Many SaaS businesses prioritize customer acquisition and retention over increasing gross margins, particularly during the startup and scale-up stages.
It makes sense. A company can accelerate its revenue growth by acquiring and retaining more new customers, rather than simply selling more to existing ones.
Yet, here’s the thing. Revenue growth measures the increase in the amount of money a business earns from sales. Gross margin growth determines the profit the business makes after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS), expenses, and taxes.
That said, how do you tell if your SaaS company is growing sustainably? And how do you know when to focus on improving profitability — rather than just capturing a larger market share or ARR?
Enter the Rule of 40 for SaaS benchmark — a key metric that helps SaaS companies balance growth and profitability.
What Is The Rule Of 40?
The Rule of 40 is a principle that states a software company’s combined revenue growth rate and profit margin should equal or exceed 40%. SaaS companies with a profit margin above 40% are generating profits at a sustainable rate, whereas those with a margin below 40% may face cash flow or liquidity issues.
A perfect example is TechnologyOne. This ASX-listed SaaS firm reported a Rule of 40 score of 49% in the first half of 2025, demonstrating how consistent, profitable growth can be embedded as a strategic priority.
A brief history of the Rule of 40
This concept has been around for about a decade. Brad Feld, a venture capitalist, popularized the term “Rule of 40%” in February 2015. In the article titled “The Rule of 40% for Healthy SaaS Companies,” he describes how he learned about it from a late-stage investor during a board meeting.
The investor stated that they used it to assess the suitability of a health software company for investment. According to the investor, the rule applied to companies with annual revenue exceeding $50 million.
However, Brad insists that the Rule of 40% could also apply to companies with $1 million in annual revenue.
How the Rule of 40 works
The Rule of 40 is an indicator of how effectively a company balances profit and growth.
Consider the following scenarios:
- A SaaS company should have a 40% profit margin if it is not growing.
- You can have 0% profits if you are growing at 40%.
- With a 20% growth, you should also generate 20% profit.
- You can afford to lose 10% if you’re growing at 50%.
Naturally, to determine whether the company is above 40% or below, it must know two things:
- Revenue growth
- Profitability margin
The Rule of 40 does not apply across every industry (it is specific to SaaS companies), but it remains a valuable benchmark for these companies.
This is because the SaaS sector manages high margins of 70%-90%, making the rule readily applicable to them compared to other subscription-based companies or more traditional business models.
Again, the primary purpose of benchmarking is to facilitate easier comparison among companies with different operating structures, varying business cycles, or other complexities that make direct comparison challenging.
Measuring Growth Rate And Profitability
Calculating revenue growth should be relatively straightforward for any SaaS company operating for at least a year. The Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) establish clear definitions for what constitutes revenue, and these definitions tend to remain consistent year over year.
Keeping this in mind, your business should be able to quickly look at the revenue column on your most recent income statements and calculate your annualized revenue change.
On the other hand, “profitability margin” is a rather broad term that can potentially be used to describe several different items on your company’s balance sheet or income statement.
A few of these possible items might include free cash flow (which may require a statement of cash flows), total operating income, and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA).
If using EBITDA, calculate profitability margin by measuring EBITDA as a percentage of total operating revenue (mentioned above).
The Rule Of 40 Formula
Using the Rule of 40 SaaS formula, Growth Rate plus Profit Margin should total at least 40%, helping SaaS operators and investors track performance more clearly:.
SaaS Growth Rate + SaaS Profit Margin > 40%
But it’s not quite there yet. It depends on how you calculate your revenue growth and profit margin.
A company’s revenue growth rate is typically measured by its monthly recurring revenue (MRR) or annual recurring revenue (ARR).
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) = The Total Number of Active Accounts X Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) = MRR × 12 months
Growth Rate = (Current Year Value – Prior Year Value) ÷ Prior Year Value
When it comes to profit margin, the most commonly used metric is the EBITDA margin for the corresponding period.
EBITDA Margin (%) = EBITDA ÷ Revenue
Using this approach, the correct formula for calculating the Rule of 40 is:

There is some debate about at what funding stage the rule should be applied (or less so), and its reliability as a metric. Yet, its simplicity and accuracy make the Rule of 40 a popular choice.
“Annual Recurring Revenue is the North Star, but expanding your margins is how you win.”
Here’s how the Rule of 40 looks in the CloudZero platform. The top line graph is the overall calculation on a month-to-month basis, with the factors contributing to the Rule of 40 graphed beneath it.
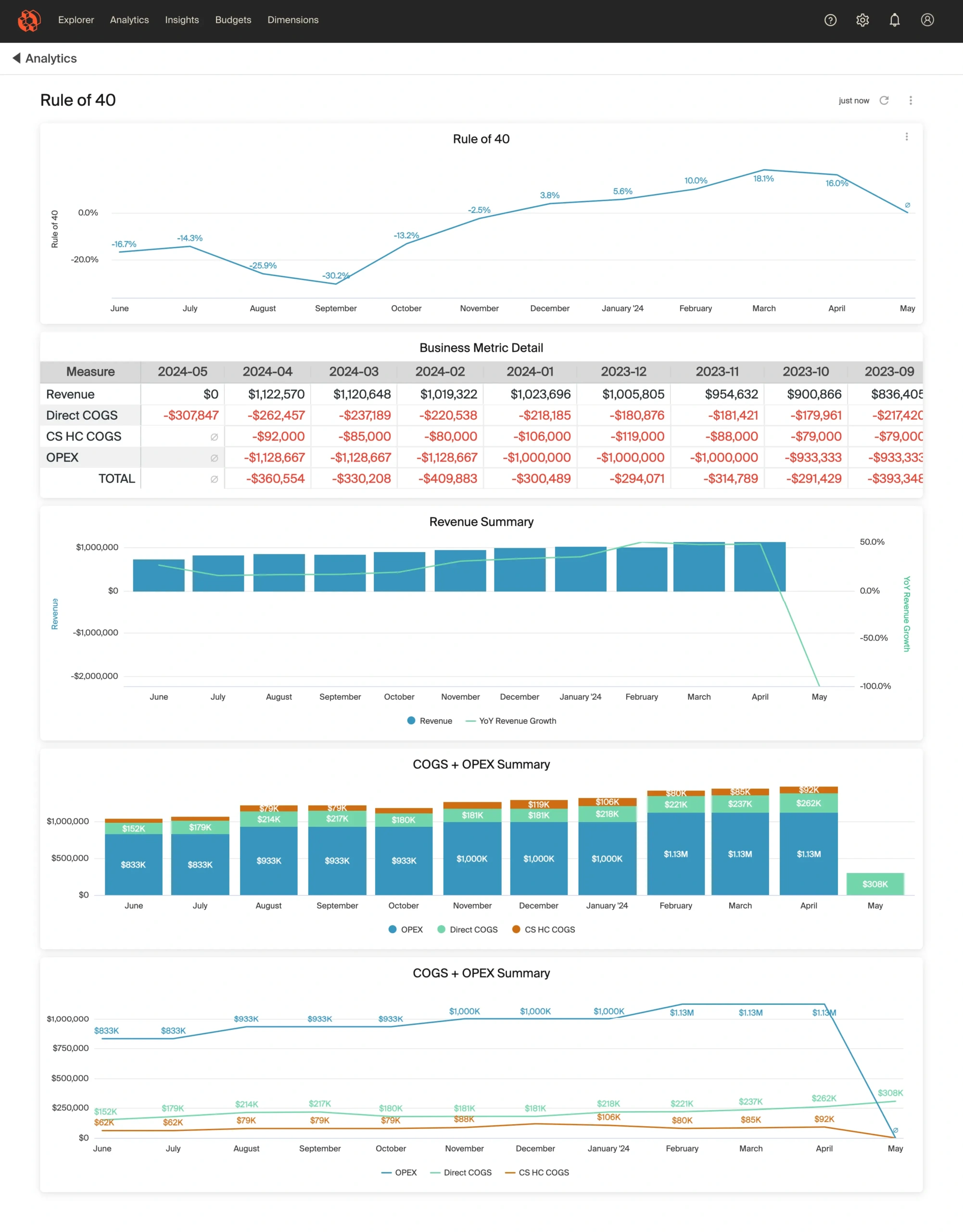
With this view, you always have an easily accessible, up-to-date view of how you’re trending against the rule. Get started on the Rule of 40 with CloudZero.
How To Calculate The Rule Of 40 (Example)
Let’s look at a simplified Rule of 40 example.
If a company generated $10 million in revenue in 2019 and $12 million in revenue in 2020, then its year-over-year revenue growth would equal 20% ($2 million divided by $10 million, then multiplied by 100%).
Suppose the same company is using EBITDA as its primary “profitability” metric and that its EBITDA for 2020 was $3 million. In this case, the company’s profitability margin would be 30% ($3 million divided by $10 million).
In this example, the company’s revenue growth plus profitability margin would equal 50% (20% plus 30%). This means that the company has “passed” the Rule of 40 and is likely well-positioned for the future.
Revenue growth and profitability margins could be negative, especially if the company has recently accrued significant amounts of debt or incurred substantial capital expenses.
However, even when either of these figures is, in fact, negative, the company can still utilize the Rule of 40 and hope that success in one area could offset any issues created by the other.
Related read: How Malwarebytes Measures The Cost Of Their Products
Real-World Rule Of 40 Examples (And What They Tell Us)
As of Q1 2025, the median Rule of 40 score across tracked SaaS companies is 12%, with a median growth rate of 10% and EBITDA margins of just 6%.
Only a handful of high performers, such as Doximity (55%), Klaviyo (25%), and MeridianLink (36%), are comfortably above the 40% threshold. Most companies continue to fall well below the benchmark.
This shows the challenge of balancing profitable growth in a market where efficiency expectations remain high.
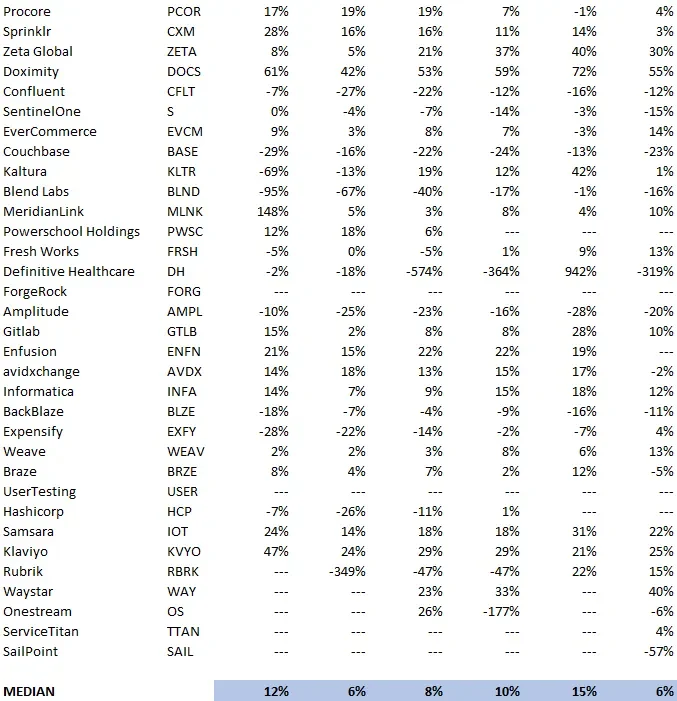
Source: Blossom Street Ventures
Related read: How UpStart Used CloudZero To Reduce Cloud Costs By $20 Million (Case Study).
Why Use The Rule of 40? Here Are Four Crucial Benefits
Benchmarking, balancing profitability and growth, as well as informing long-term and short-term decisions, are some examples of the uses of the Rule of 40 for SaaS businesses. Here are more details.
1. The Rule of 40 offers a guide to what tradeoffs a SaaS company can afford
You are running a healthy SaaS business if you manage a 20% growth rate with a 20% profit margin. You can operate at a 10% loss if you achieve a 50% growth rate. You are also on the right track if you reach 40% growth with 0% profit and vice versa.
But suppose growth and profitability fall below 40%. In that case, you’ll want to inspect your other SaaS metrics to identify any potential issues, such as increased cost of goods sold (COGS), customer acquisition cost (CAC), churn, and more.
Related read: How Drift Used CloudZero To Improve COGS By $2.4 Million (Case Study)
2. It helps assess your ability to invest without sacrificing profit
Profitability and growth rates over 40% suggest you have room to pursue hypergrowth to gain and retain more customers. A move like that can help sustain the company’s “beyond 40” performance over a more extended period.
Sustaining profitability and revenue growth at 20% each can be challenging, as you may easily remain in sub-scale mode for longer than necessary. A competitive market demands that you capture and hold the largest possible share of your targeted market as soon as possible.
Yet, you might need investors to fund that hypergrowth mode. This brings us to one of the biggest reasons for calculating the Rule of 40.
Beyond investor insights, engineering and FinOps teams can use the Rule of 40 SaaS framework to guide spend planning and architecture decisions. By comparing revenue growth with profitability, teams can model cloud spend for new features, product launches, or scaling workloads. This ties engineering efficiency and FinOps cost visibility directly to strategic growth targets..
3. Investors use the Rule of 40 to compare high-quality SaaS investment opportunities
VCs came up with the Rule of 40, after all. It is a way to quantify a SaaS company’s potential for creating value for them as it grows, regardless of whether it is yet profitable.
SaaS companies often reach high valuations, sometimes too high. But as investors consider valuation for short-term plans, they recognize that some SaaS companies destroy their value as their average annual revenue grows.
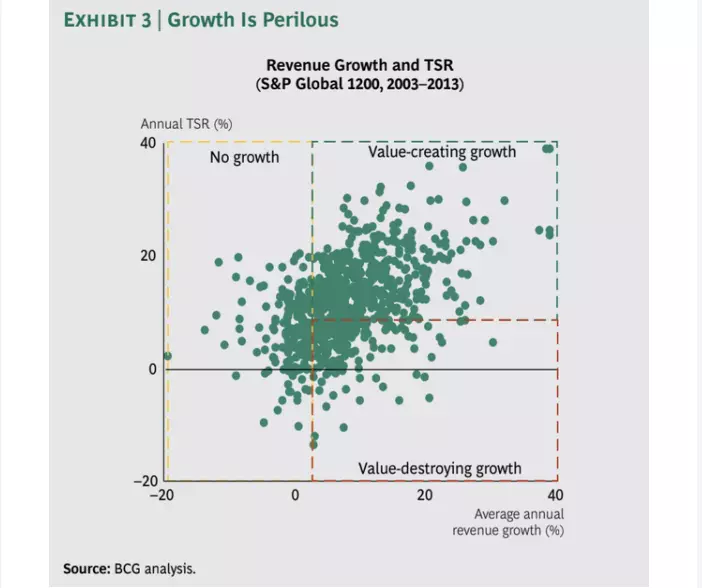
Credit: Value-creating vs. value-destroying growth analysis by Boston Consulting Group
The Rule of 40 does not take valuation into account. The approach focuses on measuring sustained value creation instead, which helps evaluate SaaS investment opportunities.
4. You can use the Rule of 40 to determine when to maximize growth or profitability at any given stage
In the SaaS sector, it is assumed that startups and smaller SaaS businesses should focus on growing revenue, even if they don’t make a profit. This is not always the case.
If you are going to justify a runaway growth rate with a skin-deep margin, you need to be able to say: “We can turn a profit right away if we slow down our growth rate.”
Still, the Rule of 40 can help mature SaaS businesses that have captured most of their attainable market share to focus more on margin growth than worry about expansion. After all, most SaaS companies see their growth rate decline over time.
Small companies can also use this metric to focus on marketing and sales tactics that attract and keep customers while yielding high enough margins to appeal to investors who can fund their growth.
When To Use The Rule Of 40: Should You Measure The Rule Of 40 As A Startup?
The Rule of 40 is useful for investors and for internal planning — but timing matters.
If you’re an early-stage SaaS company, focus first on achieving product-market fit and scalable growth. Many companies use the T2D3 growth strategy — tripling ARR in the first two years, then doubling for the next three — before turning their attention to profitability.
Once you reach at least $1M in annual recurring revenue (ARR) or have several years of consistent financial data, the Rule of 40 becomes a meaningful benchmark. It helps you:
- Attract investors by signaling healthy growth and efficiency.
- Align internal teams on balancing growth and margin, especially for finance, engineering, and FinOps teams making spend and pricing decisions.
- Plan long-term strategies by modeling how operational or architectural changes impact your margins.
For smaller companies, consider measuring the Rule of 40 after 12–18 months of stable revenue data. At this stage, use it to track trends, rather than as a rigid performance metric.
Remember, the Rule of 40 is most effective when paired with other metrics like CAC efficiency, churn, and customer segment profitability. This broader view helps you make smarter growth and cost decisions as you scale.
Related read: How Hiya Uses CloudZero To Answer “What-If” Questions Around New Business Initiatives
What Is A Good SaaS Growth Rate?
On average, SaaS revenue growth ranges from 15% to 45% year to year. But SaaS growth rate also varies widely based on a company’s development stage. The growth rate of companies with less than $2 million in revenue is often higher than that of companies with more than that.
Take a look at this SaaS Capital chart:
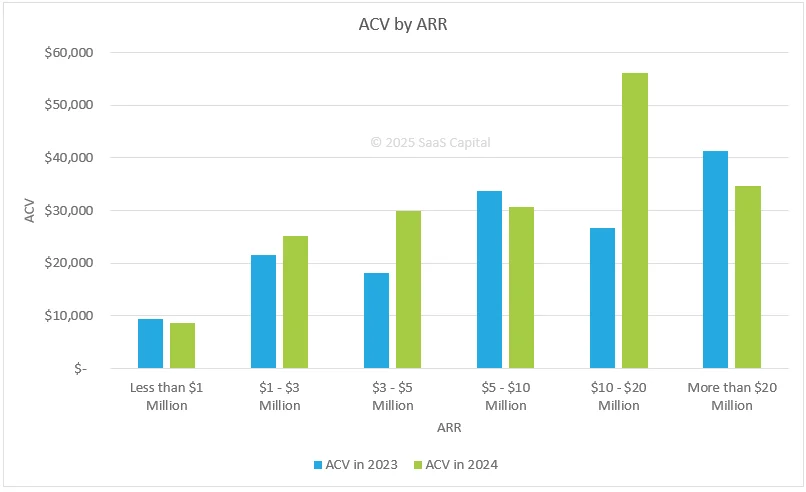
Credit: SaaS Capital
As of 2025, ACV by ARR shows key shifts. Companies earning less than $1 million ARR have an average ACV under $10,000, slightly down from 2023. SaaS firms in the $1–$3 million range climbed to about $25,000 ACV. Those with $3–$5 million ARR now average around $30,000, while $5–$10 million ARR companies hold steady at just over $30,000. The largest jump is in the $10–$20 million range, where ACV surged to nearly $55,000, and companies with over $20 million ARR average about $40,000.
So, what happens after calculating your 40% rule?
Balancing Competing Goals
Ultimately, running a business — whether in the SaaS industry or any other — is going to involve making some critical tradeoffs. One typical tradeoff is that pursuing additional revenue streams will often (at least temporarily) eat into a company’s profit margin.
Pursuing revenue-generating activities, such as reaching a wider audience, expanding a product line, or enhancing a product via additional research and development, will introduce additional expenses that can eat into marginal profitability.
At the same time, finding ways to improve profit margins — such as cutting the marketing budget — can cause revenue to decline.
This is all okay and normal.
The management team’s role is to carefully balance both competing interests at once and think about the company’s long-term financial plan. The Rule of 40 is so useful because it allows managers to consider how each of these metrics relates to one another while still ensuring the company is at least making some type of progress.
Related read: See How LawnStarter Used CloudZero To Power Efficient Growth And Reduce Cloud Storage Costs By 55% (Case Study)
Pursuing revenue growth and managing profit margins will be a vital component of running a SaaS business. The main point of emphasis here is that your business should be actively pursuing and enhancing at least one of these goals at a time.
Pros, pitfalls, and misuses of the rule of 40
While the Rule of 40 is undoubtedly something that can benefit many SaaS enterprises, it is also something that should be taken with a grain of salt.
Here are the key things to know if you want to get the most out of the Rule of 40 — without falling into the common traps.
Pros
- A simple, easy-to-communicate metric for balancing growth and profitability
- Supports decision-making for leadership, engineering, and finance teams
- Works well as a starting point for performance benchmarking. See how cost metrics drive better planning in Cloud Unit Economics
Pitfalls
- Not a one-size-fits-all benchmark. Startups that are growing rapidly but operating at thin margins may still score below 40% and remain healthy.
- Some companies with scores above 40% still fail due to poor cost controls or unsustainable sales spending.
- Market disruptions, like 2020’s volatility, can skew data. Learn how to interpret cost data accurately in Cloud Cost Intelligence: Beyond Simple Metrics.
Common misuses
- Using the Rule of 40 in isolation, without considering CAC, churn, or segment-level profitability
- Treating it as a valuation guarantee instead of just a directional signal
When to look deeper
If your score hovers around or below 40%, or if growth and profitability diverge sharply, dig into:
- CAC efficiency and payback periods
- Gross margins and COGS
- Churn and retention metrics (cost per customer: why it matters)
- Profitability by segment or feature
Bottom line: The Rule of 40 is a guide, not a verdict. Combine it with detailed cost and growth metrics to understand what’s really driving — or eroding — performance.
How?
Cut Waste, Optimize Cloud Costs, And Attract The Right Investors With Confidence
Here’s the thing. SaaS products are hard to price profitably. It is even harder to set a price that retains and attracts your best customers — without compromising your annual recurring revenue goals. Where do you begin?
Cloud costs. That nagging Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), to be precise.
Most cost tools only scratch the surface when reporting cloud costs: total and average costs. Not exactly the people, products, and processes that drive your cloud spend. CloudZero changes that.
With CloudZero, you can:
- Allocate 100% of your cloud costs: Get a complete picture of your cloud usage and spend to make cost decisions with confidence.
- Cost per Customer: Assess how much you spend supporting a specific customer so you can determine the fairest, most profitable custom pricing for them.
- Discover and keep the most profitable customers in the room: Identify the most profitable customers or segments by using metrics such as Cost Per Customer.
- Precision cost intelligence for investor-ready brands: Use hourly per-unit cost insights to pinpoint who, what, and why your costs are changing. Then know exactly where to cut costs, devote more where ROI is highest, and attract investors.
- Engineering-Led Optimization: Empower your engineers with insight into Cost per Feature, Cost per Environment, and Cost per Daily User. And they’ll learn to build cost-effective solutions from scratch and optimize existing ones at the architectural level.
- Access ongoing Certified FinOps expertise: Our team is a big reason why a CloudZero subscription pays for itself in about three months.
Heck, we’ve helped customers like Drift, Remitly, and Upstart reduce cloud costs by over 22%.
Others improved their Cloud Efficiency Rate by 33% on average (in just the first year). Don’t just take our word for it.  to experience CloudZero firsthand and risk-free.
to experience CloudZero firsthand and risk-free.
Rule Of 40 FAQs
What is the Rule of 40 in SaaS?
The Rule of 40 SaaS states that the sum of a healthy SaaS company’s annual recurring revenue growth rate and its EBITDA margin should be equal to or exceed 40%. It is a measure of how well a SaaS balances growth with profitability.
What is the Golden Rule of SaaS pricing?
It suggests that your product pricing should reflect the benefits and outcomes users gain from the software. This approach ensures that customers perceive the pricing as fair and see the value of their investment. This customer value focus beats arbitrary pricing and competitor pricing models. It fosters higher retention rates and sustainable revenue growth.
What is the 80/20 Rule in Saas?
The 80/20 Rule (also known as the Pareto Principle) states that 80% of a SaaS company’s revenue often comes from just 20% of its customers. The goal is to identify and focus on the critical 20% of customers that drive the most value to your business. Prioritizing these high-value tasks and clients is the key to maximizing ROI.
Is the Rule of 40 still relevant for SaaS companies in 2025?
Yes, the Rule of 40 SaaS benchmark remains highly relevant in 2025. While fewer SaaS companies consistently hit the 40% threshold, it’s still a trusted measure of financial health. When paired with other metrics such as CAC, churn, and segment profitability, it offers a realistic view of sustainable growth.
What is the Rule of 72 in Saas?
The Rule of 72 is also a SaaS growth strategy that helps estimate how many steps it takes to double SaaS revenue. It works by dividing 72 by the growth rate of each step in the customer journey. This gives the number of steps required to double revenue. For example, if each step grows by 9%, it would take 72 ÷ 9 = 8 steps to double revenue.
How can SaaS companies use the Rule of 40 to improve cost efficiency?
The Rule of 40 SaaS framework helps companies track growth and profitability together. Pair it with cost metrics such as cost per customer and cloud unit economics to spot inefficiencies and allocate spend wisely. Read more in our guides on cloud cost intelligence, cost allocation, and cost optimization.