Containers are a big deal today. They are software units that contain all the code, runtime, and dependencies required to run a distributed application. Thus, containers help engineers test and run apps without compatibility issues on any device and platform.
Organizations can use containers to reduce engineering costs, speed up deployments, develop and test AI models, and automate more processes.
You probably want those benefits as well.
To help you choose the right container platform, we’ll compare the three in several areas, including configurability, ease of use, scalability, and security.
Kubernetes Vs. Docker Vs. OpenShift: An Overview
There is often confusion surrounding Kubernetes, Docker, and OpenShift, despite 90% of organizations using containers in production.
For example, Kubernetes is sometimes referred to as an all-in-one containerization platform. As this guide will reveal later on, that’s not true.
Also, you might be reading this after learning Kubernetes no longer supports Docker in kubelets. So perhaps you are wondering which platform to use moving forward.
OpenShift also markets itself as a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). Yet It comprises Kubernetes components and works with Docker. Is It still reliant on Docker and Kubernetes?
Here’s a little background to get us started.
What Is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source container orchestration platform. Engineers use it to deploy and manage clusters of hosts running Linux containers. Kubernetes works on public, private, hybrid, and on-premises clouds.
In 2015, Google donated Kubernetes to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation after designing, developing, and using it as BORG for almost a decade. RedHat, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and other vendors are now contributing to the project.
A few key features of Kubernetes include:
- Auto-scaling: K8s automatically adds or reduces the capacity to match your needs, including horizontal scaling.
- Storage orchestration: It manages the storage containers need.
- Self-healing: Through self-monitoring, recovery, and healing, Kubernetes restores or replaces containers that fail automatic health checks.
- CI/CD: K8s manages Continuous Integration (CI) workloads.
- Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud support: It also runs containers across multiple clouds.
- Load balancing: Ensures optimal resource usage and smooth operation by distributing load between containers.
- Up-to-date: Provides a powerful method for rolling out application updates.
- Community support: Numerous engineers and organizations contribute to the Kubernetes open-source project.
Credit: Kubernetes features
What are the advantages of Kubernetes?
K8s has several benefits for container management, including:
- It is cloud-native, helping your containerized apps take full advantage of cloud computing.
- It is highly scalable (up to 5,000 nodes in a cluster with HPA, VPA, and cluster autoscaler), making it ideal for large-scale deployments.
- Its self-healing capability improves reliability.
- Built to be compatible with many tools (open-source and free) to enhance extensibility.
- Portable across cloud providers, reducing lock-in.
- Managed versions are available through third-party vendors to ease management (e.g., GKE, EKS, Rancher, etc.).
- Allows you to deploy and update secrets and app configurations without rebuilding container images or exposing secrets.
- Streamlined update rollouts.
- Has a large community for support and keeping up with trends and developments.
As an engineer, you can also use Kubernetes as a platform, a container operating system, or a container orchestration tool. However, it is not a stand-alone container management solution because it requires different plugins and services.
What Is Docker?
Docker is an open platform for packaging and running applications in containers. The platform provides an end-to-end solution for building, shipping, testing, deploying, and maintaining containerized applications.
Docker launched in 2003, over a decade before Kubernetes became generally available.
Several key components make up Docker:
- Docker Compose enables you to build multi-container apps on Windows or Mac.
- Docker Engine is an open-source containerization technology using Docker files and images to build portable applications.
- Docker Hub is a repository of official Docker images and images from verified partners to help you build, share, and run images faster.
- Docker Swarm (Swarm or swarm mode) is the native container orchestration tool for Docker containers. It manages multiple containers across many hosts (physical or virtual servers). When people Compare Kubernetes to Docker, they often think of Docker Swarm as an alternative.
- Docker plugins enable you to add more functionalities to Docker. Docker Engine includes a number of plugins by default, but you can also load and use third-party plugins.
What are the advantages of Docker?
Docker has the following benefits:
- It is less complex than Kubernetes, thus easier to learn and manage
- Lightweight compared to K8s, leading to faster deployments
- Quite portable and flexible, boosting interoperability
- Supports good container scalability, so it’s ideal for mid-sized environments
- Complete ecosystem for container management, including creating and managing images, orchestrating containers (Docker Swarm), Docker Engine, and more
- Highly fault-tolerant
- Built-in app discovery
- Open-source architecture, allowing extensibility
With Docker, you can develop and run distributed app architectures, run your code with standardized CI/CD pipelines, design highly scalable data processing systems, and set up fully managed platforms for your engineers.
What Is OpenShift?
OpenShift is a self-service containerization platform that Red Hat built for enterprise use. The platform enables engineers to build, deploy, and maintain container-based applications.
As part of Red Hat’s open project, OpenShift OKD, OpenShift leverages features from both Kubernetes and Docker, out-of-the-box enterprise security, and other efficiencies to deliver a powerful alternative.
Here’s an illustration of OpenShift as a Kubernetes distribution, for example.
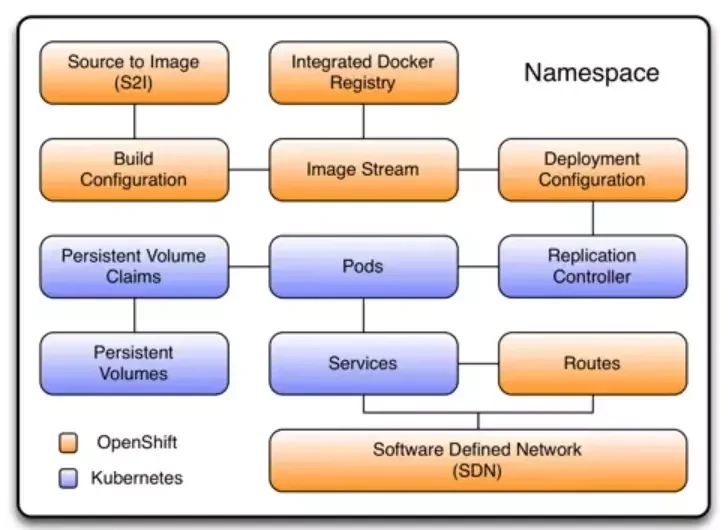
Credit: Levvel
Red Hat Openshift provides a consistent, cloud-like experience across:
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
- Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated (public cloud)
- Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift
- Amazon Red Hat OpenShift
- Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud
What are the advantages of OpenShift?
Here are reasons to use OpenShift for container management:
- Great for on-premises deployments and edge computing
- Better out-of-the-box container security compared to K8s and Docker
- Includes Istio, the service mesh tool
- Good customizability to suit your workload requirements without adding complexity
- Simplifies containerized app deployment ad management
- Seamlessly updates the underlying RHEL Core OS that the nodes run on
- Works with Kubernetes to further enhance it
- Portable across cloud providers to reduce vendor lock-in
- Available as a self-managed or as a fully managed service
- Hybrid cloud support
As with Kubernetes and Docker, OpenShift can serve as a Platform (PaaS) and a tool (CaaS). It also supports automatic and manual scaling of containers, CI/CD, and multi-tenant deployments.
There’s more to it. OpenShift also provides premium support, a user-friendly login portal, and supports multiple programming languages (Go, Node.js, Java, Ruby, Python, and PHP).
In the next section, we’ll compare Kubernetes vs Docker.
Kubernetes Vs. Docker: What Are The Differences?
The most significant difference between Kubernetes and Docker is that while K8s is a container orchestration platform, Docker aims to be a complete containerization system. For example, Docker is a container engine (runtime) with a container orchestration tool (Docker Swarm or Swarm Mode) and a dedicated image registry (Docker Hub).
Here’s a quick overview of the differences:
|
|
Kubernetes |
Docker |
|
Is it open-source? |
Yes |
Offers both an open-source project and a commercial edition |
|
Supports auto-scaling? |
Yes, by default |
No. Supports manual scaling by default |
|
Deployment type |
Pods, services, and deployment |
Services |
|
Runtime |
Supports multiple runtimes, including Containerd and CRI-O |
Currently uses RunC |
|
Health probe types |
Liveness and Readiness probes |
Vary with service |
|
Ease of set up |
Complex |
Installation with fewer commands and is less complex |
Let’s dig deeper into the details.
1. Project or product
Docker comes in two versions: the Community Edition (CE) is an open-source project, and the Enterprise Edition (EE) is a paid product with enterprise-level support. Docker EE will be ideal for teams that want to focus on their code instead of configuring an open-source platform.
The Kubernetes project is open-source and free. However, it requires investment in its infrastructure, including plugins and support services.
With Kubernetes and Docker CE, you need to download, install, set up, and oversee everything yourself, which requires skill and time. Yet, in either case, there is a large support and networking community to help you.
2. Configuration and deployment
Kubernetes and Docker work with any Linux distribution. Some examples include Ubuntu, Fedora, and Debian. CentOS supports Docker as well. Deployment options include public, private, on-premises, and hybrid cloud setups. Also, both work on Macs and Windows desktops.
Besides Windows 10, Docker is also compatible with Windows Server 1709 and 2016.
Moreover, if you need help managing Kubernetes, you can use managed services such as Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service ( Amazon EKS).
3. Ease of use
In Docker, you execute commands and automation through a single API using a client-server architecture.
A Dockerfile describes how an app is packaged into an immutable container image. The Docker server then runs the appropriate commands to build the image, which can be run on various platforms, including Docker Swarm, Kubernetes, Mesos, and HashiCorp Nomad.
In Kubernetes, kubectl, a powerful API and command-line tool, automates bulk container management tasks.
Kubernetes coordinates the resources allocated to it on your behalf. Its controllers ensure applications and containers run as specified, freeing your engineers to focus on writing and improving code rather than the infrastructure beneath it.
4. Container image management
Kubernetes does not include a native container image management system. For instance, no integrated image registry is available. However, you can create a Docker image registry, such as Docker Hub, and Kubernetes will pull images from there.
Docker includes the Docker Hub registry, where you can store and share images with compatible registries such as Azure Container Registry. Docker Pro or Team members can also access the new Advanced Image Management Dashboard.
5. Scalability and size
Unlike Kubernetes, Docker Swarm does not provide automated scaling based on resource utilization. You must manually configure scaling with a command.
Kubernetes’ inherent extensibility and horizontal scaling capabilities make it the most scalable compared to Docker. For example, Kubernetes can support up to 5,000 nodes, whereas Docker Swarm has 1,000 nodes and 30,000 containers (30 containers per node) instead of 300,000 containers on Kubernetes.
6. Security
Both Docker Swarm and Kubernetes support Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). However, Docker Swarm nodes also implement TLS mutual encryption and authentication to protect what they communicate with each other.
In Kubernetes, you need to configure your authentication safeguards. Thus, you would need to create bearer tokens or another method of authentication manually, which is time-consuming and tedious.
7. Updates
Kubernetes releases about four new versions annually. It will notify you when new versions are available and invoke the kubeadm upgrade command as soon as you decide to upgrade, simplifying the process.
However, Docker has a more frequent update schedule. It may be because it provides many tools, including Docker Engine, Hub, Compose, and Docker for Windows and Mac.
Quick reminder: if you plan to upgrade your existing installation, always create a backup first. If an update does not work as expected, you can always roll back to the stable, earlier version.
8. Networking
Kubernetes does not have a native networking solution. Meanwhile, Docker uses multi-host networking, so you can choose an overlay network for your services. During initialization or updates, the Swarm Manager automatically assigns addresses to the containers in the network.
However, while Docker runs on a single node, Kubernetes runs across a cluster. Thus, Kubernetes nodes can more easily communicate with each other than Docker nodes.
9. Templates
Docker Hub offers pre-built images. You can also create new Docker apps using a library of templates with Docker Template, a CLI plugin that offers a top-level template command.
Templates come in two forms: service templates (container images containing metadata and code) and application templates (a group of one or more service templates).
In Kubernetes, PodTemplates describes how to create pods. They are included in workload resources such as Deployments, DaemonSets, and Jobs. The controller uses the PodTemplate within the workload object for each workload resource to create actual pods. This PodTemplate belongs to whatever workload resource your app runs on.
10. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Kubernetes and Docker do not provide comprehensive CI/CD tools out of the box. Yet Docker and K8s enable developers to automate their CI/CD pipelines, adding load balancing and storage orchestration features.
Both support third-party tools like CircleCI and Jenkins to create robust CI/CD pipelines in Kubernetes or Docker.
Kubernetes Vs. OpenShift: What Are The Differences?
Red Hat designed OpenShift as an enterprise-grade, open-source container orchestration platform. OpenShift packs additional security, productivity, and hybrid cloud features to meet that grade. Besides built-in monitoring and enterprise-level security, the platform offers a self-service provisioning interface.
Here’s how Red Hat OpenShift compares with K8s.
|
|
OpenShift |
Kubernetes |
|
What is it? |
Collection of enterprise containerization tools, including a container orchestration tool (Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform) Support plans available for proprietary features and community support for open-source tools. |
Fully open-source container orchestration platform with community-based support Managed K8s services like EKS, GKE, and AKS provide support plans. |
|
Installation |
OpenShift v4.X uses a dedicated Kubernetes Operator and the configuration remains within ConfigMaps within the cluster. OpenShift v3.X uses openshift-ansible or manually following references and uses master nodes to keep the configuration. |
Uses various tools, like kubeadm, kube-spray, and kops. |
|
Supported frameworks |
Almost any platform, including cloud and on-premises, and any Linux distribution. |
Can be deployed almost anywhere but requires Red Hat’s Enterprise Linux (RHEL) or Atomic Host, CoreOS, or Fedora. |
|
Security |
Built-in encryption for application configuration data, platform secrets, and secure-by-default option. Stricter controls. For example, it disallows running containers as root, using simple images, or running many official images. |
No built-in authorization and authentication. You need to set it up manually. |
|
Networking |
Open vSwitch delivers three native plugins to support networking. Built-in DNS services. Implements HAproxy with a Router object, supporting basic routing. |
No out-of-the-box networking tool. Supports ingress for more functionality and implementation on different servers. |
|
Updates |
Multiple updates a year. Does not support multiple updates. Manually update OpenShift through the Red Hat Enterprise Linux management system. |
Releases multiple updates each year. Supports multiple, concurrent, and rolling updates. Simply run the kubeadm upgrade command. |
|
Templates |
Features a variety of templates, including Service Log, Automation Broker, and OperatorHub integration. |
Helm charts |
|
User interface |
Login with one click through an intuitive web console. |
Manually set up login authentication with the official Kubernetes Dashboard, kube-proxy, and bearer tokens. |
|
Dedicated image hub? |
Yes (Image Streams) |
No (Uses a Docker registry) |
|
Built-in CI/CD Integration |
Jenkins with source-to-image support. Supports third-party CI/CD tools. |
None. Supports third-party tools. |
Note that OpenShift Container Platform is Kubernetes-based, thus compatible with not only K8s but also most third-party tools that work with Kubernetes and other certified Kubernetes distributions.
OpenShift Vs. Docker: What Are The Differences?
Depending on your deployment, environment, or workload, Kubernetes may sometimes feel overkill. In that case, Docker and OpenShift are great alternatives to Kubernetes.
Here’s how Docker and OpenShift compare side-by-side.
|
|
Docker |
OpenShift |
|
What is it? |
Comprehensive containerization platform for small- and large-scale container deployments that builds, packages, and runs apps as lightweight containers. |
Enterprise container orchestration platform. |
|
Container runtime |
CRI-O is the default. Supports Podman for single-node use. |
RunC is currently the default runtime. |
|
Is it open-source? |
Similarly, OKD-based features are open-source and deliver community support, while proprietary services have support plans. |
Docker Community Edition (CE) is open-source, while Docker Enterprise Edition (EE) is paid and includes enterprise support. |
|
Supported frameworks |
Many platforms, but with limited capabilities unless those environments also support Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), Red Hat Atomic Host, Fedora, and CentOs. Supports cloud, on-premises, and Windows deployments. |
Almost all platforms, including cloud (public and private), on-premises, and at-the-edge Windows and Linux servers support the build, test, and deploy phases for desktop environments. |
|
Security |
Several built-in authorizations and authentication (RBAC-based), like disallowing root access to containers. |
Built-in security includes control groups, kernel namespaces, and support for hardening techniques like SELinux, GRSEC, and AppArmor. |
|
Built-in CI/CD Integration |
Jenkins (with source-to-image support) with support for third-party CI/CD tools. |
None. Supports third-party tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, Buddy, TeamCity, and Bamboo. |
|
Auto-scaling |
Automatically account for resources with OpenShift Container Platform, avoiding unnecessary auto-scaling, such as during startups. |
Supports manual scaling. |
|
Updates |
Several updates a year. Supports rolling updates (canary deployments). Manually update OpenShift through the Red Hat Enterprise Linux management system. |
Multiple updates available each year. Supports rolling updates. Use the Docker service update command. |
Also note while Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform is based on Kubernetes, it is compatible with Docker tools, like Registry, Builder, and Docker Hub.
So, which container platform should you choose?
Choosing The Right Container Platform: Kubernetes, Docker, And OpenShift
Kubernetes, Docker, and OpenShift each offer unique advantages that can be leveraged individually or together to build a robust containerized infrastructure.
When and how to use Kubernetes, Docker, and OpenShift
- Docker is ideal for small to medium-sized deployments and can scale with Kubernetes for larger needs. It offers a rich image registry, broad compatibility with environments and tools, and supports robust CI/CD pipelines. Docker Swarm requires less setup than OpenShift or Kubernetes and simplifies building, deploying, scaling, and securing containerized applications.
- Kubernetes excels in large, dynamic environments needing auto-scaling, self-healing, and advanced orchestration across hybrid or multi-cloud infrastructures.
- OpenShift is ideal for enterprises needing built-in security, compliance, hybrid/multi-cloud capabilities, and simplified Kubernetes management. It improves Kubernetes with added security features and operational tools.
Combining Kubernetes, Docker, and OpenShift in deployment scenarios
- Docker for development, Kubernetes for deployment. Use Docker for container development and testing, then deploy and scale applications in production with Kubernetes for orchestration and resource management.
- OpenShift as an enterprise Kubernetes solution. OpenShift integrates Kubernetes with enterprise-grade security and management tools, while Docker serves as the container runtime for building and running container images.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud deployments. Docker can handle lightweight microservices development, Kubernetes can manage orchestration across cloud environments, and OpenShift can secure and govern enterprise workloads.
- End-to-end CI/CD pipelines. Docker manages image creation, Kubernetes automates deployment pipelines, and OpenShift ensures security and compliance throughout the development lifecycle.
How To Understand, Control, And Optimize Your Container Costs
No matter how you use containerized architecture, collecting, analyzing, and interpreting container cost data can be challenging. All three platforms support monitoring, but most cost tools only provide total and average costs, not more actionable details such as cost per customer, per feature, or per environment.
Therefore, it can be challenging to determine who, what, and why your container costs are changing to optimize them.
But CloudZero can help.
- With CloudZero’s cloud cost intelligence approach, you can capture, analyze, and share immediately actionable cost insights across containerized and non-containerized infrastructure.
- You get industry-leading Kubernetes cost analysis. This includes understanding your K8s costs by concepts like cost per pod, node, or namespace and business metrics such as cost per feature, service, environment, customer, team, and more.
- View the people, products, and processes that drive your containerized costs. This includes per-unit cost views, such as cost per customer, per team, per deployment, etc.
- No perfect tags are required. Get the most complete Kubernetes and containerized cost visibility of any tool today.
- Allocate 100% of your cloud spend in minutes or hours, no matter how large and complex your containerized environment is.
- View your K8s costs down to the hour to prevent surprise costs.
- Combine, compare, and contrast your Kubernetes, AWS, Azure, GCP, Oracle, and even platform costs in a single place. No separate dashboards are necessary.
CloudZero customers, such as Remitly and MalwareBytes, are already saving 6-10 hours weekly on managing costs. In addition, Drift is on track to save $4 million in AWS costs. You can, too.
 to see how CloudZero simplifies your Kubernetes cost management.
to see how CloudZero simplifies your Kubernetes cost management.
Frequently Asked Questions About Docker, Kubernetes, And OpenShift
Can I use Docker without Kubernetes?
Yes. Kubernetes is an open-source platform for managing containerized applications at scale. It works with different container runtimes, including containerd, CRI-O, and RunC. Still, if you choose, K8s will deploy, scale, network, and manage your Docker containers at a large scale.
Can I use Docker without Kubernetes?
Yes. Docker builds, deploys, and runs container images without Kubernetes. The Docker Hub lets you store, search for, and retrieve the images. Docker Compose helps package containers into a multi-container app, while Docker Swarm manages and optimizes container resource utilization.
Does OpenShift support Docker images?
Yes. Despite OpenShift’s Kubernetes-based architecture, you can seamlessly work with Docker images.
What runtime does OpenShift currently use?
The Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform currently uses Container Runtime Interface – Open Container Initiative (CRI-O) as its runtime.
Can I use Kubernetes and Docker together?
Yes. Experienced engineers often prefer Docker for development and Kubernetes for the operations phases of their deployments.