeral storage by default. You can increase this by 1 MB up to 10,240 MB, with pricing starting at $0.0000000309 per GB-second.
Provisioned concurrency
When enabled, provisioned concurrency keeps your functions warm. This ensures they are ready to respond immediately, reducing latency. You’re charged based on the concurrency level and the amount of memory allocated to the function, with additional charges for requests and duration.
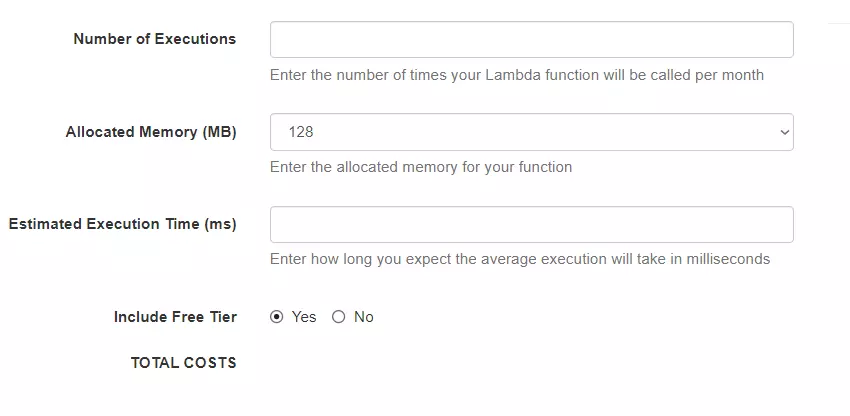
The following formula will help you calculate your AWS Lambda costs in GB-seconds:
Number of executions X (Lambda memory size/1024) X (Lambda duration in milliseconds/1000) = GB-seconds
You can see an illustration of how Lambda calculates your bill from this image:
At CloudZero, we are all about breaking down costs to make sense of your business so you understand what you’re paying for. That’s how you maximize performance and keep costs low without compromising other crucial factors, such as availability. So, in the next section, we’ll help you unravel these Lambda pricing factors in more detail.
1. How does the number of AWS Lambda requests affect pricing?
The Lambda service counts a request from the time it begins to execute in response to an event notification trigger or an invoke call.
An event notification trigger may come from Amazon EventBridge or the Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS). In contrast, an invoke call may come from the Amazon API Gateway or the AWS SDK (including test calls from the AWS Console).
A request lasts until it is either returned or terminated. Lambda charges per request or invocation ($/request or invoke call).
- There is no charge for the first 1 million requests and the first 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time in a month.
- The free allowance applies to functions running on both Graviton2 (Arm-based) and X86 CPUs.
- After that, you pay $0.20 per 1 million requests.
The final bill will be for the total number of requests made across all your Lambda functions.
2. How does code execution duration affect AWS Lambda pricing?
Lambda also counts the duration from when your code starts to execute to when it returns or terminates, rounded to the nearest one millisecond. Duration pricing is in dollars per hour ($/hour).
- The free tier provides up to 3.2 million seconds of compute time per month free, and
- 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month free
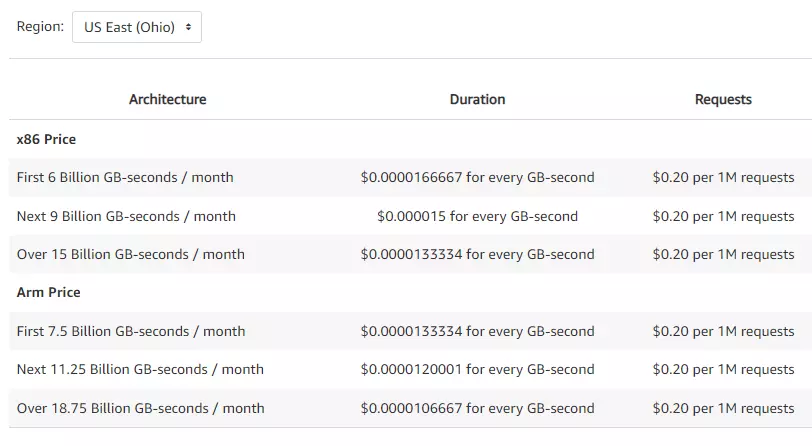
However, the exact duration price you’ll pay will depend on the amount of memory you’ll allocate to your function (min 128 MB; max 10 240 MB or 1 GB). Here’s what we mean based on prices in the US East (Ohio) region:
Memory amount in MB | Price per 1 millisecond (1 ms) for X86 CPU Architecture | Price per 1 millisecond (1 ms) for Arm CPU Architecture |
128 | $0.0000000021 | $0.0000000017 |
512 | $0.0000000083 | $0.0000000067 |
1024 | $0.0000000167 | $0.0000000133 |
1536 | $0.0000000250 | $0.0000000200 |
2048 | $0.0000000333 | $0.0000000267 |
3072 | $0.0000000500 | $0.0000000400 |
4096 | $0.0000000667 | $0.0000000533 |
5120 | $0.0000000833 | $0.0000000667 |
6144 | $0.0000001000 | $0.0000000800 |
7168 | $0.0000001167 | $0.0000000933 |
8192 | $0.0000001333 | $0.0000001067 |
9216 | $0.0000001500 | $0.0000001200 |
10240 | $0.0000001667 | $0.0000001333 |
3. How does memory allocation affect AWS Lambda costs?
Your Lambda cost will vary depending on how much memory (RAM) you allocate to your function. The previous table shows how pricing changes with changes in allocated memory.
One more thing. The service automatically allocates you a proportional amount of processing power (CPU) and other resources based on the amount of memory you allocate to your function. That means increasing your Lambda memory size triggers an equivalent increase in CPU power available to your function.
4. How does AWS Lambda ephemeral storage pricing work?
Ephemeral storage pricing starts at $0.0000000309 per GB-second. You can allocate between 512 MB and 10 240 MB of ephemeral storage to your function and its execution duration (in milliseconds). 512 MB is complementary, and both X86 and ARM architectures are supported.
You only pay extra for additional ephemeral storage, which you can increase in 1 MB increments.
5. How does provisioned concurrency affect AWS Lambda pricing?
Provisioned concurrency is a Lambda feature that seeks to reduce startup latency. When active, provisioned concurrency keeps your functions initialized and ready to respond to requests from your workload in double-digit milliseconds.
Some things to note here are that you:
- Pay for the level of concurrency you specify, as well as the duration you configure it.
- Both X86 and Arm-based CPUs support Provisioned Concurrency.
- Provisioned Concurrency also charges you for Requests and Duration when enabled and executed for your function.
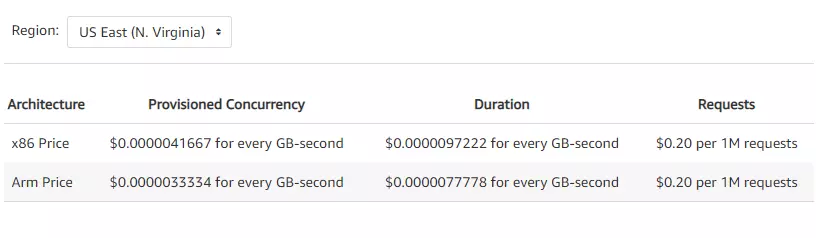
- The service calculates the PC from when you enable it on your function to when you disable it, rounded up to the nearest five minutes. The price varies with the amount of memory you provide to your function AND the level of concurrency you configure on it.
- The service calculates Duration from when your code begins running until it returns or terminates and then rounds it to the nearest one millisecond. The price varies with the amount of memory you dedicate to your function.
- The free tier doesn’t apply to Functions that have Provisioned Concurrency enabled.
There’s just one more billable consideration.
6. Additional AWS Lambda charges
Additional charges may apply for the following:
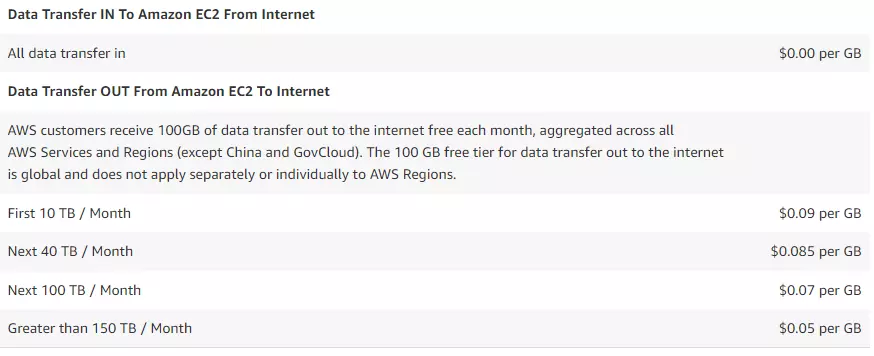
Data transfer
When data is transferred into and out of AWS Lambda functions from locations outside the region where the function is running, expect charges at the Amazon EC2 data transfer rates below.
Using Lambda@Edge
This option enables you to improve performance and reduce latency by running your code closer to your users using AWS CloudFront. Prices are $0.60 per 1 million requests or $0.0000006 per request and $0.00005001 per GB-second you use.
Say you allocate 128 MB of memory for each execution of your Lambda@Edge function. Then your duration cost will be $0.00000625125 per 128 MB-second you use, measured in 1 ms intervals.
Lambda Costs: AWS Lambda Pricing Plans And Tiers
This table gives you a quick view of AWS Lambda’s pricing options and eligibility for the free tier, on-demand, and savings plans.
Pricing plan | Description |
Free tier | Lambda offers 1 million requests and 400,000 GB-seconds of compute each month for free. Subtract this free allowance from your monthly total requests and code execution time to calculate your billable balance. |
On-demand | For usage above the free allowance, a $0.20 fee applies per 1 million requests, and a $0.0000000167 fee applies per 1024 MB-second (1 GB-second) of execution time. Duration pricing varies based on allocated memory. |
Savings plans | With AWS Lambda, you can take advantage of discounted compute rates (up to 17% off) by committing to a certain usage over one or three years. Compute Savings Plans apply to Duration and Provisioned Concurrency. |
AWS Lambda Cost Optimization: 7 Tips You Need To Know
As you can tell, there are many factors affecting AWS Lambda pricing. You do not want these to catch you off guard if you do not pay close attention during account setup and budgeting.
For that reason, here are some tips to look out for to help you control your AWS Lambda costs.
1. If your Lambda function transfers data to or from other AWS services, there are additional charges
If your AWS Lambda requests are involved in any way with a different AWS service, you’ll be charged for both services. The additional charges are based on the prices of the specific AWS services you use. For example, when your functions write to or read data from Amazon S3, you’ll be billed for the requests and any data stored in S3.
2. Memory size is configurable
You can set the maximum memory size and execution time for each Lambda function. Your function automatically gets more CPU power the more memory you provide.
3. Decide between X86 and Arm-based CPUs
AWS designed Graviton2 processors based on Arm processor architecture to deliver up to 34% better price performance versus running Lambda functions on x86 processors. Some applicable use cases include serverless workloads like data and media processing, serverless websites, and mobile backends.
4. You can configure things further
You can specify limitations for the amount of CPU, memory, and storage resources that serverless functions can use. Several resources are subject to these limits, including:
- Number of concurrent executions
- Storage for uploaded functions, as well as quotas for function configuration
- Deployment and execution parameters like memory allocation
- Timeout
- Environment variables
- Layers
- Burst concurrency
Here’s something else.
5. About the Memory Size (GB) you allocate
You allocate this amount of memory to your function through the AWS console. However, this isn’t actually how much memory the function uses. Reducing your function’s memory usage without tweaking this configuration may not yield much cost savings.
6. About the Execution time (ms)
Functions take a certain amount of time to execute their code logic. Here is the thing. When a function makes an outgoing call and waits for the response, the Lambda service counts the idle time in between as part of the function’s execution time.
7. Configure your environment with CloudZero Advisor
CloudZero Advisor provides customized insights about the best resources for your AWS Lambda projects. It considers factors such as pricing, AWS services, resource type, and AWS region. For example, you can use CloudZero Advisor to determine whether an X86 or Arm-based CPU is right for your serverless computing. Learn more about CloudZero Advisor here.
How To View, Control, And Optimize Your Lambda Costs
Depending on the size of your operation, calculating AWS Lambda costs can be challenging. AWS Lambda costs can pile up quickly, probably before you can pinpoint what you’re paying for. Plus, traffic can vary significantly from hour to hour, day to day, week to week, and month to month.
It’s also unwise to wait until the end of the month to see your Lambda bill because there’s no way to change it by then. Perhaps you experienced some cost spikes that you didn’t notice until the bill arrived, and you can’t figure out why they occurred or how you can prevent them in the future.
This is where CloudZero can help.
With CloudZero, you can capture, analyze, and present your AWS costs per unit for business concepts you care about, such as:
- Cost per customer
- Cost per feature
- Cost per product
- Cost per team
- Cost per project
- Cost per environment
With this intelligence at your fingertips, you can pinpoint exactly who, what, and why your AWS costs are changing. Most other tools show you total costs and averages — not this level of instantly actionable cost insight.
Also, CloudZero detects cost anomalies in real time.
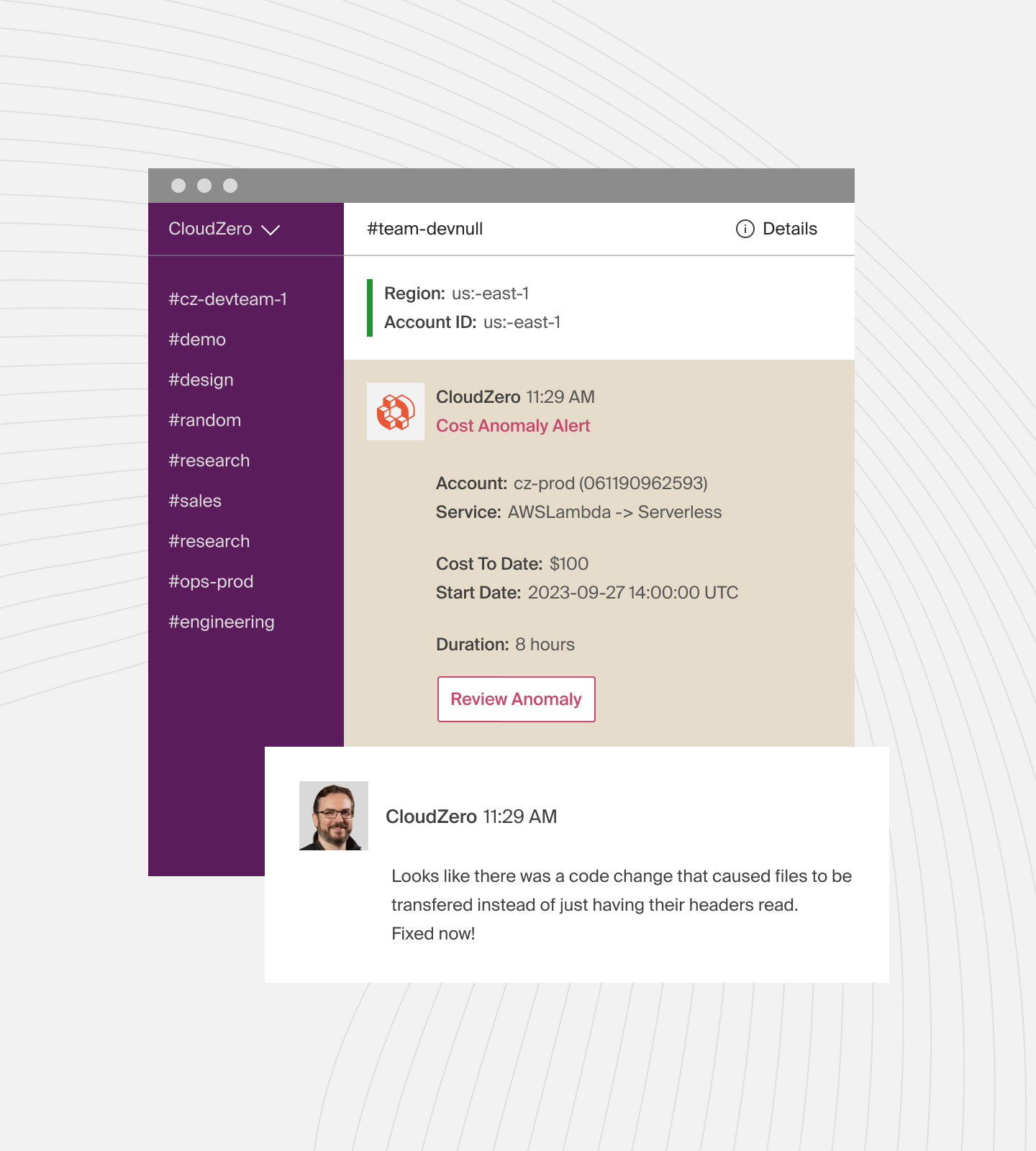
CloudZero then alerts individual engineers or your entire FinOps team via Slack or email to the anomalies so you can stop the bleeding before it wipes out your budget.
With CloudZero, you can also forecast and budget costs, analyze Kubernetes costs, and consolidate costs from AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure in one platform. Our customers, like Drift, have already reduced their annual AWS spending by $2.4 million. You can, too.
 to see how you can optimize your costs.
to see how you can optimize your costs.
AWS Lambda Pricing FAQs
The following are answers to frequently asked questions about AWS Lambda pricing.
What is the AWS Lambda pricing model?
You pay per use. If your code isn’t running, there are no charges to you.
How does AWS Lambda billing calculate charges?
AWS Lambda charges you for the serverless compute time you use, the total time it takes your code to execute and the number of requests for your functions.
Several variables determine Lambda costs, including the type of CPU architecture (Arm-based or X86), the number of requests, the time frame (code/function execution duration), the duration of each request (measured in milliseconds), and the amount of memory you allocate it (in GB-seconds).
Is AWS Lambda cheaper than Amazon EC2 for compute usage?
EC2 pricing may appear lower and more straightforward than Lambda pricing. However, depending on your use case, this may vary. For example, the Lambda service eliminates many of the costs associated with provisioning and managing your own servers.
Also, unlike EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions terminate as soon as they finish executing a task instead of incurring charges for idle time.
Are there any free tier options for AWS Lambda?
Yes, AWS Lambda offers a free tier that includes 1 million free requests and 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month. This enables you to run your functions without incurring charges, provided your usage stays within these limits. The free tier is available indefinitely, applies to all AWS customers, and doesn’t expire after 12 months.