Over the last few years, more organizations have switched from relying solely on one cloud service provider (CSP) to several. The primary reasons for the change are minimizing dependence on a single CSP, preventing vendor lock-in, and providing greater flexibility.
Recent trends include using a mix of cloud providers to take advantage of the cost savings several CSPs offer and using best-of-breed services for different applications, teams, or departments.
Yet managing multi-cloud deployments has been the biggest challenge. The following guide shares the best multi-cloud management tools you can use right now.
Not so fast, though. Let’s start at the beginning.
What Is Multi-Cloud Management?
Multi-cloud computing refers to using two or more public cloud services from at least two public clouds for different organizational purposes.
For example, you might use one public cloud for authentication, another for Exchange servers, and another as a database.
Most multi-cloud infrastructure users are enterprises because they have multiple use cases that can leverage various public cloud providers.

One more thing. A multi-cloud approach differs from a hybrid cloud strategy –– although the two terms often appear interchangeably.
What is the difference between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud computing?
A multi-cloud strategy involves using multiple public clouds. In contrast, a hybrid cloud strategy uses multiple public clouds and your company’s own data center (on-premises or private).
The on-premises infrastructure may be an in-house data center or any other IT infrastructure operating within its corporate network.
A hybrid cloud infrastructure ensures some applications, workloads, or processes remain on-premises or in a private cloud with controlled access. A multi-cloud strategy is best for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of public clouds (more about that in a moment).
The State Of Multi-Cloud Adoption In 2025
According to the Flexera 2025 State of the Cloud Report, 89% of enterprises have adopted multi-cloud strategies to reduce risk and enhance flexibility. Additionally, 54% of organizations utilize a hybrid cloud environment for better cost control. Gartner projects that global cloud revenue will reach $723.4 billion in 2025, marking a 21% increase from the previous year.
Here are over 90 fascinating cloud computing stats you should know in 2025.
What are the benefits of a multi-cloud approach?
Multi-cloud infrastructure can be beneficial for several reasons, including:
- Achieve best-of-breed outcomes for different requirements. AWS for its variety and cost flexibility, Microsoft Azure for its compatibility with Windows solutions already deployed in enterprises, or Google Cloud for Machine Learning and Kubernetes.
- Use more of the most affordable provider’s services to reduce costs.
- Increase flexibility, including switching providers during outages.
- Avoid vendor lock-in.
- Limit dependence on a single provider.
- Take advantage of the latest cloud offerings from a variety of providers at the same time.
Now picture this:
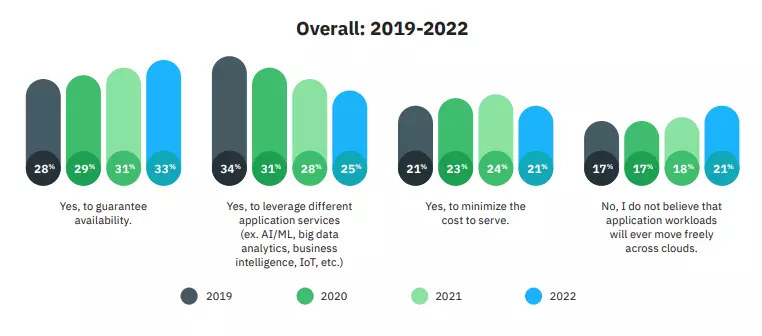
This image from the IBM survey shows how opinion has shifted about the primary driver of multi-cloud deployments. For example, more respondents believe multi-cloud infrastructure is ideal for ensuring high availability, but less for leveraging different application services.
That’s because implementing a multi-cloud strategy can be challenging.
What are the challenges of implementing a multi-cloud strategy?
Multi-cloud deployments are generally more complex than other strategies. The following challenges make implementing a multi-cloud strategy challenging:
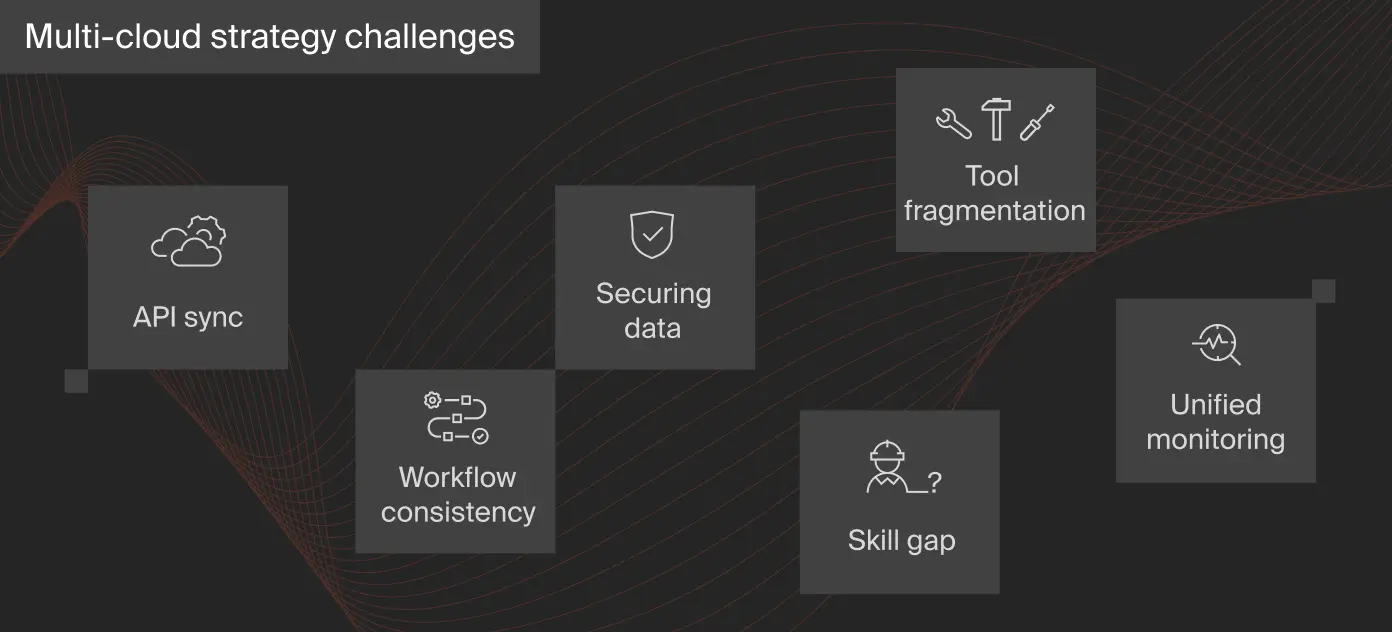
- Finding people with the skills for your particular multi-cloud deployment can be difficult, so you may need to train them yourself.
- Because cloud providers’ APIs differ, synchronizing workloads across multiple clouds can be challenging.
- It can be challenging to secure data and workloads across different clouds.
- Each cloud may require managing a different tool for the same job.
- Each cloud may require a different workflow, which can slow down productivity.
- Visualizing and monitoring everything in one place can be challenging without a robust multi-cloud management tool.
So, how does multi-cloud management work, and what can you expect from it?
What Are Multi-Cloud Management Tools?
Multi-cloud management is the process of monitoring, securing, and optimizing workloads and applications across multiple public clouds. A multi-cloud management tool provides a unified platform for monitoring, securing, and optimizing cross-cloud deployments.
Many cloud management tools are excellent for managing a single cloud, but several cross-cloud management platforms are available today. So, how do you know which tool is best for your organizational needs?
Necessities When Choosing A Multi-Cloud Management Tool
Consider the following:

- Compatibility. Ensure the tool supports all cloud platforms you use. It should integrate well with your existing systems and third-party applications.
- Scalability. As your organization grows, the platform should scale to support increasing cloud resources and services.
- Automation. The tool should automate routine tasks such as backups, scaling, and updates. This reduces manual effort and increases efficiency.
- Vendor lock-in. Ensure the platform doesn’t lock you into specific vendors, allowing flexibility in switching providers.
- Cost management. The tool should help you track and control costs across all cloud environments. Look for platforms that offer cost anomaly detection, budgeting and forecasting, cost allocation, and multi-cloud visibility.
- Compliance and governance. The platform should help you comply with relevant regulations and offer governance tools to manage access and usage policies.
- User interface. Choose a tool with an intuitive interface. It should be easy to navigate, minimizing your team’s learning curve.
- Support. Opt for a tool that offers reliable customer support. Timely help can prevent downtime and other critical issues.
These platforms can improve cross-cloud visibility and reduce the tools needed to monitor and optimize your multi-cloud deployment.
Multi-Cloud Management Tools For Every Need
Here they are with a quick overview of their work, which covers multi-cloud cost monitoring, infrastructure, and application performance management.
1. CloudZero AnyCost – Multi-cloud cost intelligence platform
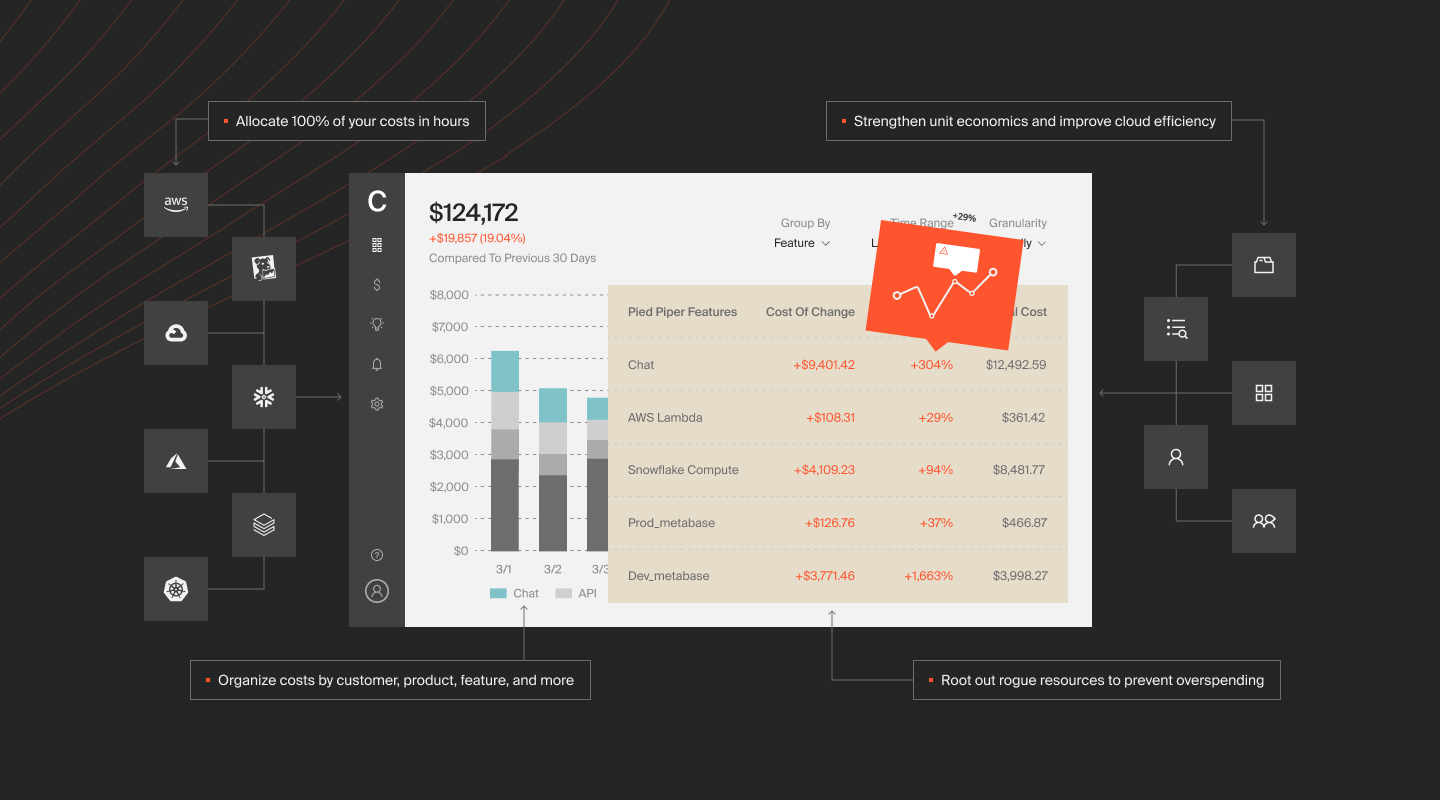
CloudZero AnyCost ingests, normalizes, and presents cost intelligence from cloud providers like AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, and software platforms like Snowflake, New Relic, MongoDB, and Databricks.
No cost allocation tags are required. CloudZero will correlate costs and help you get a complete picture of the cost to build and run your products, from tagged, untagged, untaggable, and multi-tenant resources.
CloudZero is extra special because you can view your multi-cloud costs from an individual customer, product, software feature, team, environment, and more.
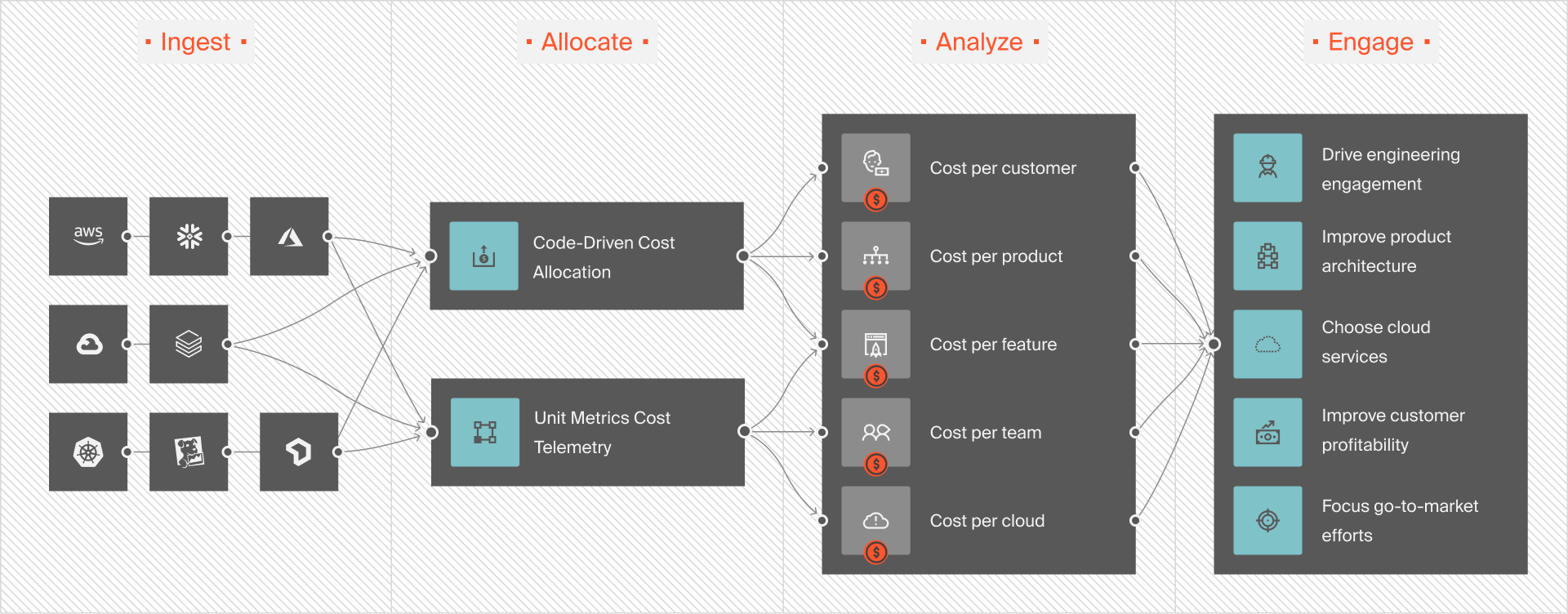
By speaking the same cost language, your finance, engineering, and FinOps teams can pinpoint precisely where to cut costs or invest more to maximize returns.
For example, by analyzing the costs of supporting a particular customer, you can decide how to price your services at renewal to protect your margins.
Or, you can discover cost centers you could do without. Drift used CloudZero to do just that, reducing their annual AWS spend by $2.4 million. You can, too.
2. LaceWork – Multi-cloud security platform
LaceWork manages threats and secures your accounts across Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud (GCP) in one exceptional platform.
You can also use it to secure your Kubernetes and hybrid cloud (private, on-prem, and public cloud combo) environments. Whether you choose an agentless or agent-based deployment, Lacework continuously collects, monitors, and enables you to act on application, user, process, network behavior, vulnerabilities, and configurations.
3. Terraform – Multi-cloud deployment platform
Terraform helps you leverage the same workflow to coordinate multiple providers and manage cross-cloud dependencies efficiently. You can use a single workflow to govern, provision, secure, and audit any infrastructure.
This simplifies orchestration and compliance management for your multi-cloud infrastructures at scale, reduces risks, minimizes management effort and costs, and improves productivity.
By composing features from over 200 providers, Terraform enables you to use best-of-breed features using logical topology.
4. RedHat Ansible – Open-source multi-cloud platform
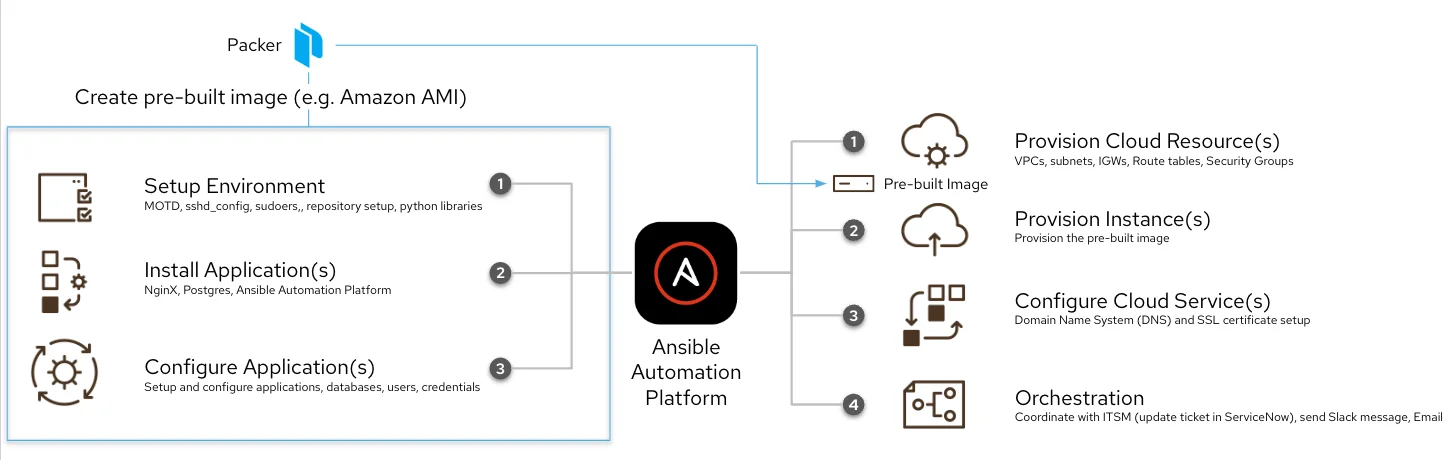
If you are looking to build a custom multi-cloud management tool, Ansible can help. You can use Ansible to ensure your cross-cloud infrastructure components work together to satisfy your use case requirements, whether you use only servers, virtual private networks, specific OS configurations, load balancers, and subnets in your application environment.
Ansible aims to eliminate the guesswork involved in multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployments. You can also automate your environments with policies rather than training entire teams on how to work with each cloud vendor in your setup.
5. Cisco CloudCenter Suite – Application-centric multi-cloud management
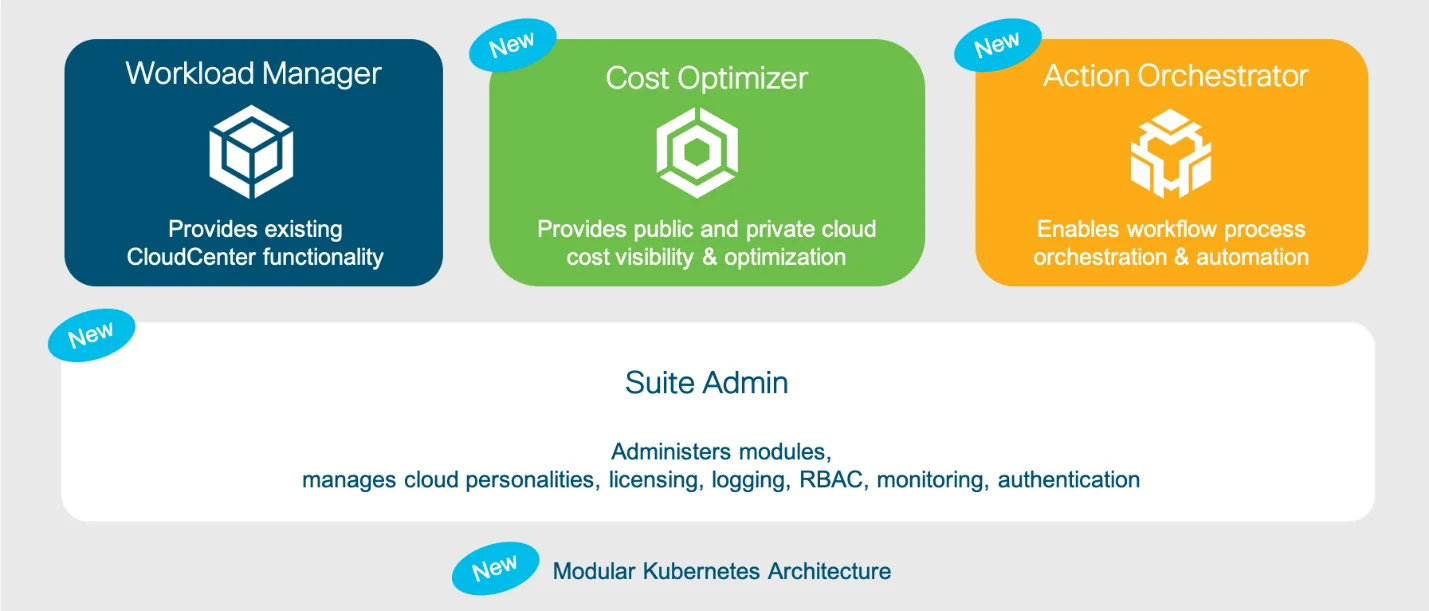
Cisco CloudCenter Suite simplifies application deployment across clouds. It helps define and enforce security, scaling, and governance policies — all at the application level.
It supports AWS, Azure, GCP, VMware, and on-premise environments. You can model, deploy, and manage workloads from one dashboard without rebuilding for each platform.
With built-in cost controls and compliance tools, it reduces cloud sprawl and risk.
6. Cloudify – Environment-as-a-Service platform
Cloudify acts as middleware for users to deploy applications or services in cloud computing environments. With its open-source cloud orchestration tool, you can run applications across multiple clouds and data centers — with a single click — for premium multi-cloud, hybrid cloud, and infrastructure management.
Cloudify helps you design and streamline your app’s entire lifecycle. This includes deploying to different cloud environments or data centers, managing the deployed application, detecting failures, and performing continuous maintenance.
Cloudify is ideal for users wanting to launch pre-built applications in multiple clouds without dabbling in much technical detail.
7. Flexera One – Unified cloud and IT asset management
Flexera One combines IT asset management, SaaS governance, and FinOps in one platform.
It delivers cloud spend analytics, forecasting, and automated policy enforcement. You can also track license usage and ensure compliance across multiple environments.
Flexera One also integrates with ITSM and CMDB tools, giving IT, finance, and procurement teams a single source of truth.
Related article: Flexera Vs. CloudHealth: An In-Depth Comparison
8. Morpheus Data – No-code multi-cloud management tool

Morpheus helps you use AWS, Microsoft Azure, and GCP cloud-native services. It also simplifies the provisioning of VMs, bare metal, containers (IaaS/CaaS), and complete application stacks (PaaS) using virtually any public cloud.
That includes Kubernetes, VMware, HPE OneView, OpenStack, and Cisco UCS, without requiring your IT teams to learn each public cloud in your toolset.
Using a unified API and console, the platform lets you expose cloud-native PaaS, IaaS, Kubernetes, and infrastructure-as-code (IaC) blueprints. You can then use a single public cloud account that everyone can access. Morpheus then manages governance and reporting.
9. Platform9 Managed Kubernetes – SaaS-Based Kubernetes for Multi-Cloud
Platform9 Managed Kubernetes (PMK) is a SaaS-managed service that simplifies Kubernetes operations across private, public, and edge clouds. It gives teams a single control plane to deploy, monitor, and upgrade clusters in any environment.
The platform supports high availability, built-in monitoring, and automated upgrades. These features help reduce the complexity of managing Kubernetes at scale without requiring deep in-house expertise.
But tracking Kubernetes costs can be tricky. Here’s how to analyze your K8s costs with clarity.
You can also explore the best Kubernetes monitoring tools and practices to improve visibility and performance.
10. IBM MCMP – Multi-cloud management platform
IBM’s MCMP supports both multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud deployments. The IBM Multicloud Manager supports app-centric management (health, policy, deployments, and operations).
Besides providing visibility across clouds and clusters, it also delivers policy-based compliance management.
MCMP also includes management for your Kubernetes clusters (containers and microservices).
11. Dynatrace – Full-stack observability platform
The Dynatrace solution lets you pull, correlate, and monitor data from public, private, or hybrid clouds. It covers most public clouds, including AWS, Azure, and GCP, as well as popular platforms, such as RedHat (OpenStack and OpenShift), VMware Tanzu, SAP Business Technology Platform, and the IBM Cloud Foundry.
The service automatically detects, collects, and analyzes metadata, revealing the interrelationships among all your system components and the dependencies between apps and services.
12. VMware Aria – Monitoring, observability, and performance management
VMware Aria is VMware’s unified platform for intelligent operations management across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. It offers complete visibility into applications, infrastructure, and cloud environments through customizable dashboards and real-time analytics.
It utilizes machine learning to forecast capacity needs, detect anomalies, and prevent potential issues before they impact operations.
VMware Aria also Integrates with VMware and third-party tools to automate corrective actions. This reduces manual intervention and improves efficiency.
Related article: 9 VMware Alternatives To Consider In 2025
13. Hystax OptScale – Open-source FinOps for multi-cloud efficiency
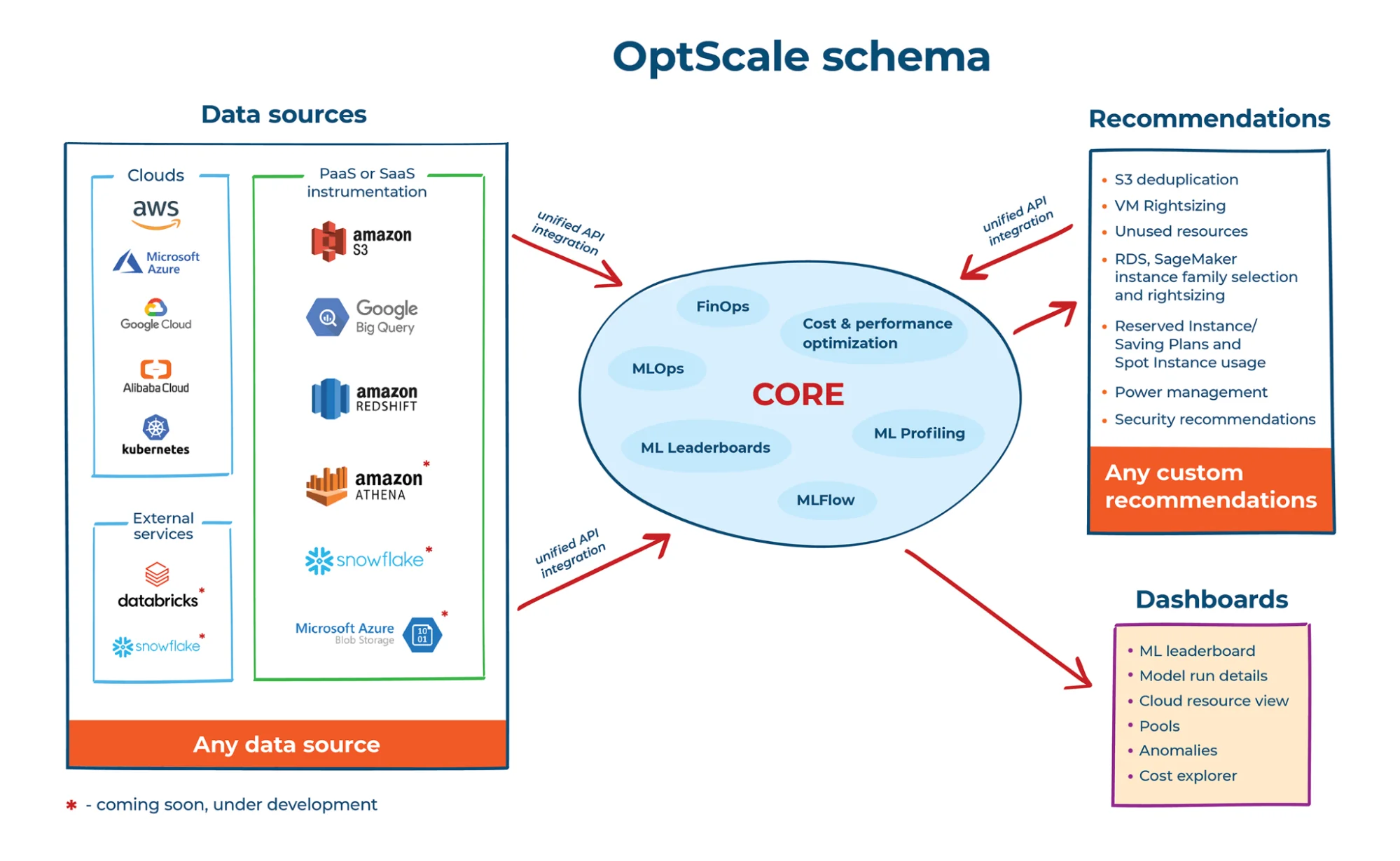
Hystax OptScale is a FinOps platform that supports AWS, Azure, GCP, Alibaba Cloud, and Kubernetes.
The platform offers cost visibility, smart resource sizing, and cost tracking tools.
OptScale also encourages FinOps adoption by helping engineering teams take ownership of their cloud usage. It’s built to support smarter, leaner multi-cloud operations.
Related articles:
14. CAST AI – Automated cost optimization for multi-cloud Kubernetes
CAST AI is a cloud cost optimization platform for Kubernetes workloads. It integrates with your AWS, GCP, or Azure clusters and instantly finds ways to reduce waste.
Its engine continuously rightsizes resources, removes idle nodes, and automatically selects the best pricing options, such as Spot Instance. This means less manual tuning and more savings.
CAST AI also helps prevent overspending by offering real-time insights, autoscaling, and security checks.
15. Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) – Unified data management across clouds
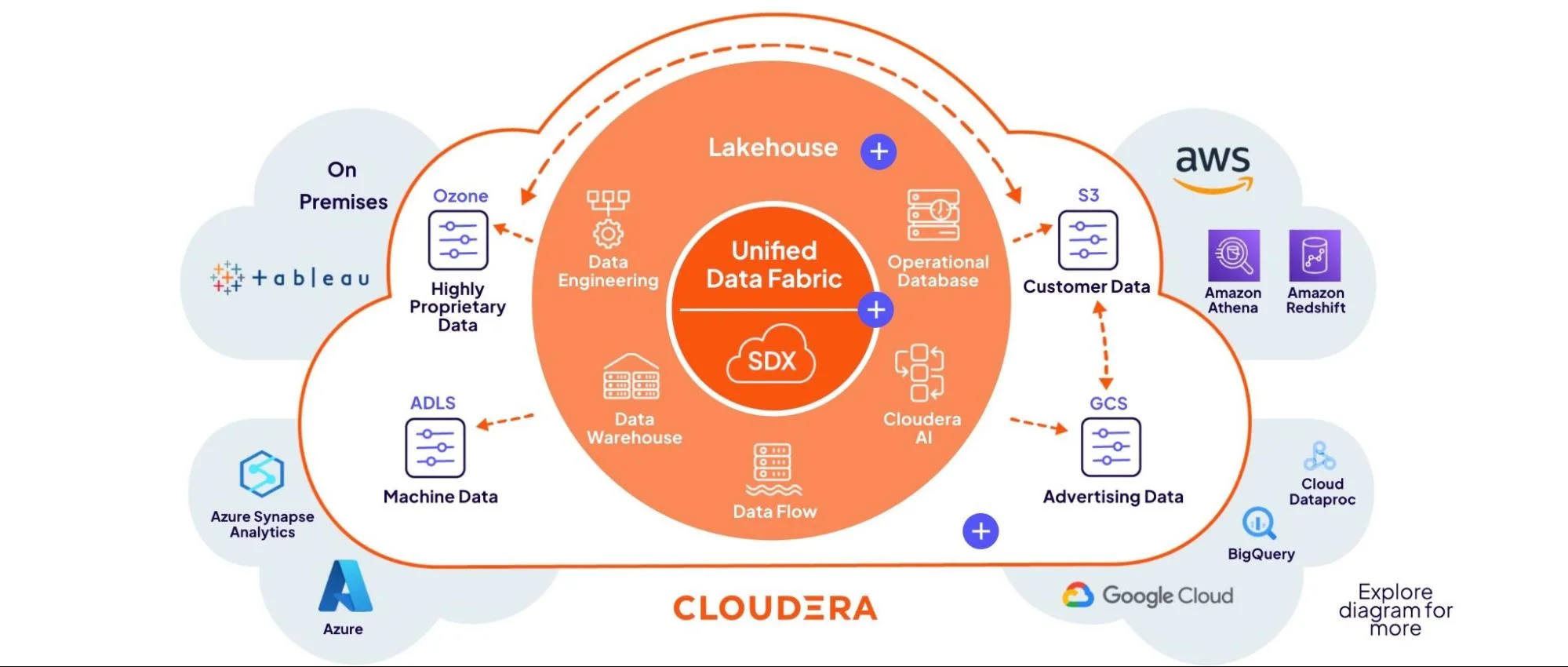
Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) offers a centralized solution for managing data across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. It supports AWS, Azure, and GCP, enabling teams to migrate, govern, and analyze data from one control plane.
With built-in security, governance, and machine learning tools, CDP helps organizations unify their data pipeline without vendor lock-in. It simplifies complex workloads and supports modern data architectures.
16. Nutanix Cloud Manager – Hybrid multi-cloud platform
Nutanix’s Cloud Platform combines hybrid cloud infrastructure with multi-cloud management and unified storage, database, and desktop services. The goal is to support any application and workload wherever it is deployed — in private, public, hybrid, or multi-cloud deployments.
Expect a unified, self-service cloud control plane that delivers AI-powered app automation and cost and security governance.
17. CloudBolt – Multi-cloud and hypervisor management platform
CloudBolt is a multi-cloud management abstraction layer that enables the use of different solutions within one catalog. To deliver this, CloudBolt has a pluggable architecture, allowing you to support new technologies as required.
You can integrate more than 20 resource handlers, including Hyper-V, vCenter, AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, and SCVMM, in the catalog, which eases provisioning and orchestration.
18. Scalr – Cloud provider configuration platform
Scalr is a cloud management platform that is a backend for Terraform and OpenTofu (OTF). It supports remote operations by executing runs and centrally storing state data, enabling collaboration across organizations.
Scalr manages multi-cloud environments securely by authenticating with various cloud providers. It helps users manage credentials in one place, eliminating the need for hardcoded configurations. This approach ensures secure access management and maintains compliance with organizational policies.
19. BMC Multi-Cloud Management – Multi-cloud migration
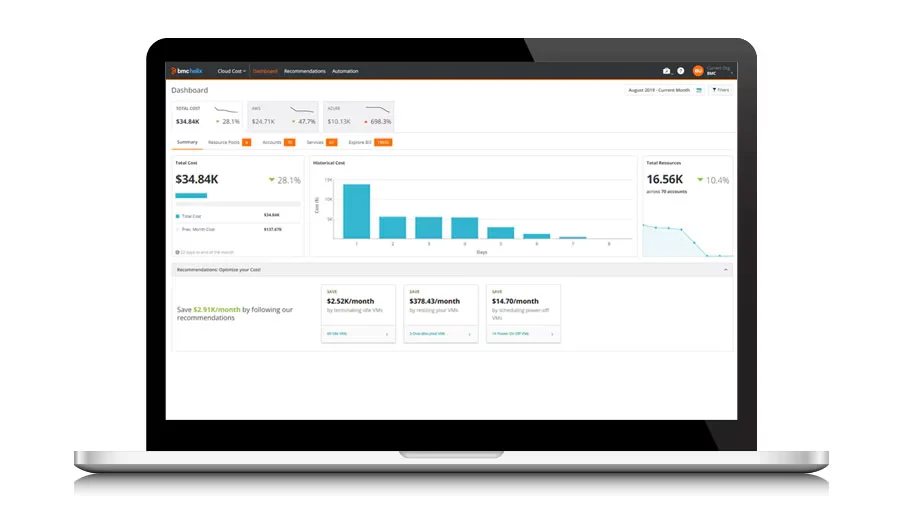
BMC Multi-Cloud Management helps businesses create detailed migration plans across multiple cloud providers. This ensures they understand what to migrate, the potential costs, and how to secure their data during the transition.
BMC also automates various tasks to reduce errors and downtime. The platform’s governance features maintain ongoing security and compliance, making it easier for businesses to manage their resources post-migration. This approach reduces complexity and improves control during multi-cloud migrations.
20. Zerto – Multi-cloud disaster recovery and backup platform

Zerto supports disaster recovery and backup across multi-cloud environments. It integrates with AWS, Azure, GCP, IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, and more than 350 managed service providers to allow businesses to replicate, recover, and migrate data effectively.
Zerto’s software-only approach eliminates the need for traditional backup windows or snapshots, making it a reliable tool for managing multi-cloud workloads. Its features ensure high availability and resilience, which is crucial for organizations in complex, multi-cloud environments.
What’s Next: Untangle Your Multi-Cloud Costs With CloudZero
CloudZero’s cloud cost intelligence platform empowers you to transform telemetry into granular and actionable cost insights. You can then answer any cost question, drill down, zoom out, and get the most granular, context-rich intelligence without endless tagging.
You can get a full picture of your cost of goods sold (COGS), unit economics, and even the cost of supporting a specific customer, all within a single platform. CloudZero AnyCost has you covered across Azure, AWS, and GCP public clouds — and even platforms like K8s, Snowflake, and Databricks.









