Big data empowers enterprises to uncover valuable insights and make sound business decisions. The rigid schemas of traditional databases are increasingly unable to meet the demands of today’s data-hungry businesses.
Enter data lakes — a modern approach to data management that harnesses the power of big data to unlock actionable intelligence. Here are insights you need to know right now.
What Is A Data Lake?
First, what is a data lake, and is it different from a traditional database?
A data lake is a central repository that stores vast volumes of both structured and unstructured data “as-is” in a native format. Data lakes break down the silos between different data types like audio, video, images, and text and combine them to provide a holistic view of an organization’s data assets.
In a data warehouse, a schema is defined for each data source. This can be time-consuming. In contrast, data lakes have a “schema on read” approach, which means users can apply the schema as and when they view the data.
Thus, schema-on-read lets each user create a schema specific to the use case and derive value from it instantly. This is extremely useful for businesses as they can conduct experiments and do ad hoc analysis on data to arrive at actionable results.
With the wave of big data invading systems, data lakes seem to be a viable option in not only handling data but also making sense of it. While machine language algorithms can extract information from historical data, they cannot work with transformed data.
For ML systems to work effectively, raw data is essential, and this is where data lakes fit the bill perfectly.
Analytical practices like data mining, data exploration, ML, and AI can be applied easily to data present in the data lake architecture to find answers to pressing business queries.
What Is Data Lake Architecture?
Data lake architecture refers to a centralized repository designed to hold vast volumes of data in its raw format. The architecture also leverages a flat architecture, enabling flexibility in accommodating various data types and evolving data analytics needs over time.
The design accommodates structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. The architecture includes core components like ingestion, storage, processing, and consumption layers, with options for on-premises, cloud, or hybrid configurations to suit different organizational needs.
No matter how much data is present in your data lake, it is going to be of little use if you lack the means to utilize it effectively. Therefore, implementing proper data lake architecture is important for organizations to obtain optimal results from their data.
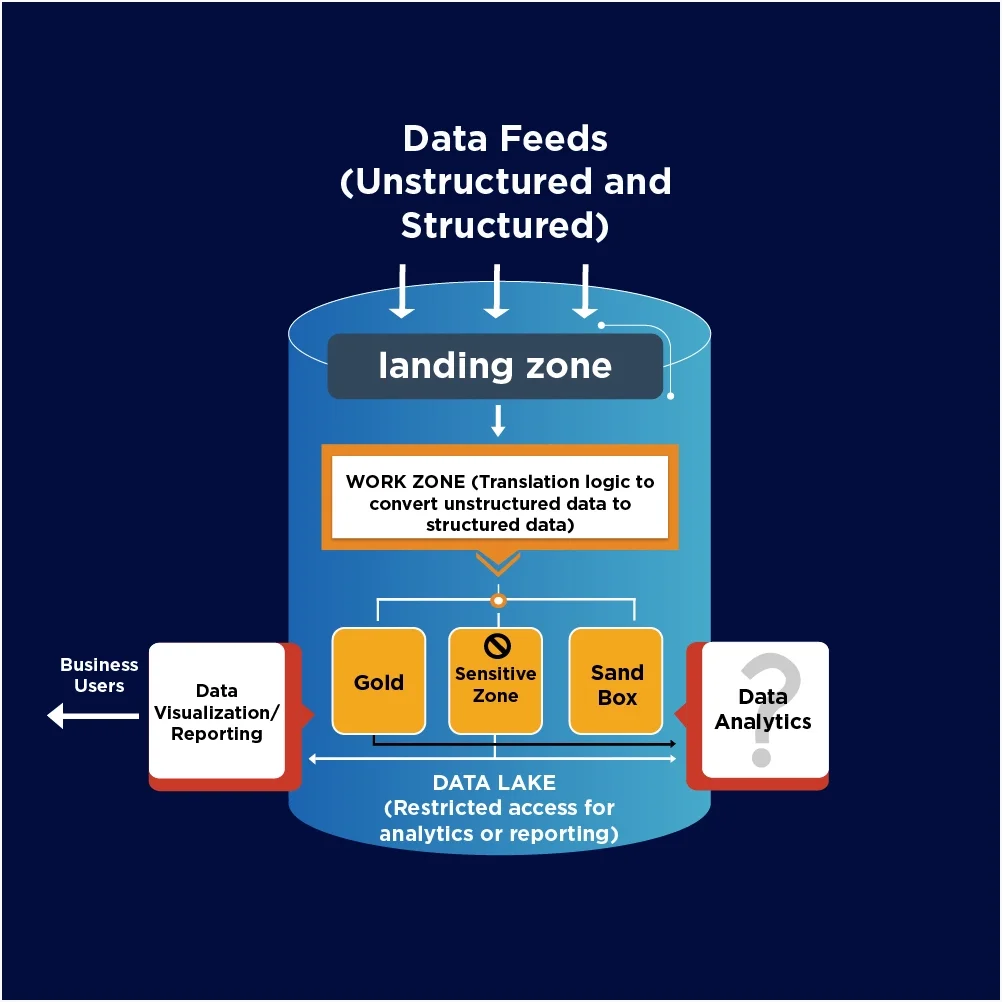
Data lake architecture usually consists of 3-5 layers. They are:
- Landing zone – This is the staging area where data is ingested into the data lake. Here data is kept in raw form and can be stored indefinitely.
- Sandbox – In the sandbox region, data scientists work with raw data to create prototypes and build new use cases. They run experiments on the data without having to move the data anywhere.
- Work zone – In the work zone, engineers and data scientists clean and convert the data into an analysis-worthy format. Once the data has been altered, it moves to the gold zone.
- Gold zone – This zone stores clean and processed data. This is where business analysts apply BI tools and ML algorithms to the data to create visualizations and reports.
- Sensitive zone – This zone contains sensitive data, whether because of business needs or government regulations.
Key Data Lake Concepts to Know
Consider the following illustration by MongoDB:
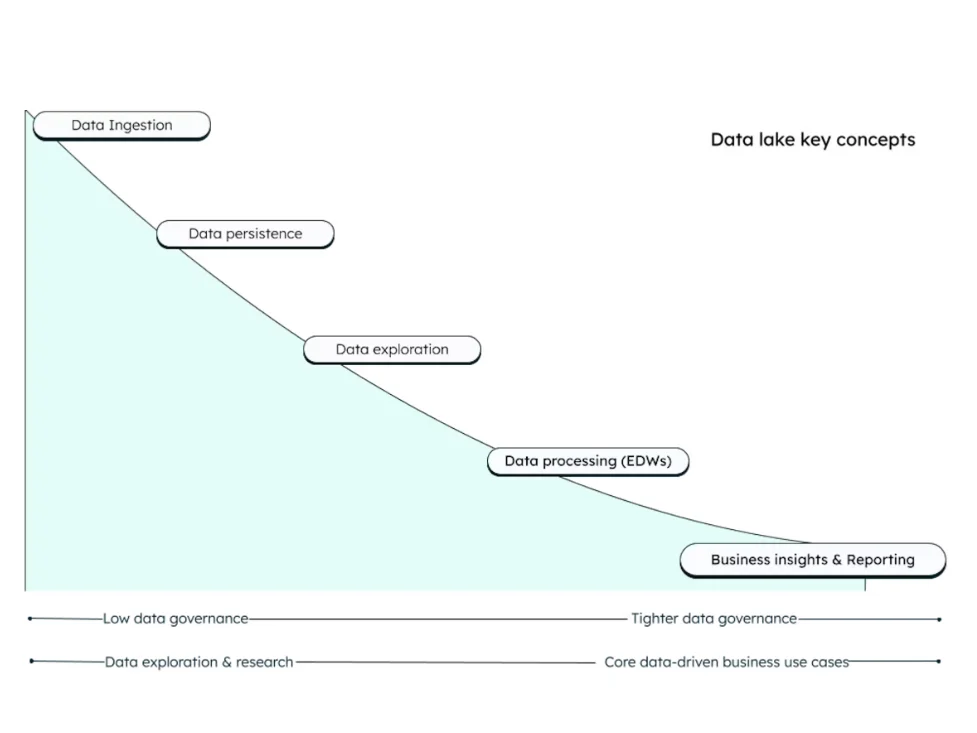
Credit: MongoDB
The data lake architecture involves five main concepts; ingestion, persistence, exploration, processing, and insights and reporting. Here’s a quick brief about each concept.
1. Data ingestion
This is the point at which data is collected. It is also known as the landing zone for all types and volumes of data. The data lands in its raw form from apps, SQL/NoSQL databases, live streaming, devices, and other sources. Because the data is unprocessed, there isn’t much governance required at this point.
2. Data persistence
Data persistence requires storing data on a non-volatile medium to retain it for long-term use. The goal here is to keep data intact even in a power outage, across sessions, and other scenarios.
In data lakes, persisting data involves storing it in object storage, in devices like hard drives, SSDs, or cloud storage. It also includes providing metadata and indexing mechanisms, guaranteeing accessibility and durability over time.
3. Data exploration
This stage comprises exploratory analysis. This involves scrutinizing data to discover patterns, trends, and additional insights. Data lakes enable in-depth analysis of diverse datasets for real-time analytics, machine learning, and advanced insight.
Practical applications here include real-time analytics for e-commerce, sentiment analysis, predictive maintenance in industries, and exploratory data analysis (EDA) without the need for predefined structures — and this enables flexibility and advanced analytics.
4. Data processing
Processing data standardizes it. This standardization uses functions and queries. It also involves extracting, cleaning, sorting, aggregating, normalizing, indexing, and replicating data. This process is often in the form of Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) or Extract, Load, Transform (ELT). ELT is particularly preferred for data lakes because it is designed to handle large datasets of unstructured data.
5. Business insights and reporting
This stage deals with refined, enriched data, also known as true data. It is stored in EDWs (Enterprise Data Warehouses). This data is actual business intelligence that is ready or almost ready to use for specific use cases and lines of business. And as such, the data needs strict governance to protect business secrets, for example.
Data governance is a management aspect that involves coming up with, enforcing, and improving data security guidelines, procedures, and policies.
6. Data lineage and cataloging
Data lineage involves tracking the transformation of data from its original state to the refined form. By tracking this process, you can pinpoint where improvements can be made to create the most useful, practical data possible.
Meanwhile, cataloging data involves using labels and metadata (data mapping) and creating inventories of data in structured and unstructured formats, enabling quick searches.
What Is The Difference Between A Data Lake And A Data Warehouse
The biggest difference between a data lake and a data warehouse is that while a data lake stores unprocessed data in any format (original state), a data warehouse is a repository for pre-processed data that is ready to use for business intelligence, reporting, or additional analytics.
Data Lake | Data Warehouse | |
Types of data | Unstructured, semi-structured, structured, | Structured |
Data processing | Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) | Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) |
Ideal use case | Storage of raw data for future processing | Performing queries |
Schema | Schema-on-read | Schema-on-write |
Curation level | Raw data | Highly curated data |
Example solutions | Informatica’s Intelligent Data Lake, AWS Data Lake Formation, Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage | Snowflake, AWS Redshift, Databricks |
Four Best Practices For Successful Data Lake Architecture
Regardless of which data lake architecture you choose, the following best practices can help you make better use of your organization’s data lakes.
Catalog the data
Without proper organization, a data lake can turn into a data swamp. If users get confused by the contents of a data lake, then it loses its purpose. Data catalogs typically include details about the health and location of data, and applications that use the data. By providing accurate info about the data that exists within the data lake architecture, data cataloging makes it easy for organizations to work productively with data.
Data governance and access control
Simply pushing data into a data lake will get you nowhere, as unregulated data can quickly turn into a data sprawl. A clear data governance strategy will allow users to extract useful facts from the stored data and make smart, data-driven decisions for the benefit of the organization.
Secure your data lakes
This one is an easy decision. An absence of security measures can play havoc on a company’s data. Basic security features to implement in a data lake include encryption, authentication, and access control of data to prevent unauthorized access to the data lake. It is also necessary to adhere to compliance requirements and ensure that sensitive information stays secure.
Leverage automation and AI
Given the sheer variety and scale of data present in data lake architecture, it can be difficult to handle it manually. Automating the process helps. Enterprises would do well to use next-generation analytical techniques to analyze data and unearth precious information.
Benefits And Disadvantages Of Using Data Lake Architecture
The benefits of data lakes to organizations are manifold. Combined with data mining tools, data lakes enable you to get detailed insights about your business. The benefits include:
Data stored in raw format – In a data lake, you do not have to pre-model the data at the time of ingestion. Data is simply stored in its raw form. Data analysts apply exploratory analytics on this raw data to help businesses optimize their performance.
Democratize data – Data lakes democratize data as data is made available to all employees in the organization through a data management platform. It is left to the users to choose data as per their business requirements.
Agility – Since data lakes lack the structure of a data warehouse, they are far more agile and flexible. While warehouses are ideal for repetitive tasks, data lakes are a boon when data sources and their magnitude keep changing. The agility of data lakes makes it easy for data scientists to keep experimenting with data models and arrive at solutions that spur business growth.
Versatility – A data lake is extremely versatile as it stores data from varied sources such as social media feeds, XML, multimedia, IoT sensors, binary, and log files.
Offers schema flexibility – Data warehouses require data to be in a specific schema. While it is great for OLTP, it acts as a barrier for analytics when you want to analyze the data “as-is.” Since a data lake is schema-free, it is very helpful for analysts to perform experimental analysis and develop new patterns without having to worry about the initial structure of data.
Empowers users – Data lakes empower data scientists to directly access the data lake and run queries on it. It thus does away with the dependency of analysts on IT teams and helps save time.
While data lakes have a host of benefits, they are not without disadvantages. Some disadvantages of data lake architecture are:
Lack of data prioritization – Data is useful only when it is of use to someone. If a company has a difficult time locating data, then it doesn’t serve any purpose. A lack of data prioritization can lead to a data sprawl and slow down the analytic process ultimately benefiting no one. This can be avoided by providing some structure to the data before storing it in data lakes.
Security and compliance risks – Data lakes store data regardless of its origins thereby exposing your organization to a host of risks, including compliance risks. Also, the disparate data in the data lake have different security policies. Thus, mixing them up altogether without proper controls can muddle up the process and cause a lot of complications.
Lack of user adoption – Data scientists are probably the only ones who are comfortable working with unstructured data. Because of the complexity involved, a large swathe of users stay away from data lakes detracting from the very reason data lakes were set up in the first place.
Data Lake Solutions
The highly elastic nature of cloud computing and low storage costs offered by cloud companies make them a feasible option for implementing a data lake. Some data lake options in the cloud are:
AWS S3
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is an object storage service that offers 99.999999999% durability, unlimited scalability, and centralized data architecture for hosting data lakes.
Once data is on S3, AI and ML techniques are applied to run ad-hoc analysis, generate reports, and create dashboards. S3 integrates with the broader AWS ecosystem and third-party services to provide useful business details to customers seeking answers.
Snowflake
One of the most competitively-priced data lake solutions in the market, Snowflake offers data storage and analytical services to corporate clients.
A big advantage of Snowflake is that even though customers can have data lakes housed on S3, Azure, or Google Cloud, they can still integrate them inside Snowflake. Built on ANSI SQL, Snowflake generates sound analytics allowing you to maximize the full potential of your data lake.
Gaining A Holistic View Of Your Data Lake And Cloud Costs
A big benefit of data lakes is that they provide users the flexibility to study and analyze data in an experimental way rather than being restricted to the structured schema sets of databases.
Data lakes enable organizations to import multiple sources of data and store it in their raw format. By using advanced analytics on this raw data, companies can derive beneficial and actionable insights that can help them get ahead of their competitors.
While data lakes are of immense benefit to organizations, they do have some demerits. Chief among them being understanding the massive volume of data streaming in from numerous devices and managing the costs of maintaining a data lake.
Companies should understand that building a data lake architecture is no easy task. It is therefore crucial to select a cost management platform that can help engineering teams monitor and measure their data lake costs.
How CloudZero Can Help You
Whether you go with AWS or Snowflake as your preferred solution, CloudZero can help you analyze the costs associated with both and how costs affect your business.
Combining cost insights from both AWS and Snowflake, CloudZero gives you a holistic view of the cost of goods sold (COGS) and unit cost. From there, you can get immediately actionable insights such as:
- Cost per product feature
- Cost per tenant
- Cost per customer
- Cost per dev team and more — all without manual tagging.
Ambitious brands, including Drift, Applause, and Shutterstock already use CloudZero to understand, control, and optimize their cloud costs. Drift saved over $2.4 million and Applause resuced their cloud spend by 23% with CloudZero. Want similar successes or better? Take a product tour here or  to experience CloudZero in action firsthand.
to experience CloudZero in action firsthand.








