Here is the thing. You don’t need more than one cloud service provider unless you are considering a multi-cloud strategy. And even if you plan to work with all three cloud vendors, you’ll want to know which one is right for specific services.
To help you decide, we’ll share the strengths, pricing, and other differences between Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) below.
Let’s start from the very beginning.
What Is Cloud Computing (And Why Does It Matter)?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more, over the internet, or “the cloud.”
Instead of owning and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you access these resources on-demand from cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Cloud computing is like renting a fully equipped office space instead of buying a building. You get the facilities you need without the overhead of ownership.
- It is also like “renting” computing power and paying only for what you use, much like paying for utilities such as water or electricity.
Cloud computing matters because:
- It supports diverse applications, from web hosting to big data analytics and AI.
- Your organization can scale resources, and thus operations, up or down based on demand, pay only for what you use, and access advanced technologies without substantial upfront investments.
- You can deploy applications rapidly instead of building physical data centers first.
- Adapting to market changes doesn’t require overhauling complex IT systems, so it’s quicker and less painful.
Overall, the cloud model enables scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. AWS, Azure, and GCP are the leading cloud service providers. The platforms provide the infrastructure and services that power modern applications, enabling businesses to transform and stay competitive in the digital landscape.
What Is Amazon Web Services (AWS)?
AWS is the world’s largest cloud service provider with 34% of the global market. The company provides more than 240 cloud services, ranging from compute to edge to serverless computing.
Among the most popular AWS services are Amazon EC2 (compute), Amazon S3 (object storage), Amazon EBS (block storage), Amazon Lambda (serverless), and Amazon RDS (relational databases).
Who uses AWS services today?
AWS customers include large enterprises and smaller organizations across multiple industries. A few notable examples include:
- Samsung
- Disney
- Adobe
- DoorDash
- Crypto.com
- US Department of State
- Airtable
- Verizon
- Wix
- UK Ministry of Justice
- GoPro
Customers needing global coverage or coverage in specific locations where Azure and GCP are restricted should consider AWS. If you’re looking for flexibility, high scalability, edge computing, and robust security and compliance standards, the AWS ecosystem fits the bill.
What Is Azure Cloud?
Azure is Microsoft’s cloud services arm and a part of its Microsoft Intelligent Cloud ecosystem. Azure Cloud, like AWS, offers a variety of options for your engineers, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services.

Who uses Microsoft Azure services today?
Like AWS, Azure customers comprise Fortune 500 and smaller organizations across diverse industries and use cases. Some of the most successful Azure customers include:
- BP
- Coca-cola
- Chevron
- Delta
- AmtrakBMW
- DocuSign
- Whole Foods
- Uber
- PwC
- Fujitsu
- University of Sydney
Microsoft Azure is most popular among enterprises for several reasons:
- Existing Microsoft licenses: Since many enterprises already use Microsoft products, such as Microsoft 365, SQL Server, SharePoint, and PowerBI, moving to and integrating Microsoft cloud services is often fairly painless.
- Hybrid cloud: Azure offers seamless integration of on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud services. This enables Azure customers to retain their own data centers while taking advantage of the cloud’s benefits.
- Global data centers: Azure has the second-largest data center network worldwide, right behind AWS, to support global deployments or reach underserved regions.
So, how does GCP compare?
What Is Google Cloud Platform (GCP)?
GCP is best suited to companies with cloud-native applications such as Kubernetes, containers, and AI/ML requirements. Google pioneered Kubernetes (container orchestration platform), Istio (service mesh), and several other popular open-source tools.
In addition, the technology that supports Google’s Search powers the platform’s machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data analytics tools.
Who uses Google Cloud Platform services today?
GCP customers include:
- Mercedes Benz
- Bayer AG
- PayPal
- Unilever
- Swiss Airlines
- Total Energies
- Orange
- Data Lab
- Delivery Hero
- TrustPilot
- UbiSoft
GCP is also popular with startups looking to leverage open-source, but tested platforms to grow faster. In addition, agile scaleups usually use GCP’s rapid innovation to grow their revenue and capture market share.
Introductions aside, in what ways do AWS, Azure, and GCP differ?
AWS Vs. Azure Vs. GCP: How to Choose The Best Cloud Service Provider Today
Choosing the best cloud provider for your applications, budget, location, etc., begins with analyzing your requirements. Identifying what you want will lead to the following considerations.
Size matters
A provider with a global footprint can store and back up your data in more geographic locations, improving disaster recovery and resilience. Having access to more Regions, Availability Zones, and edge locations means more room to grow into. It also enables you to take your services closer to your target customers, reducing latency. Yet, more isn’t always better. So, verify that your preferred Availability Zones support the actual services you require.
Security and compliance
All providers offer adequate cloud security measures. However, the specific data encryption, access controls, and security auditing techniques each uses vary. You’ll want to explore these variances for your specific use cases. And, while at it, ensure the measures comply with relevant industry standards and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
Cloud scalability and flexibility
Not all providers offer auto-scaling, increasing and reducing compute capacity based on workload demand. The ones that do also require you to toggle the feature on and off. So, look for a provider that will help you easily scale resources up or down based on your changing needs. This is crucial for meeting optimal performance goals without overspending.
Reliability
Select a provider with a good track record of crucial SaaS metrics, like uptime and low latency. Consider the SLAs of specific services you plan to use rather than a provider’s overall uptime rating. Additionally, verify that your preferred cloud vendor offers explicit SLAs (99.95% and better) and redundant systems to assure uptime.
Cost and pricing
Pay attention to the provider’s pricing model and any additional fees. AWS, Azure, and GCP offer flexible pay-as-you-go approaches. However, they charge differently, and even similar offers, such as commitment use discounts, vary in discount amounts. So, beyond initial costs, consider pricing models that align with your usage patterns and budget goals.
Anticipate and beat vendor lock-in
Don’t limit yourself to one vendor’s capabilities. You can use some functions from one provider and some from another. Look for providers that support multi-cloud or hybrid cloud configurations. Then you won’t have to rely on a single vendor. While at it, consider the cloud provider’s ability to integrate with your existing systems and tools.
Support
Yes, most providers have strong support, especially when you are paying a premium for it. The key is to explore their different service packages. Consider their responsiveness in your region, whether they offer 24/7, email, or phone support, and what specifics are covered by your service level agreements. Also, remember that a strong community and a rich ecosystem of third-party tools and integrations can drastically improve your cloud capabilities.
Ultimately, you want a reliable, cost-efficient, and secure vendor. Take time to research the provider’s reputation and customer reviews. Ask around and talk to people in the industry to get a sense of the provider’s level of service. Ultimately, request a free trial (and use their Free Tiers) to test their ecosystems.
A Quick Comparison of AWS vs Azure vs GCP
Amazon Web Services | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud Platform | |
Launched | 2006 | 2008 | 2011 |
Services provided | 240+ | 200+ | 150+ |
Available in/Global data center locations | 33 Regions, 41 Local Zones, 105 Availability Zones, 135 Direct Connect Locations, 245+ countries | 60 Regions, 300+ data centers | 40 Regions, 121 Zones, 187 Edge locations, 200+ countries |
Strengths | Public cloud, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (SaaS), cloud storage, multi-cloud support | Public cloud, Windows-based workloads, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Hybrid cloud support | Private/public cloud, Kubernetes, Data analytics and AI/ML, Database-as-a-Service (DaaS) |
Pricing | Pay-as-you-go Committed use discounts (Reserved Instances, Savings Plans) | Pay-as-you-go Committed use discounts (Reserved Instances, Savings Plans) | Pay-as-you-go Committed Use Discounts (CUDs), Sustained Use Discounts (SUDs) |
Table: AWS vs Azure vs GCP comparison. You’ll notice that each cloud provider defines regions and locations differently. Overall, AWS offers the broadest physical and service coverage.
AWS Vs. Azure Vs. GCP: 9 Key Differences That Make The Difference
All three of them support self-service, instant provisioning, autoscaling, compliance, and identity management. Here are some areas where Azure, AWS, and GCP differ.
1. Availability Zones
CSPs offer varying types and levels of service depending on Regions and AZs. Certain services might be available in that location, but their capabilities may be limited in comparison to other locations. Be sure to confirm these details before purchasing.
Amazon Web Services cloud infrastructure spans 105 Availability Zones across 33 regions (with more launching soon).
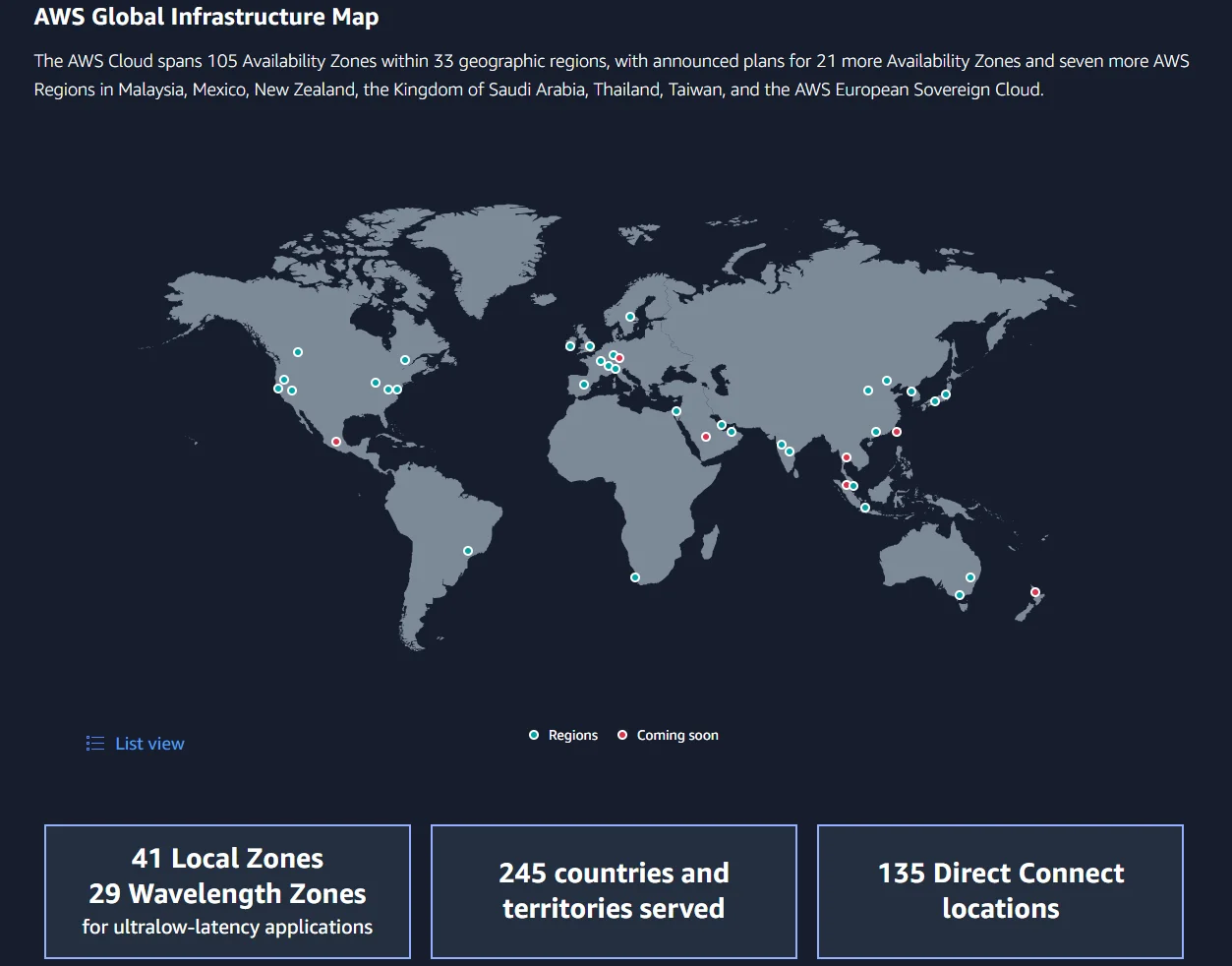
AWS Regions and Availability Zones
In addition to 600+ points of presence, the vendor has Edge computing sites on every continent except Antarctica. In addition to seamless scalability and low latency, a large network can also offer multi-regional data backups for disaster management.
In comparison, Azure’s global network covers 160 data centers.
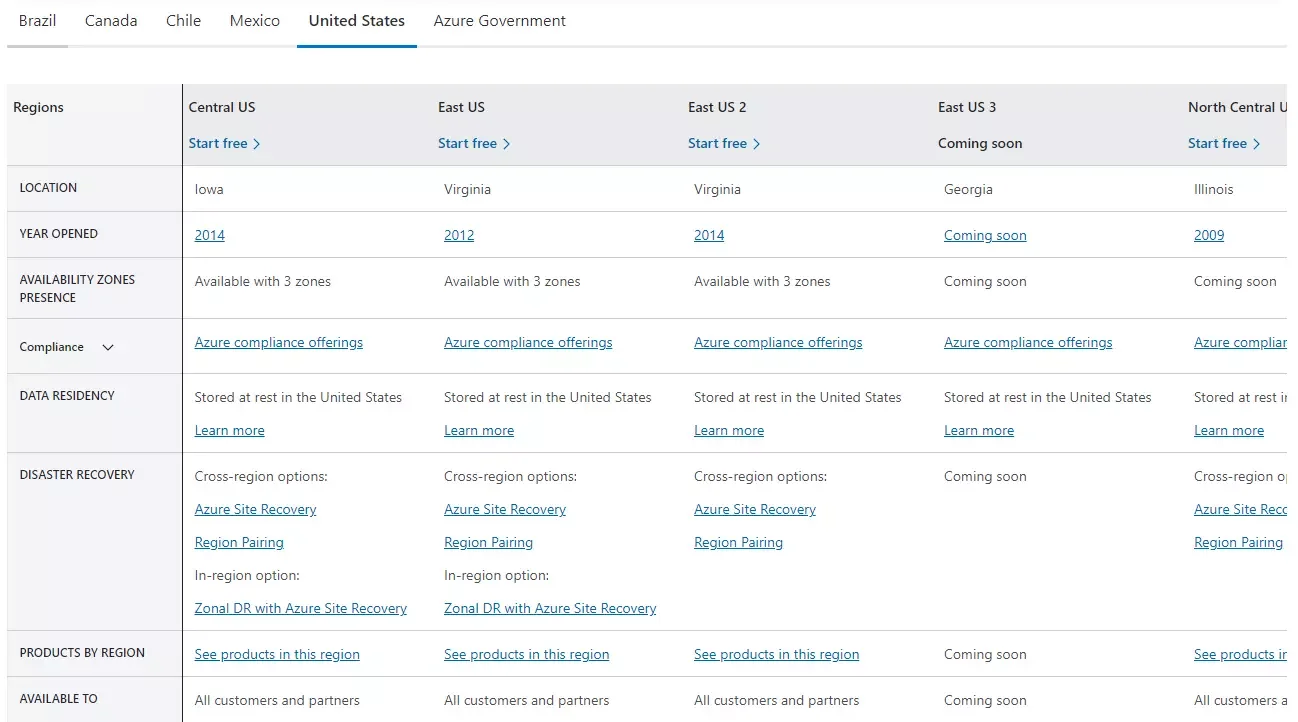
Azure Availability Zones in the US
Just like AWS AZs, each Azure Region offers three separate Availability Zones (AZs), each with independent power, cooling, and networking infrastructure. If one or more zones within a region fail, there will be a backup.
Similarly, GCP has a global reach, not as deep as AWS and Azure, but still more than Alibaba Cloud, for example.
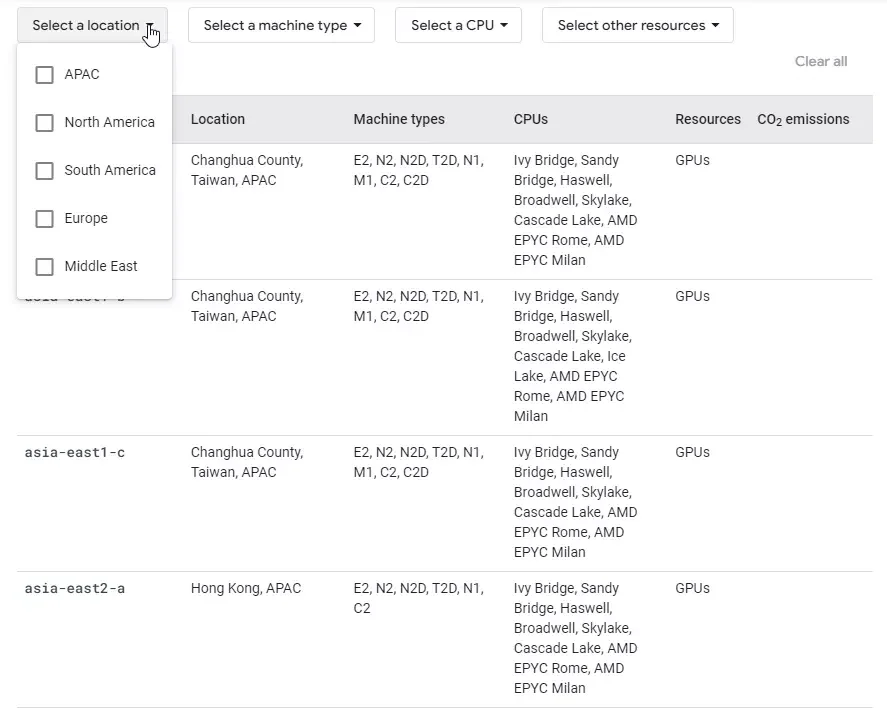
GCP Regions worldwide
The closer the services are to the end user, the lower the latency and the better the performance. The over 40 GCP Regions also offer two or three independent Zones in case one or two zones fail or have issues.
2. Services
AWS offers over 243 fully featured cloud products and services, the most by any cloud provider today. The vendor organizes its services and products across categories, including compute, storage, networking, serverless, databases, analytics, and security/compliance/identity management.
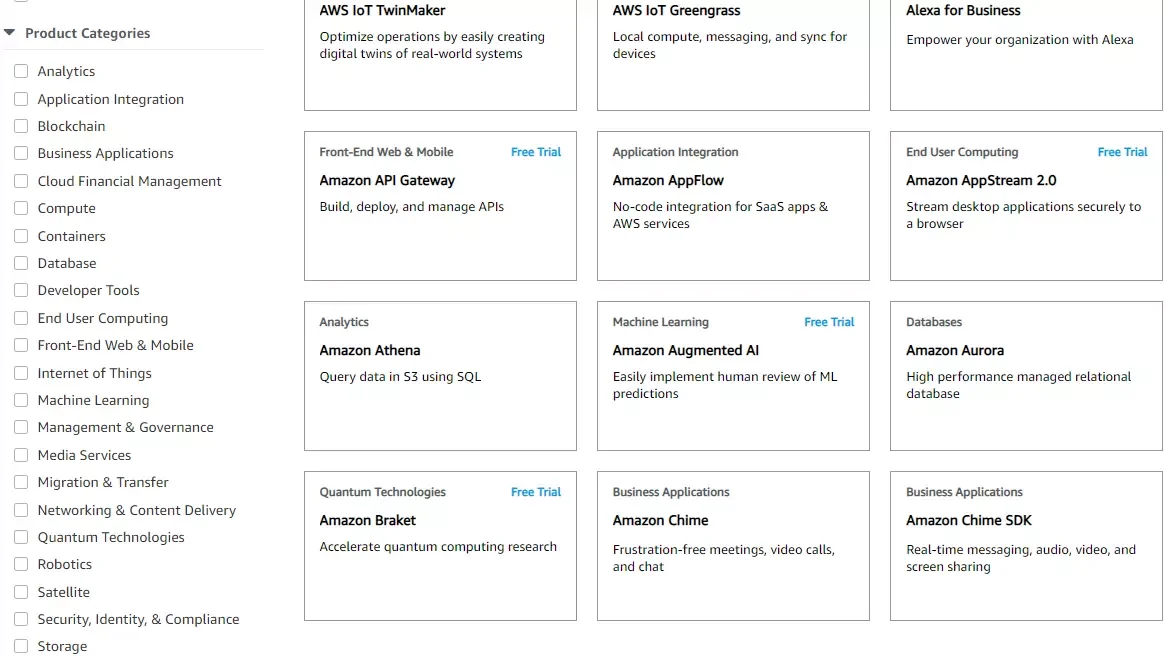
AWS cloud services and products categories
Similarly, Azure Cloud offers a wide range of cloud services, with multiple products under each cloud service category.
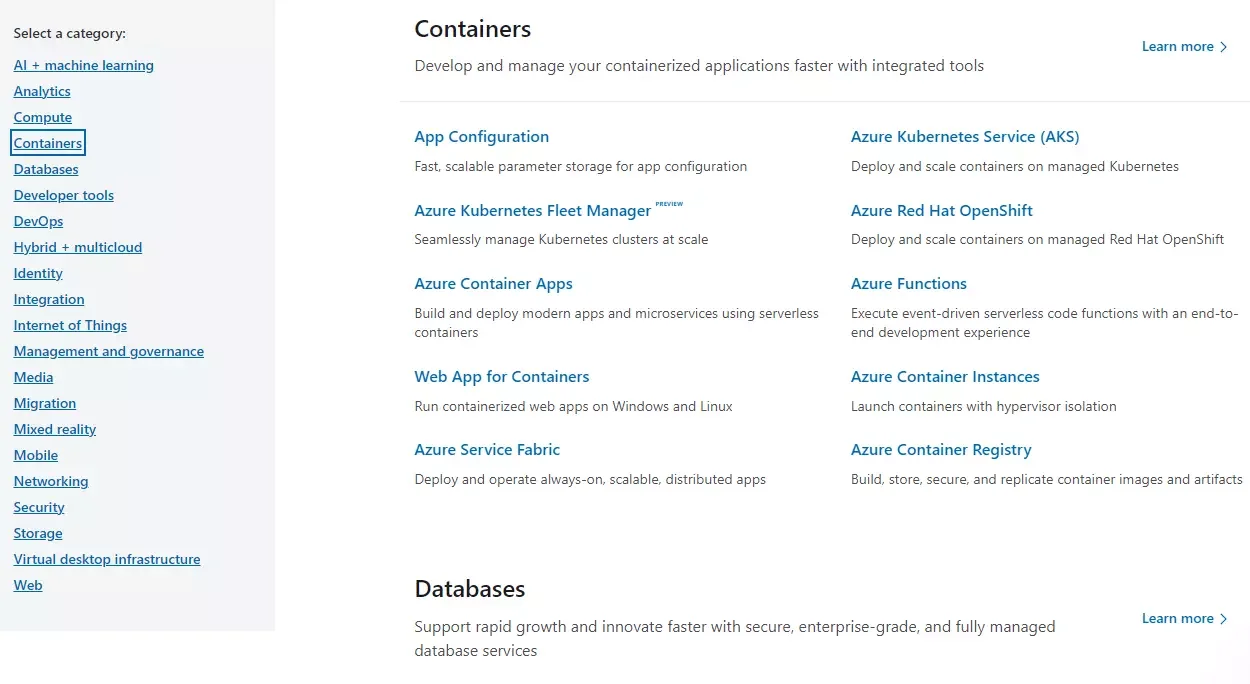
Azure cloud services and products
While the Google Cloud Platform seems to offer fewer products, at just over 100, you are likely to find the solution you need. Check this out:
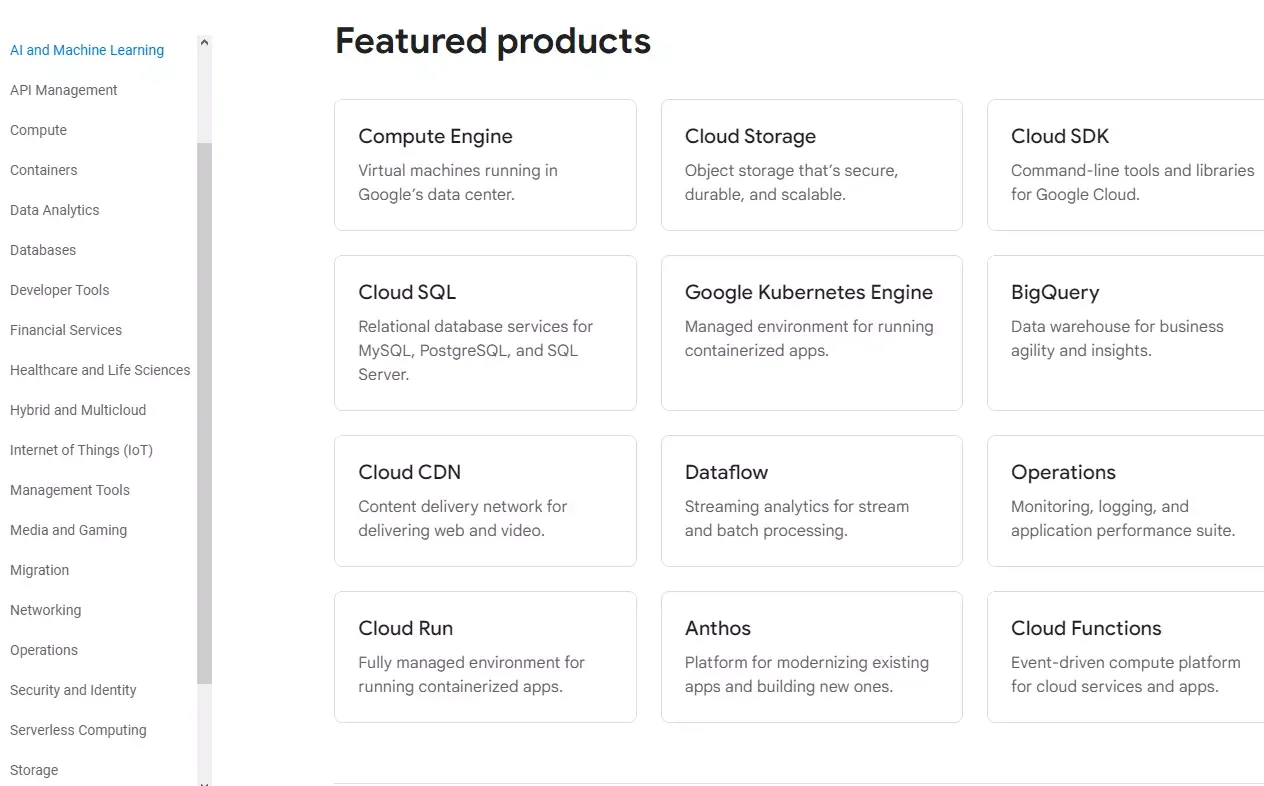
Google Cloud Platform services and products
Again, before choosing a provider, be sure to review their service specifications thoroughly to ensure that they will meet your workload requirements.
3. Compute, storage, and networking
The vendors group their instances or virtual machines into different categories based on their suitability to specific workloads, such as:
- Compute-optimized instances/VMs for compute-intensive workloads, or
- Network-optimized instances/VMs for workloads that require low latency and high throughput.
For workloads that require balanced compute, memory, and networking resources, all three also offer general-purpose instances and bare metals.
As far as instance or virtual machine sizes go, GCP’s M2 series virtual machine, which features 12 TB RAM and 416 virtual processors, is the largest of the three cloud service providers. In comparison, AWS and Azure offer instances with a maximum of 128 virtual CPUs and 3.84 terabytes of RAM as well as 128 virtual CPUs and 3.89 terabytes of memory, respectively.
Now, we get it. Finding the right instance type or virtual machine for a specific use case can be tough. A trial-and-error approach might not be feasible for you, and you may not have the funding and luxury to experiment.
That’s why we recommend using CloudZero Advisor, a free tool that helps you pick just the right machines by instance or VM type, size, service, budget, workload, and other factors.
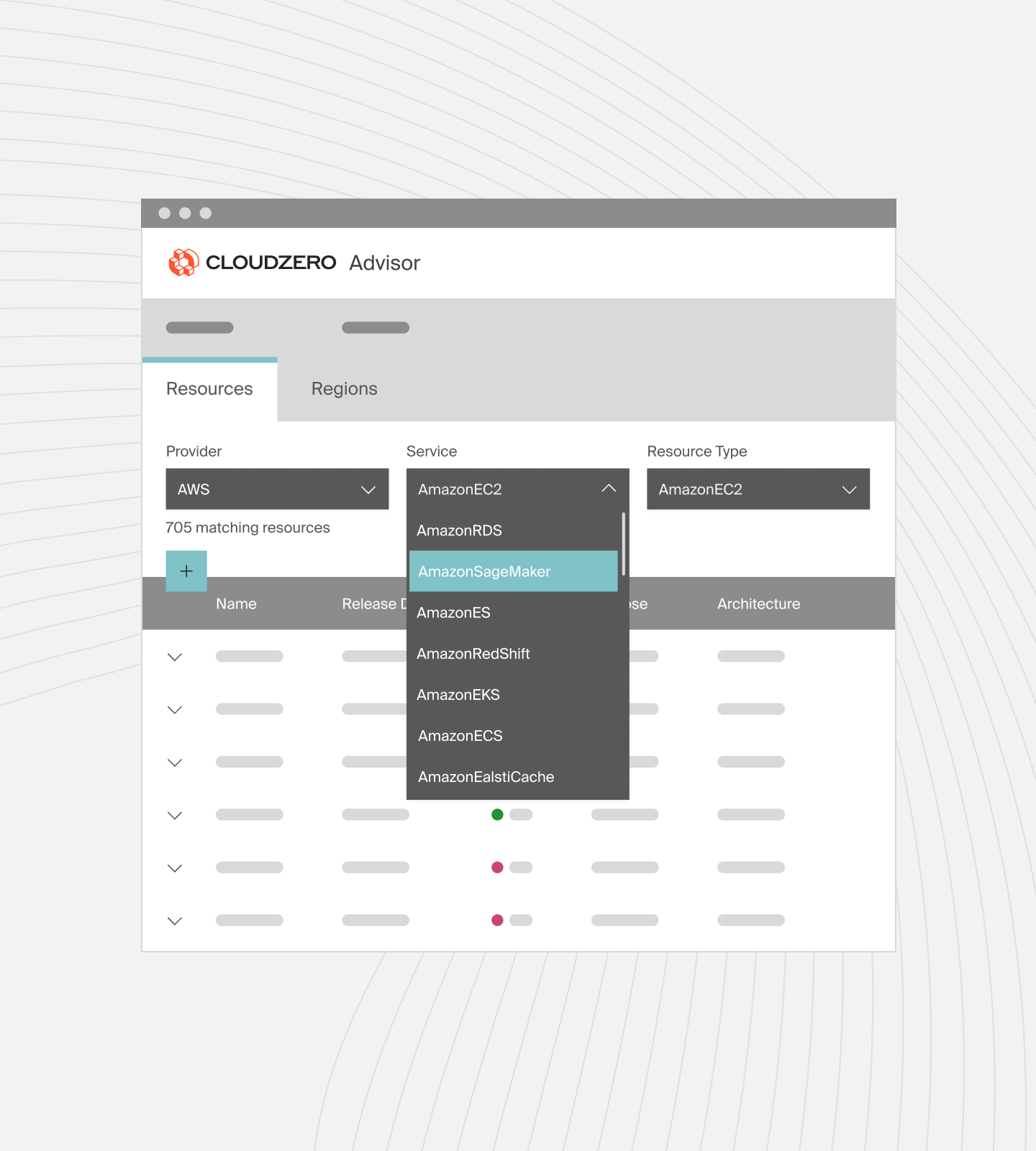
Something else. You can run Linux or Windows machines on Azure, GCP, and AWS. Azure lets you use your existing Microsoft licenses, whereas GCP and AWS require additional Windows licensing costs.
AWS, Azure, and GCP share a lot of similarities in terms of storage, such as fast SSDs, cheaper hard drives, and multiple archiving options. All three vendors also offer object, file, persistent block, and other types of cloud storage.
Some differences here include:
- Azure offers an actual data backup service; Backup
- AWS offers Snowball, a service that allows users to physically carry and transfer petabytes of data when internet transfers aren’t feasible.
- Transfer Appliance, a GCP service, provides a similar feature.
On to the next.
4. Open-source support
AWS has a long history of working with open-source communities. Examples include Apache Kafka, Linux, MySQL, and OpenTelemetry. It also open-sourced projects like .NET Porting Assistant and Babelfish for PostgreSQL to enable developers to switch from proprietary to open-source software.
The Azure cloud platform is increasingly supporting open-source projects, although many are still handled by third parties such as RedHat, Terraform, and Databricks.
However, Google went bigger. Among Google’s Open Source projects are Kubernetes (container orchestration), Istio (service mesh), TensorFlow (machine learning), and Go (programming language), most of which it donated to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). If you intend to integrate or leverage such platforms or tools, GCP may be the best choice.
5. Containers
All three vendors offer managed Kubernetes services to simplify K8s deployments;
Amazon EKS supports a broader range of earlier Kubernetes versions than AKS and GKE, which mainly support the latest versions.
Also, while AKS and GKE offer more pre-configured solutions out-of-the-box, EKS provides more flexibility to customize the cluster setup. For example, you can create custom AMIs for EKS worker nodes. This provides greater customization and control over your Kubernetes environment.
In addition, AWS’s vast, multi-AZ (Availability Zones) support ensures high availability and fault tolerance even for large-scale deployments.
In addition, AWS also offers the Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS), an AWS-native, managed service for Docker containers. ECS uses Amazon ECR for storing, encrypting, and managing container images.
You can also provision, run, and self-manage Kubernetes on AWS using Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances. Self-managing Kubernetes on Azure or GCP isn’t as straightforward.
It costs an extra $0.10 per hour per cluster to run containerized apps with EKS than with ECS.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Expect strong integration with Azure services like Azure Active Directory, Azure Monitor, and Azure DevOps. AKS also offers excellent support for developers with integration into Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code. There are also advanced hybrid cloud capabilities with Azure Arc and Azure Stack.
Better still, AKS automatically upgrades the Kubernetes version of your control plane, reducing upgrade burden. You can then upgrade the node pools manually or automatically to match the control plane version.
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE):
GKE is often seen as the most aligned with the upstream Kubernetes project because Google originated Kubernetes. GKE is also deeply integrated with the broader Google Cloud ecosystem, including Cloud Storage, BigQuery, and Cloud Pub/Sub.
Also, expect seamless integration with Google’s AI/ML services like AI Platform and TensorFlow. It also supports advanced networking capabilities, including global load balancing and VPC-native clusters.
Better yet, GKE offers a per-second billing model, making it more cost-effective for workloads with fluctuating resource demands compared to AKS and EKS.
6. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics
In terms of big data, predictive analytics, and data lakes for AI and machine learning, the three offer quite similar services, but with subtle differences.
GCP offers the most advanced Deep Learning models and powerful hardware accelerators (Cloud TPUs).
Meanwhile, Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure both offer ML studios for developing machine learning models. Azure’s studio does not require a deep knowledge of data engineering, Python coding, or open-source libraries the way Amazon SageMaker does.
7. Support and pricing
AWS, Azure, and GCP all use pay-as-you-go pricing, with varying rates if you use the resources on-demand or on a reserved basis (committed use discounts).
About GCP pricing:
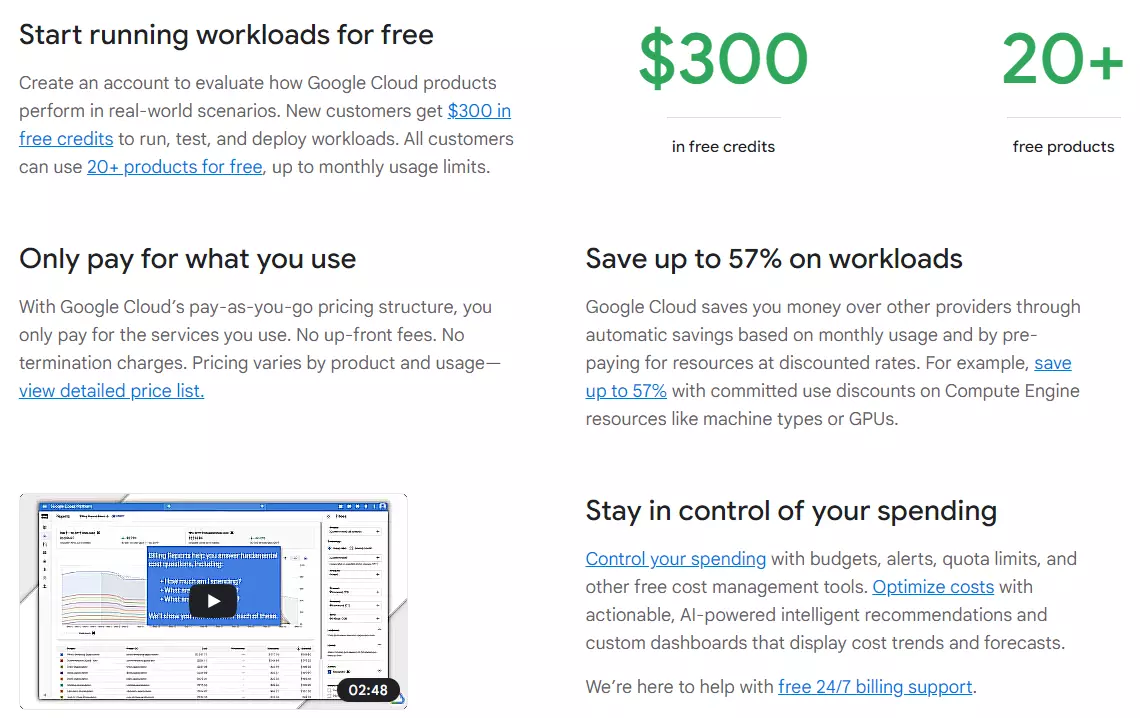
- Get sustained use discounts of up to 30% when you use the same instance repeatedly.
- Save up to 80% on compute costs when you use Preemptible VM Instances for workloads you can start, pause, and restart later.
- You can get up to 57% off when you use a particular VM long-term (reserved capacity)
- The GCP Free Tier offers more than 20 always-free products
- Get a $300 credit to test out paid GCP services
About AWS pricing:
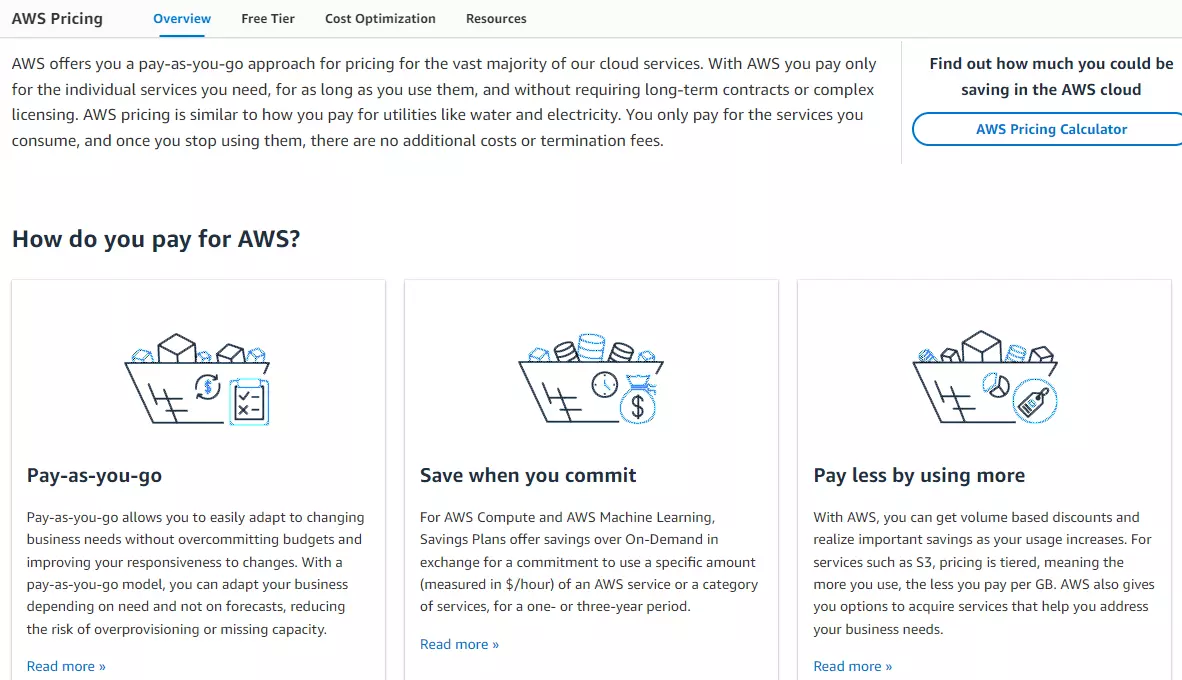
- Save up to 72% on compute costs with Reserved Instances (fixed instance capacity over a 1- or 3-year period).
- Use Spot Instances to cut compute costs by up to 90%.
- Use more than 40 AWS services for free forever with the Free Tier.
- Get free trials across 100 AWS products.
- Use specific services free for 12 months to test out the AWS platform.
- AWS Credits are available for eligible startups.
- Get up to 750 hours worth of free compute per month to use across most AWS services
About Azure pricing:
- It is up to 5X cheaper than AWS for Windows VMs, SQL Managed Instances, and SQL Server VMs.
- Get up to 72% off when you adopt committed usage across one or three years (Reserved VMs).
- Enjoy up to 40% off Azure Hybrid Benefits if you use Microsoft software on-premises.
- Developers and testers get substantial discounts for using Visual Studio.
- Grab additional discounts across Azure services when you have a Microsoft Enterprise Agreement (EA).
- Azure offers a free tier with minimal services, many more popular services for 12 months
- Get a $200 credit to try any other paid service.
Want even more specifics? Check our AWS vs Azure pricing comparison for an in-depth guide on what costs to expect.
8. Uptime and latency
Azure, AWS, and GCP all claim 99.99% (four nines of uptime). However, their Service Level Agreements (SLAs) often guarantee 99.5% uptime for some services and 99.99% for others.
For exact guidelines, the AWS SLAs page details how compensation for service unavailability works (you earn service credits for lower than promised uptime, for example). The Azure SLAs page also talks about this variation in more detail as does GCP’s SLA documentation.
Amazon Web Services: Pros And Cons
These are some of the benefits and drawbacks of using Amazon Web Services.
AWS Pros
- Extensive coverage: The vendor provides over 240 cloud and on-premises services, superior IaaS and PaaS, and multi-cloud support.
- Global data center locations: Amazon’s cloud infrastructure spans 33 Regions, 105 Availability Zones, 245+ countries, and 450 Edge computing sites.
- AWS community: AWS has the largest market share and a very active community. In turn, this translates into extensive documentation, tools, and third-party support.
- User-friendly setup: AWS is relatively easier to use than Azure for new cloud users. With several low-cost, free, and open-source solutions, AWS also tends to be more suitable for small and medium businesses.
- Developer-friendly: Expect vast configuration options, self-service provisioning, and fully managed services.
- AWS Marketplace: Offers a wide variety of compatible and secure third-party add-ons.
- Extensive data backup: The vendor leverages its vast global infrastructure to backup data across multiple locations.
AWS Cons
- Potential overwhelm: There are a lot of cloud products, services, and features to choose from.
- Complex pricing: When combining different products and processes on AWS, it can be difficult to determine what costs to expect.
- Basic cloud cost management tools: AWS Cost Explorer, Cost and Usage Report, and Cost Calculator display cost overviews rather than in-depth cost insights, such as cost per customer and cost per product feature.
- Vested interest: In some verticals where Amazon is an increasingly prominent player, some enterprise customers view AWS as a competitor, opting to use another cloud service provider.
- Limited hybrid and on-premises capabilities: AWS is relatively new to the on-premises and hybrid cloud space, so it hasn’t matured as much as say, Azure.
- Costly support: Getting enterprise-level technical support can be costly.
When should you use AWS?
Any organization, regardless of size, industry, budget, or location can use AWS services. Its broad range of services, IaaS infrastructure, and pay-as-you-go pricing make AWS stand out. The provider is ideal for multi-location data backups.
Microsoft Azure: Pros And Cons
As with any service, Microsoft Azure has its benefits and drawbacks as well.
Azure Pros:
- Superior enterprise support: Microsoft has provided enterprise solutions for years, making it a natural choice for large businesses. Additionally, it offers superior hybrid cloud and on-premises services vs AWS and GCP.
- An extensive network of global data centers: The vendor offers the second-largest cloud data center network, accessible 24/7 from (almost) anywhere in the world.
- Integrate seamlessly with Microsoft business applications: These include Microsoft 365, Azure Virtual Desktop, Microsoft SQL Server, and Power BI.
- Use existing Microsoft licenses: Azure makes it easy to integrate existing Microsoft licenses to prevent additional costs.
- Cost-effective: It is relatively cheaper than AWS for enterprises, but not for SMBs.
- Extensive support for Linux OS: It also offers a wide range of tools for monitoring, managing, and securing Linux applications.
Azure Cons
- Complex pricing: Azure pricing, like AWS, can be challenging to unravel down to the individual services and products.
- Basic cost management tools: Native Azure cost tools provide high-level cost information. Actionable cost intelligence requires third-party tools.
- Not SMB-friendly: Focuses primarily on enterprise customers.
- There are customer complaints about technical support quality.
When should you use Azure?
The best choice for large enterprises, especially those that already use Microsoft products and licenses, such as Microsoft 365 and Windows SQL Server. Microsoft Azure is ideal for hybrid cloud deployments in which enterprises want to use both public and private clouds.
Google Cloud Platform: Pros And Cons
Consider the following.
GCP Pros:
- Better price/performance: While Azure offers lower prices, GCP delivers overall more affordable services.
- Exceptional containerization support: Google has contributed to container technologies for years, including Kubernetes and Istio.
- Suitable for SMBs: The vendor offers cloud solutions for small and medium businesses as well as smaller projects at large companies.
- Superior open-source support: GCP has extensive relationships with the open-source community, participating in numerous projects with partners such as RedHat.
- Advanced ML and blockchain capabilities: From Google Search to YouTube, GCP has a huge database supporting its Deep Machine Learning and blockchain capabilities.
- Seamless integration with Workspace: Companies using Gmail for Business, Spreadsheets, Forms, and Google Docs will find GCP a natural fit.
- Support for multi-cloud deployments: Azure pioneered hybrid cloud deployments, but Google Cloud Platform is championing multi-cloud deployments.
- More user-friendly pricing model: Pricing on GCP is more straightforward than on AWS and Azure.
- An excellent DaaS service: Like Azure, GCP has a robust virtual desktop offering.
- Global fiber network: Supports speedy operations
GCP Cons
- The limited availability of data centers in certain regions limits its uptake and capabilities.
- Limited enterprise solutions support
When should you use GCP?
GCP is perfect for SMBs who want to grow with cloud-native operations, AI, ML, and data analytics. The service is also great for companies that want to use GCP with two or more public clouds.
How To View, Control, And Reduce AWS, Azure, And GCP Cloud Costs
These vendors offer a wide range of products, services, and processes. This flexibility has the downside of making understanding, tracking, and optimizing cloud costs challenging. Companies end up wasting about 33% of their cloud budgets due to this cost invisibility.
In addition, AWS, Azure, and GCP offer basic cloud cost management tools. Due to their limited features, it’s difficult to figure out what drives your cloud costs.
Enter CloudZero’s Cloud Cost Intelligence approach
CloudZero uses a code-driven approach to gather, analyze, and share detailed cost insights without overwhelming you. Unlike AWS, Azure, and GCP cost tools, you don’t need perfect tags to collect accurate cost insights with CloudZero.
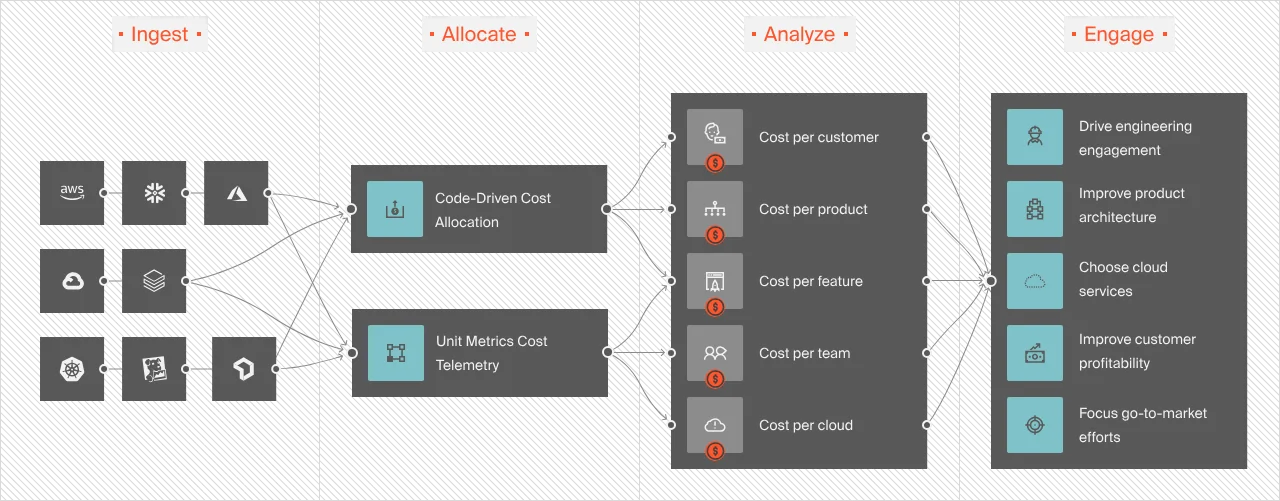
CloudZero also empowers you to:
- Unit cost economics: Use Cost per Customer, as opposed to Average Cost per Customer, to identify the cost of supporting a particular customer. You can then decide how to price their contract competitively while maximizing profit.
- Multi-cloud cost intelligence: View, understand, and analyze AWS, Azure, and GCP costs in one place. Also analyze platform costs, such as from Kubernetes, Snowflake, New Relic, MongoDB, and more. Truly a single source of truth. No separate dashboards. No need for extra cost tools.
- Pick the best VMs and instances: Use CloudZero Advisor to choose the right instances or VMs based on your workload, budget, service, and other factors.
- Avoid cost surprises: Set, track, and optimize your custom cloud budget. Then get real-time cost anomaly detection and smart alerts via email, Slack, and text to prevent overspending.
- Engineering-Led Optimization: Empower your engineers to see how their technical choices affect cloud costs so they can build efficient solutions. ELO provides the insights in their own language, such as Cost per deployment, per environment, per service, per feature, and more.
- CloudZero Discount Optimization Portal: Get the most out of your Reserved Instances and Spot Instances with CloudZero’s partners, ProsperOps and Xosphere.
- Certified FinOps expertise: Get ongoing, experienced advice to allocate 100% of your cloud costs and have CloudZero pay for itself in about three months.
Don’t just take our word for it. We helped Drift save $2.4 million in annual costs. Upstart has saved $20 million. Malwarebytes saves up to 10 hours weekly managing cloud costs now. You can, too. Risk-free.  to experience CloudZero yourself.
to experience CloudZero yourself.