Imagine you are building an e-commerce app. Every time a customer places an order, a lot happens behind the scenes. For example, you need to charge their card, update inventory, create a shipping label, and send a confirmation email.
You could try to write one giant program that does everything in the correct order, but that quickly becomes a tangled mess — especially if something fails halfway through (say, payment succeeds but inventory update fails).
Now imagine instead of writing that big, fragile script, you could map out each step of the process like a flowchart. One box for “charge card,” another for “update inventory,” another for “send email.” You decide the order, conditions, and what to do if something goes wrong; the system takes care of the rest.
That’s kind of what AWS Step Functions does for organizations and using the cloud. Think of AWS Step Functions as the coordinator behind that whole order process.
In this guide, we explore what AWS Step Functions is, how it works, pricing, benefits, and more.
What Is AWS Step Functions, And How Does It Work?
AWS Step Functions is a serverless orchestration service that enables users to coordinate multiple AWS services into automated workflows. It manages workflow logic — ordering steps (sequentially or in parallel), tracking inputs/outputs, and handling retries and errors to improve reliability across your cloud environment.
How AWS Step Functions works
Let’s go back to our e-commerce analogy.
We said AWS Step Functions keeps the entire chain of events running smoothly.
Inside Step Functions, you create something called a state machine. This is like a digital flowchart that maps every step your process needs. Each box, or state, represents a task such as “Charge Customer,” “Update Inventory,” or “Send Confirmation.” These tasks can trigger different AWS services based on the specific requirements at the time.
For example, a Lambda function might handle charging the customer’s card. DynamoDB might update stock levels, and SNS could send out an email or text message confirming the order.
AWS Step Functions ties all these together, automatically moving from one step to the next.
It also manages decisions in real time. In the same way your team might pause an order if payment fails, Step Functions can include a choice state that says, “If payment succeeds, move to shipping; if not, send a cancellation notice.” You don’t need to write complex logic for that — it’s all defined visually.
Here’s a sample state machine that automates a “check stock price and buy/sell” workflow:
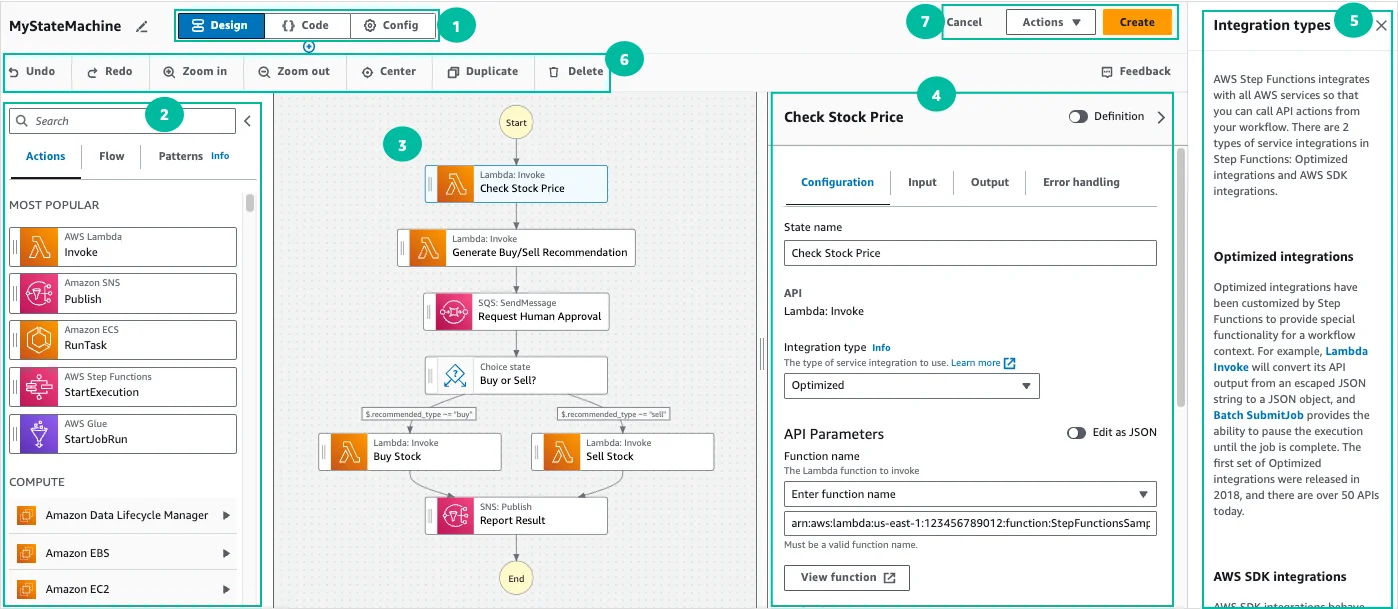
Source: AWS
At the same time, Step Functions handles parallel actions seamlessly. Similar to checking payment and stock simultaneously, it can run multiple steps in parallel. For instance, verifying payment details while confirming delivery options. Once both are complete, the workflow continues automatically.
Every time the system moves from one step to another, Step Functions tracks the transition, records the result, and updates a visual dashboard. You can see exactly where each order is in the process, which steps have passed, which are still running, and where something failed.
And since Step Functions is serverless, you don’t need to manage any servers or schedulers. AWS takes care of scaling, reliability, and error recovery behind the scenes. Whether your application handles ten orders or ten thousand in an hour, Step Functions runs them all in sequence, reliably and securely.
The Benefits Of AWS Step Functions
Coinbase used Step Functions to automate deployments, improving the success rate of mission-critical deployments from 90% to 97% and giving engineers step-by-step visibility. Thomson Reuters reduced typical video processing from 20 minutes to 2 minutes by parallelizing it with Step Functions. Xylem reduced daily data processing from 20 hours to 2 hours after moving to a Batch + Step Functions pipeline.
These are just a few of the many real-world success stories from organizations that use AWS Step Functions to speed up their workflows and improve efficiency.
Other benefits of AWS Step Functions include:
- Prevents duplicate executions. Step Functions can help prevent duplicate executions if configured properly. This helps maintain data consistency and avoid wasted compute.
- Faster troubleshooting. Every workflow shows clear logs and visual traces of what happened. This enables teams to spot where things failed in seconds, eliminating the need to dig through code or CloudWatch logs.
- Clean, maintainable architecture. By separating logic (workflow) from execution (tasks), Step Functions keeps your application code lightweight and focused.
- Scales automatically. Because it’s serverless, Step Functions grows with your workload. It handles thousands of executions without you managing servers, schedulers, or queues.
- Cuts costs and saves developer time. No need to build orchestration logic or manage infrastructure. Teams ship faster, code less, and pay only for the steps that actually run.
AWS Step Functions Use Cases
Here are a few real-world scenarios where AWS Step Functions is applicable:
- Order processing. In e-commerce, Step Functions ties together payment, inventory, shipping, and notifications. It ensures each step runs in the right order and recovers automatically if one fails.
- Customer onboarding. When a customer signs up, Step Functions coordinates billing, CRM, and email services, ensuring every system updates consistently.
- Data pipelines and ETL. Organizations use Step Functions with AWS Glue or Batch to manage data workflows. Here is an example:
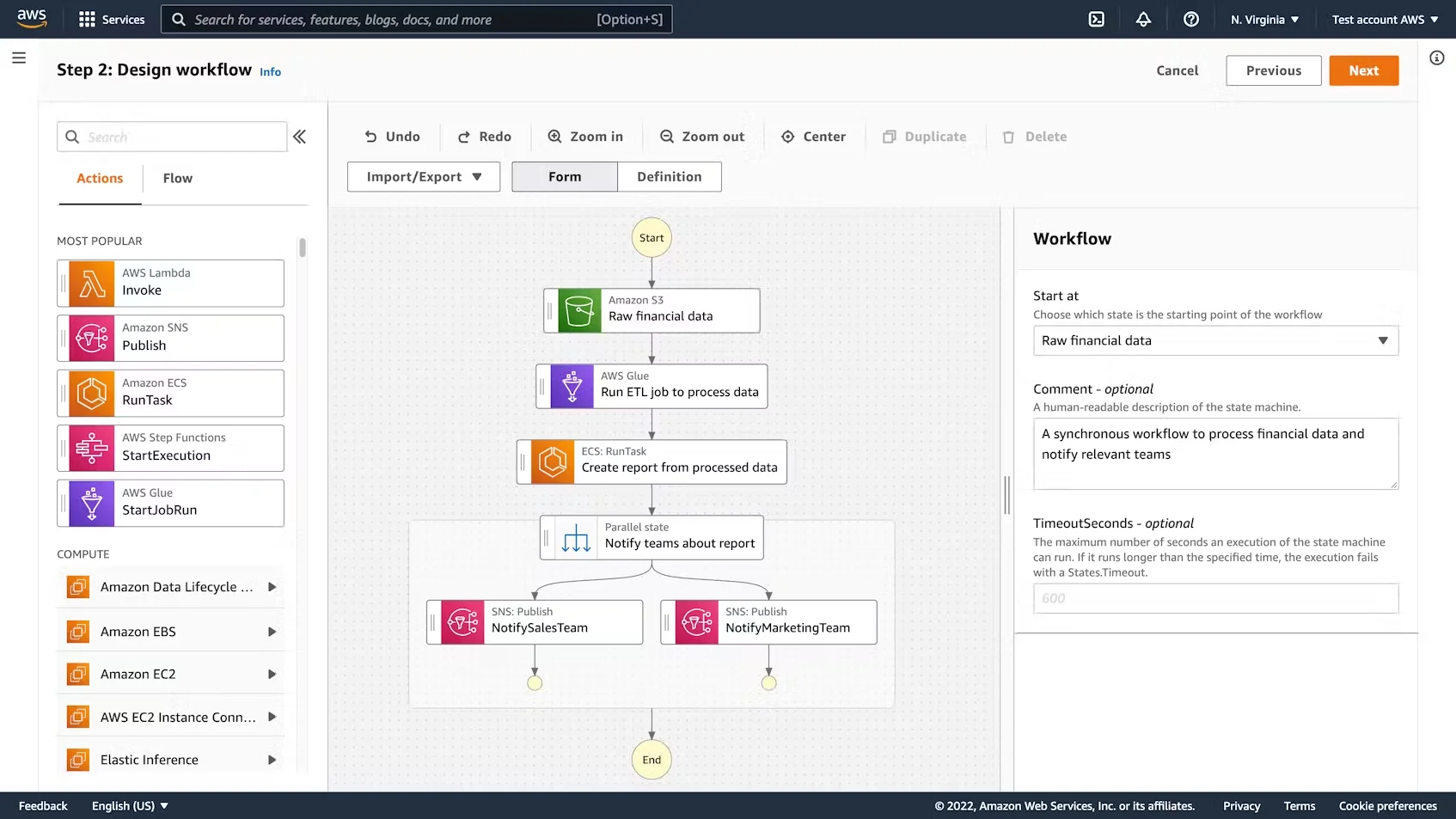
See also: 30+ Essential ETL Tools For Data Pipelines
- Machine learning workflows. Teams orchestrate model training and deployment by integrating services such as SageMaker, Lambda, and ECS. Each stage runs only after the last succeeds, simplifying MLOps pipelines.
- CI/CD and DevOps. Organizations use Step Functions to automate deployments and rollbacks. It sequences build, test, and deploy steps, improving reliability and visibility.
- Approvals and financial processes. Banks and fintech firms use Step Functions to manage loan approvals or payment workflows. It can pause for human review, branch based on conditions, or resume automatically.
- IoT and event-driven systems. Step Functions processes IoT data in real time by triggering Lambda or Kinesis tasks. It’s ideal for monitoring, alerts, or automating device actions.
- Microservices orchestration. It acts as the central conductor for microservices. It handles call sequences, retries, and dependencies across APIs without complex coordination code.
- Multi-region or multi-account operations. Large organizations use Step Functions to run the same workflows across global environments. This ensures consistent deployments and reporting.
And now to pricing, how much does AWS Step Functions cost?
AWS Step Functions Pricing And Cost Considerations
Like most AWS services, Step Functions pricing is usage-based. You pay only for what you use.
The service supports two workflow types:
- Standard Workflows. These are ideal for long-running, business-critical processes. They can run for up to one year, provide exactly-once execution guarantees, and have a detailed visual history. They are billed per state transition. AWS offers 4,000 free Standard workflow state transitions per month as part of the AWS Free Tier.
- Express Workflows. These are built for high-volume, short-duration, event-driven workloads such as streaming data or API calls. They can run for up to five minutes and offer at least once execution semantics. They are billed based on requests, execution duration (GB-seconds), and memory used.
When your workflow calls Lambda, S3, Glue, DynamoDB, and other services, each incurs its own standard AWS charges.
Check out:
Note: Step Functions pricing and available features also differ by AWS region. The cost per state transition or execution in one region may not be the same elsewhere. Also, if your workflow spans regions (or triggers services in another region), cross-region data transfer charges may apply.
See: AWS Data Transfer Pricing Guide And How To Reduce Costs
Here’s a quick summary of how AWS Step Functions looks:
Component / Type | Cost Model | Description |
Free tier | 4,000 free state transitions/month | Always-free quota for Standard Workflows under AWS Free Tier |
Standard Workflows | $0.025 per 1,000 state transitions | Each step change counts as one billable transition |
Express Workflows | Execution + duration (GB-seconds), rounded to 100 ms | Best for high-throughput, short-lived workflows; billed by run time and memory size (in 64 MB increments) |
Triggered AWS services | Standard AWS pricing applies | You still pay normal rates for Lambda, S3, SNS, and Glue |
Cross-account / cross-region usage | Possible data transfer charges | Cross-account is supported via IAM; cross-region requires API calls and may incur transfer costs |
Retries, branches, or error paths | Counted as extra transitions or runtime | Each retry or parallel branch adds to billable usage |
AWS Step Functions cost-saving tips
Here are practical tips to control Step Functions costs:
- Choose the right type of workflows. Use Express for short, frequent jobs; Standard for long or critical ones. Combining both can also cut costs.
- Limit retries. Add retry caps or exponential backoff to avoid runaway loops that inflate your bill.
- Monitor costs. Track transitions, execution time, and expensive workflows with tools like Cost Explorer or CloudWatch.
- Keep workflows in one region. Cross-region calls add data-transfer costs. Keep related steps close together.
- Reduce state transitions. Combine simple steps or use built-in functions instead of extra Lambda calls. Every step transition adds cost.
- Avoid passing large amounts of data between steps. Store big data in S3 and pass a link. Small payloads = cheaper, faster runs.
- Use an inline Map for small loops. Distributed Map charges per child workflow; the inline Map keeps costs low for lightweight iterations.
- Set timeouts. Stop hung tasks from waiting forever — unfinished runs can pile up and waste money.
- Simplify design. Remove unnecessary branches or “just in case” logic. Fewer paths result in fewer transitions, which, in turn, lowers the cost.
How To Monitor, Optimize, And Reduce AWS Step Functions Costs
For new users, the free tier helps you monitor your Step Functions usage and associated costs. Express workflows are cost-effective for experimenting with or automating quick jobs.
AWS monitoring tools can help you track your usage. But these native tools will only tell you what’s running. Not what’s costing you and why.
CloudZero bridges this gap.
How CloudZero adds cost intelligence for step functions
CloudZero runs on AWS, built with serverless technology from day one. The same services our customers depend on — Lambda, Step Functions, and others are the foundation of how we run too.
And yes, we use CloudZero to manage CloudZero. Our team monitors and optimizes our serverless environment directly through the platform. A true “we drink our own champagne” approach that proves our cost intelligence in action.
That’s why we have a deep, practical understanding of how modern, event-driven systems behave and what drives their costs.
With CloudZero, you can:
- Allocate costs to products, features, and teams. CloudZero’s CostFormation maps 100% of your cloud spend. This includes serverless and orchestration to dimensions such as team, feature, and customer. You can see which state machine or workflow drives your Step Functions bill, even without perfect tags, in real-time.
- Catch anomalies early. CloudZero automatically flags cost spikes, such as runaway retry loops or unexpected surges in Distributed Map executions, before the bill arrives.
- Unify Step Functions with all connected services. CloudZero combines Step Functions transitions with all their associated costs, including Lambda, S3, Glue, ECS, and data transfer, providing a complete cost per workflow — not fragmented totals per service.
- Make cost a design input. CloudZero helps engineers treat cost as a design metric — not an afterthought. Check out how we help teams make cost a non-functional requirement.
CloudZero also integrates with most of the SaaS tools you use, including Snowflake, Databricks, Kubernetes, MongoDB, and OpenAI. It connects cost data across these services and your Step Functions workflows, giving you a complete picture of how they impact spend.
For example: If a Snowflake query runs inside a Step Functions workflow, CloudZero links that cost directly to the workflow, team, or feature that triggered it — showing your true end-to-end cost for data or AI pipelines.
AWS Step Functions FAQS
What is the difference between workflows and Step Functions?
In AWS, you define state machines (workflows) in Amazon States Language (ASL). AWS Step Functions is the managed service that runs them. In other words, workflows are what you design; Step Functions is the engine that runs them.
Step Functions vs AWS Lambda — which should I use?
Lambda runs code in response to events. Step Functions orchestrate multiple steps. Lambda is best for standalone tasks. Step Functions is best suited for orchestrations, retries, branching, and dependencies. Most teams use them both, but you can replace one with the other as they serve different purposes.
Is AWS Step Functions free?
No, but there is a free tier for Standard workflows: 4,000 free state transitions per month in many regions. After that, you pay per state transition.