In our post, 9 Continuous Delivery Tools For Reliable Releases, we explored why continuous delivery is critical to building robust development pipelines — and how it helps teams deliver customer value while boosting the bottom line.
Today, we’re diving into the next evolution of that pipeline: continuous deployment. Today’s technology companies need to release quality features quickly and put them in users’ hands even quicker. According to the State of DevOps Report, organizations with CI/CD tools deploy 208X more often and have a 106X shorter lead time than organizations without one.
You can release software with minimal downtime for your customers when you use robust continuous deployment tools. In this article, we’ll look at how it differs from continuous delivery, the advantages it offers, and which parts of the CD workflow are well-suited for automation.
Plus, we’ll share the top continuous deployment tools you can explore to deploy faster, spend smarter, and boost your team’s morale.
Quick note: This guide focuses specifically on continuous deployment tools. If you’re looking for all-in-one solutions, check out our selection of the top 50+ CI/CD tools or explore this guide on essential DevOps tools every team should know right now.
Let’s start at the beginning.
What Do Continuous Deployment Tools Do?
Trying to manually release software features, functional updates, security patches, and others is not just time-consuming and detrimental to engineering velocity. In today’s highly dynamic world, it is also unsustainable.
Continuous Deployment (CD) is a software engineering approach where every code change that passes automated testing is automatically pushed to production. No manual approvals are required here (as in continuous delivery pipelines).
This approach builds on continuous delivery by eliminating manual approval steps before releasing code into production environments.
As such, continuous deployment tools enable automation throughout your deployment pipeline, from code commits to production releases.
DevOps automation tools help ease, accelerate, and control these processes at scale. In particular, CI/CD tools help engineers to deliver continuous software improvements at any scale, platform, environment, etc.
Researching, choosing, and implementing the best continuous deployment tool can be quite the hands-on process. But the payoff is well worth it.
Features and benefits of continuous deployment tools
Choosing the right CD tool can help you eliminate or significantly reduce the challenges of implementing continuous deployment. Here’s how:
- Automate the release process: By eliminating manual steps, CD tools help you reduce delays and human error, without compromising software quality.
- Enable continuous, automated testing: The best tools run rigorous tests (unit, integration, performance) at every stage of the deployment pipeline to ensure only stable, production-ready code is released.
- Support the “fail fast” philosophy: By deploying small, frequent changes, CD tools help your team catch issues early, closest to when they’re introduced, so you can fix problems before they escalate.
- Speed up time to market: Automating the entire deployment pipeline ensures that what used to take days or weeks can now happen in hours or less, helping your business respond faster to market shifts.
- Improve software quality faster: Consistent, automated testing ensures quality is built into every release, accelerating your ability to deliver reliable updates.
- Enable quicker feedback loops: Frequent deployments encourage your users to share real-time feedback, enabling your team to validate assumptions and improve the product based on actual usage.
- Manage complexity at scale: That is, whether you’re running microservices, working across multiple environments, or deploying to hybrid cloud setups.
- Boost developer productivity: By automating repetitive tasks, the top continuous deployment tools free developers to focus on building features, improving both productivity and morale.
- Ensure consistency and reliability: CD tools standardize deployments across environments by managing configuration differences, integrating with version control, and offering monitoring and rollback features to reduce disruption.
- Support effective monitoring and alerting: Integrated monitoring and alerting help detect production issues in real time. This can minimize end-user impact and enable faster incident response.
- Reduce tooling and pipeline complexity: A robust CD platform simplifies setup by consolidating tools and standardizing workflows. The result? It becomes easier to build and manage reliable pipelines.
Taken together, these benefits can significantly boost your bottom line, strengthen your competitive edge, and improve your developer satisfaction.
What Are The Stages of Continuous Deployment (And Which Tools Support Each One)?
The following list of continuous deployment (CD) tools covers the key stages of the CD pipeline, a process that includes:
- Configuration management
This involves automating and managing the setup of servers, storage, networks, and software to ensure a consistent and stable environment across all stages of the pipeline.
- Version control/commit
Developers commit code changes to a version control system like Git. Each commit automatically triggers the pipeline, ensuring traceability, accountability, and seamless collaboration across teams.
- Build
The source code is compiled and packaged into deployable artifacts. This stage may also include dependency resolution and static code analysis to catch early errors or vulnerabilities.
- Code review
Automated code analysis tools evaluate the quality and structure of the code. This step helps maintain coding standards and catches issues before testing begins.
- Automated testing
A suite of automated tests (unit, integration, system, and end-to-end tests) validates the functionality, security, and performance of the code. Only code that passes all required tests proceeds to the next stage.
- Acceptance/staging
The approved build is deployed to an acceptance environment that mirrors production. Here, automated and sometimes manual testing simulate real-world usage.
- Deployment automation
Once validated, the build is automatically deployed to production using scripts or deployment tools.
- Monitoring and feedback
After deployment, the application is monitored in real time for errors, performance issues, and user behavior. Monitoring tools, alerts, and feedback loops help your team detect issues early and respond quickly.
- Rollbacks
In the event of unexpected issues, robust rollback mechanisms are essential. Strategies include:
- Blue-Green deployments: Two identical environments allow seamless switching and quick rollback.
- Rolling deployments: Gradually replace old versions with new ones across instances.
- Canary releases: Deploy changes to a small subset of users before full rollout, making it easier to catch issues early.
Next, let’s look at the actual tools.
What Are The 15+ Best Continuous Deployment Tools Right Now?
Some Continuous Deployment platforms also support Continuous Integration (CI) workflows, while others are dedicated CD platforms. It’s up to you whether to use an all-in-one CI/CD platform or separate tools for CI and CD.
We will also include open-source and proprietary CD tools. Yet, the CD tools we’ll cover here are among the best, not an exhaustive list of the best CD tools for every DevOps team.
Be sure to explore each tool in more detail to find the one that best fits your team’s continuous deployment workflow and goals. In the meantime, start here:
1. CircleCI
CircleCI boasts an enterprise-grade CI/CD tool that helps DevOps teams to build, test, and release new code more rapidly. Initially developed as a CI platform, CircleCI now supports robust build deployments at scale to businesses of any size.
Circle CI runs in the public cloud, on-premises (CircleCI Server), or in a private cloud (behind a firewall). Build on Linux, Windows, Arm, macOS, or on your own computer (self-hosted); the tool supports it.
Engineers often rate CircleCI as their top CI/CD tool because it is easy to set up, customizable, and allows them to split, share, and reuse builds across multiple containers.
It also supports unlimited builds and quick tests. In addition, it automates parallelization, branch-specific and continuous deployments, as well as merging. CircleCI supports all of the major repositories, including GitHub, BitBucket, and GitHub Enterprise.
2. Buddy
Buddy Deployments is a fast CI/CD platform for teams who want to build, test, and deploy websites and applications in minutes. It is ideal if you work with BitBucket, GitHub, and GitLab code. It is also ideal for running tests with a simple interface, actionable feedback, and quick-to-customize Docker-based images.
Buddy’s highlights include smart change detection, scalable compute resources (vCPU and RAM), repository and artifacts caching, and reusable environments.
The tool also supports concurrent pipelines and steps, Docker layer caching, and 360-degree optimizations. In addition, you can track progress in real-time with unlimited history.
3. Atlassian Bamboo
A major draw of Atlassian’s Bamboo is its support for end-to-end continuous deployment workflows. Its deep integration with Jira and Bitbucket supports full traceability and highly customizable deployment pipelines.
Bamboo CD capabilities:
- Bamboo automates the entire process from code commit to production deployment
- Supports parallel builds and automated testing
- Manages build artifacts efficiently and automates deployments across multiple environments, making it easy to track, promote, and verify releases
- Designed to scale with your organization
- Expect detailed reports and real-time insights into your build and deployment pipelines
- Works with a wide range of languages, build tools, and deployment targets, including Docker and AWS
Ideal for: Large teams or enterprises, especially teams using other Atlassian products.
4. RunDeck (PagerDuty Process Automation)
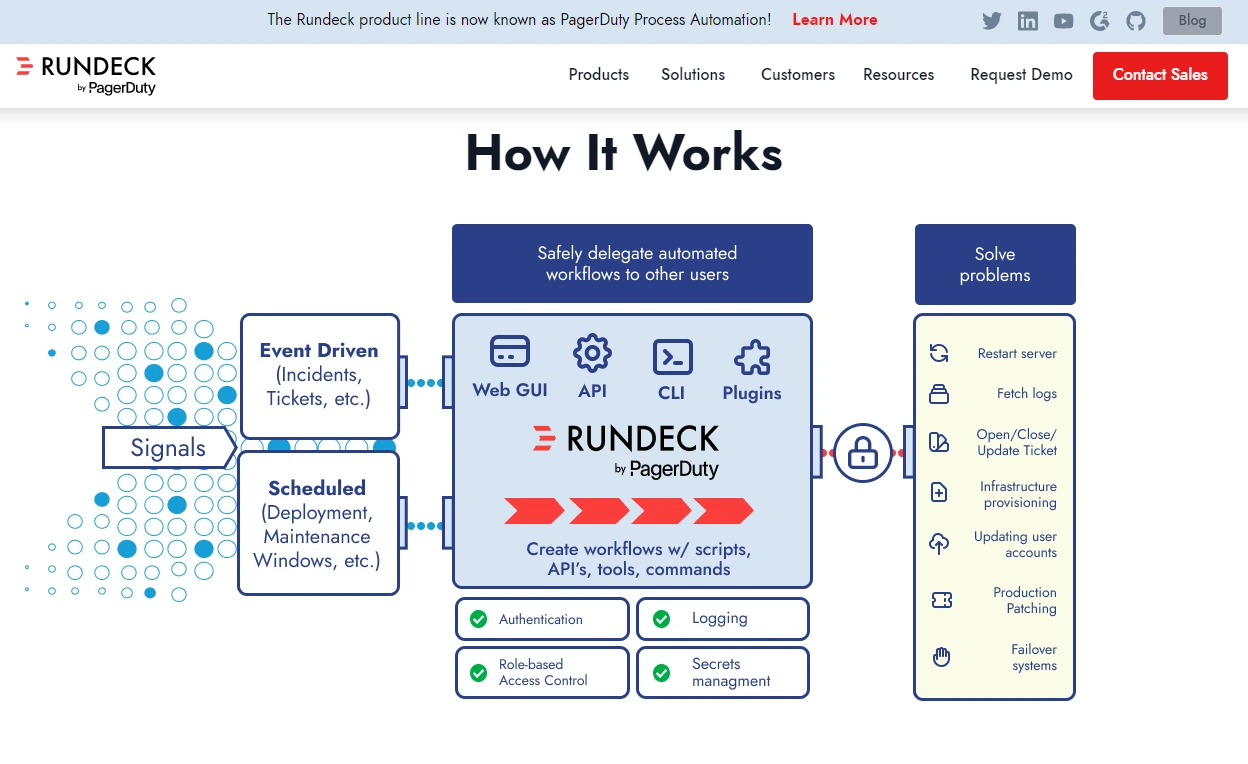
Rundeck is an open-source platform for managing cloud or data center operations. You can run tasks on as many nodes as you like using a web-based or command-line interface. Its logging, access control, workflow creation, scheduling, and the ability to integrate external sources make scalability easier.
RunDeck is a Java-based CD tool that supports both Docker-based and package installations, plus 120+ plugins and shell commands/scripts. In terms of scalability, you can assign nodes as job executors or register deployment targets.
It is also useful for establishing standard operating procedures and synchronizing actions between tools, scripts, and APIs. Build reruns, orchestration, and pipelines are also supported.
5. GoCD
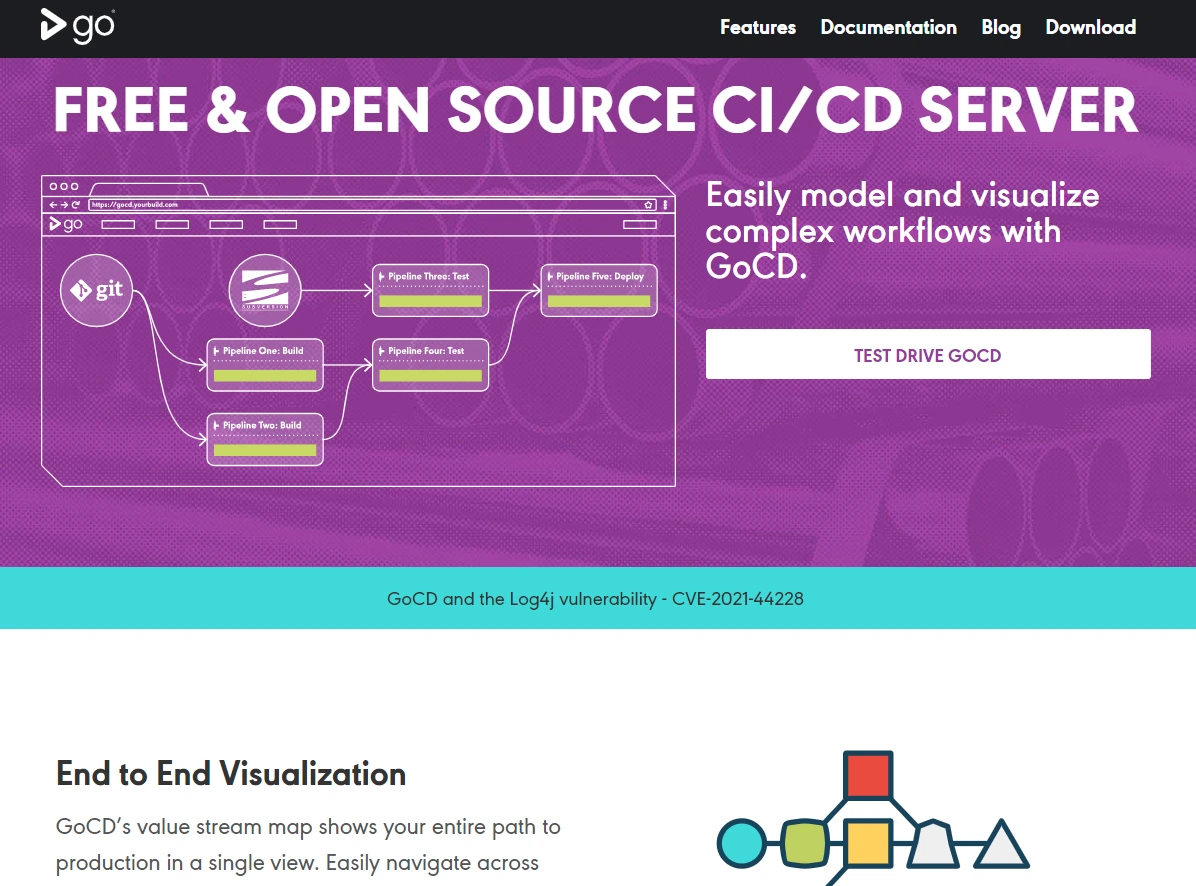
ThoughtWorks’ GoCD enables your team to create Value Stream Maps quickly so you can track every change from commit to code deployment. If something isn’t working, it’s then easy to identify both its upstream and downstream causes. Using self-service environments and manual triggers, the QA team can push builds into production after testing them.
Moreover, GoCD runs tests written in various languages, supports cross-platform and parallel executions, and reports the exact changeset and platform from which an error originated. You can also generate a straightforward bill of materials using the Compare Builds feature.
As an added benefit, GoCD’s templates system allows you to reuse pipeline configurations to keep things tidy.
6. GitHub Actions
Most people know GitHub for its code hosting, version control, and collaboration features. But with GitHub Actions, it’s now easy to build, test, and deploy software directly from GitHub.
Automated workflows help push new capabilities to users more quickly. You also get to launch workflows with GitHub events like issue creation, push, or a new release.
In addition, you can configure actions for the services you use, which are built and maintained by the community.
Something else. There are actions for everything, from building a container to deploying web services to adding a new user to your open-source project. You can also use GitHub Packages with Actions for easier package management, like version updates, faster distribution with GitHub’s global CDN, as well as dependency resolution (use your existing GITHUB_TOKEN).
7. DeployBot

If you’re looking for a straightforward deployment solution, DeployBot delivers without the need for complex scripts, cookbooks, or configurations.
DeployBot CD capabilities:
- Supports deployments via SFTP, FTP, and popular cloud services
- Offers pre- and post-deployment scripts for added customization
- Provides real-time deployment logs and notifications
- Integrates with Slack, email, and other communication platforms
- Supports environment-specific configurations and variables
Ideal for: Small to medium-sized teams that want a flexible, no-fuss deployment automation tool.
8. Travis CI
If you are using BitBucket or GitHub for version control, TravisCI provides a hosted CI/CD platform that helps you test your builds and deploy them either on-premises or in the cloud in minutes. In the past, it was a Ruby-only platform dedicated to CI.
Now, Travis CI lets you automatically detect when your team pushes new commits to your GitHub repository, run tests after every new code commit, and use a range of configurations and languages, from Python and PHP to Node, Pearl, and Java.
Also, expect clean VMs for each build, pre-installed database services, and live build views. And if you are wondering, Travis CI is compatible with Linux, FreeBSD, Windows, and macOS. Travis CI Enterprise is also available for on-prem use cases. It includes on-demand scaling, enterprise-grade security (access control), and parallel testing.
9. UrbanCode Deploy
IBM’s UrbanCode Deploy, formerly Udeploy, automates application deployments on any platform and across environments. With audit trails, versioning, and approvals for production, it facilitates continuous development and fast feedback.
Your team can use its self-service style of continuous delivery. Or, you use production deployments for more complex configurations and applications.
It comes with a drag-and-drop process designer that makes it easy to design processes. You can then deploy and monitor multi-tiered application components together.
After that, you can deploy to a public, private, or hybrid cloud of your choice. Aside from scalable distribution automation, UrbanCode also offers inventory tracking and Quality Gates for approvals.
10. Codefresh
Argo’s Codefresh was the first Kubernetes-native CI/CD solution when it launched. That means Codefresh employs container-based principles for CI/CD actions in Kubernetes (but also in Docker, Helm, and Terraform).
In terms of scalability, Codefresh empowers you to manage multiple Argo runtimes and deployments in one interface. This enterprise-grade management at scale helps you see everything in your code-to-cloud deployment.
The build-to-deploy pipeline also provides deep historical trend analysis so you can spot trends and use the insights to streamline your deliveries.
Codefresh also integrates with many of the tools you already use — from your source control manager, security scanner, and testing suite to your package manager, cloud platform, or a tool built in-house.
11. TeamCity
From a dedicated Continuous Integration tool to an improved CI/CD framework, JetBrain’s TeamCity supports seamless build management, CI server, and Continuous Delivery in one place. It enables you to develop, test, and deploy apps, containers, and various packages; multi-cloud, multi-platform, and multi-language.
You can use TeamCity to automate complex CI/CD pipelines and analyze failures in real-time. It is Java-based and offers both free and paid plans.
The free license includes up to 100 configurations and three build agents. But it offers hundreds of free plugins, supports multiple version control platforms, and integrates with IDEs like IntelliJ, Visual Studio, and Eclipse.
12. Jenkins

One reason Jenkins remains a popular automation server is its flexibility. You can configure it to build, test, deliver, and deploy code your way. It doesn’t enforce Continuous Delivery or Deployment out of the box — instead, you define exactly how your pipeline behaves based on your setup.
Jenkins CD capabilities:
- Expect a vast plugin ecosystem (over 1,800) covering nearly every DevOps need, including tools such as Maven, Got, and Docker
- Offers strong community support, documentation, and regular updates
- It supports pipeline-as-code via Jenkinsfile
- Highly customizable pipelines using Groovy-based scripting
- Cross-platform compatibility and support for nearly all programming languages
- Scales easily from small teams to large enterprise-grade deployments
Ideal for: Teams that want full control over their pipelines and are comfortable managing infrastructure hands-on.
13. GitLab CI/CD

If GitLab is your preferred code hosting and version control platform, you can automatically build, test, and publish software releases within GitLab with Auto DevOps. Auto DevOps is a set of pre-configured components and integrations that support seamless software delivery.
With Auto DevOps, you can also detect, measure, and monitor your code’s language, quality, and real-time actions.
Once enabled, it uses CI/CD templates to set up and automatically run default pipelines. Whether you have a predefined deployment configuration in place or not, Auto DevOps will still build and test your apps. It then creates the jobs required to deploy your applications to production and/or staging.
In addition, it provides Review Apps that let you preview branch-specific changes.
14. Semaphore
The Semaphore CI/CD platform is faster than GitHub Actions, CircleCI, and Travis CI. It also helps that Semaphore integrates seamlessly with GitHub. It also enables easy building, testing, and deployment actions on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
Semaphore is ideal for integrating IOS and Android applications as well — in part because it supports multiple programming languages (14).
The platform will let you run CI/CD workflows in Kubernetes and Docker images in the cloud. Its Command Line Interface (CLI) improves visibility into running jobs (inspects logs) and detects failures within seconds. With its programmable pipelines, it also facilitates parallel and sequential builds.
You can also use self-hosted agents and leverage its monorepo support to speed up development.
15. CodeMagic CI/CD
Nevercode’s CodeMagic helps build, test, and deploy cross-platform and native mobile applications rapidly. Whether you work with Native Android, IOS, React, Ionic, Cordova, or Flutter apps, CodeMagic supports it. This means you can automatically set up, configure, test, and publish to Google Play, iTunes Connect, TestFairy, Crashlytics, and HoneyApp.
Tests include UI and unit tests, test parallelization, code analysis, and real device testing.
The mobile CI/CD platform integrates seamlessly with cloud-based and self-hosted Git repositories, including GitHub, BitBucket, and Azure DevOps. You can also build your mobile apps with premium or standard Linux, Windows, or macOS instances.
Automatic testing also provides actionable notifications and feedback.
16. Octopus Deploy
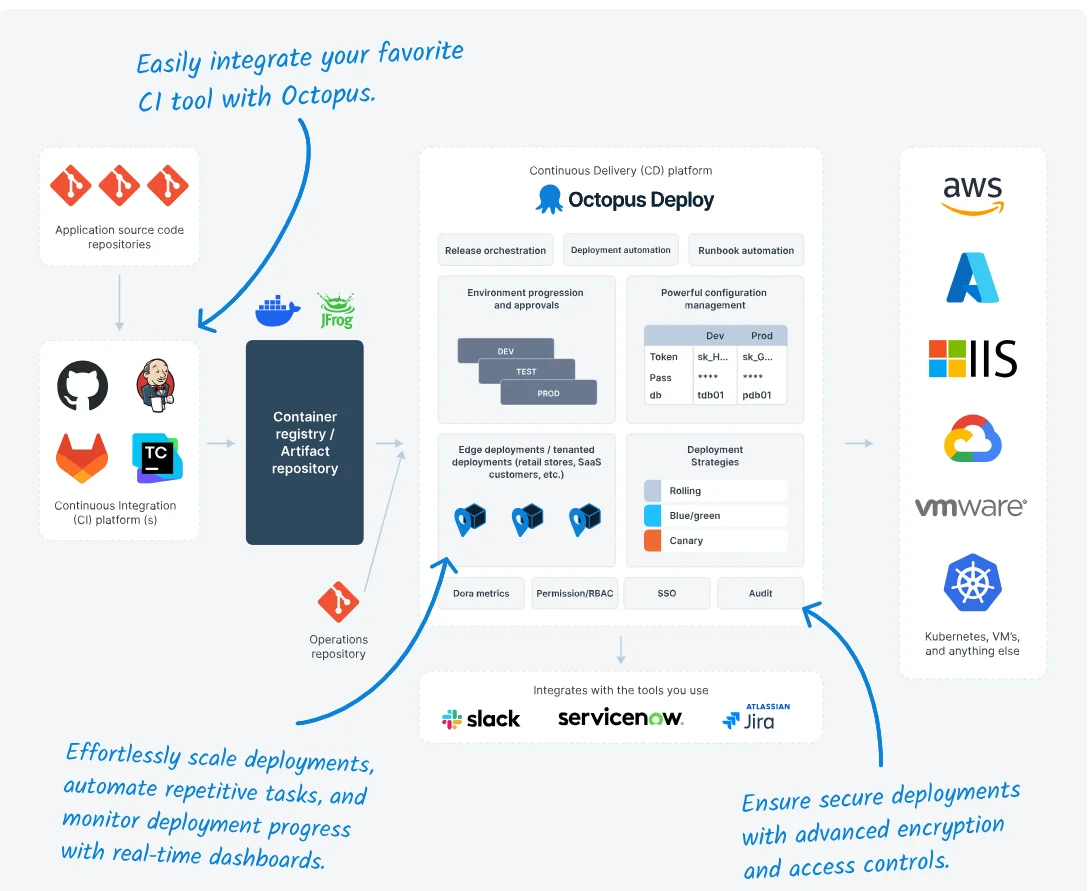
Octopus Deploy is a specialized continuous deployment tool that automates the entire release process. It’s unique for its powerful orchestration capabilities, multi-environment management, and flexible deployment strategies across diverse platforms, including Kubernetes and on-premises infrastructure.
Octopus Deploy CD capabilities:
- Supports deployments to cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments
- Offers multi-tenant deployments for managing multiple customers or environments
- Provides runbooks for automating routine operations tasks
- Integrates seamlessly with popular CI tools like Jenkins and Azure DevOps
- Includes robust role-based access control (RBAC) and audit logs for security and compliance
Ideal for: Teams seeking a thorough deployment automation platform with strong environment management capabilities.
17. Spacelift
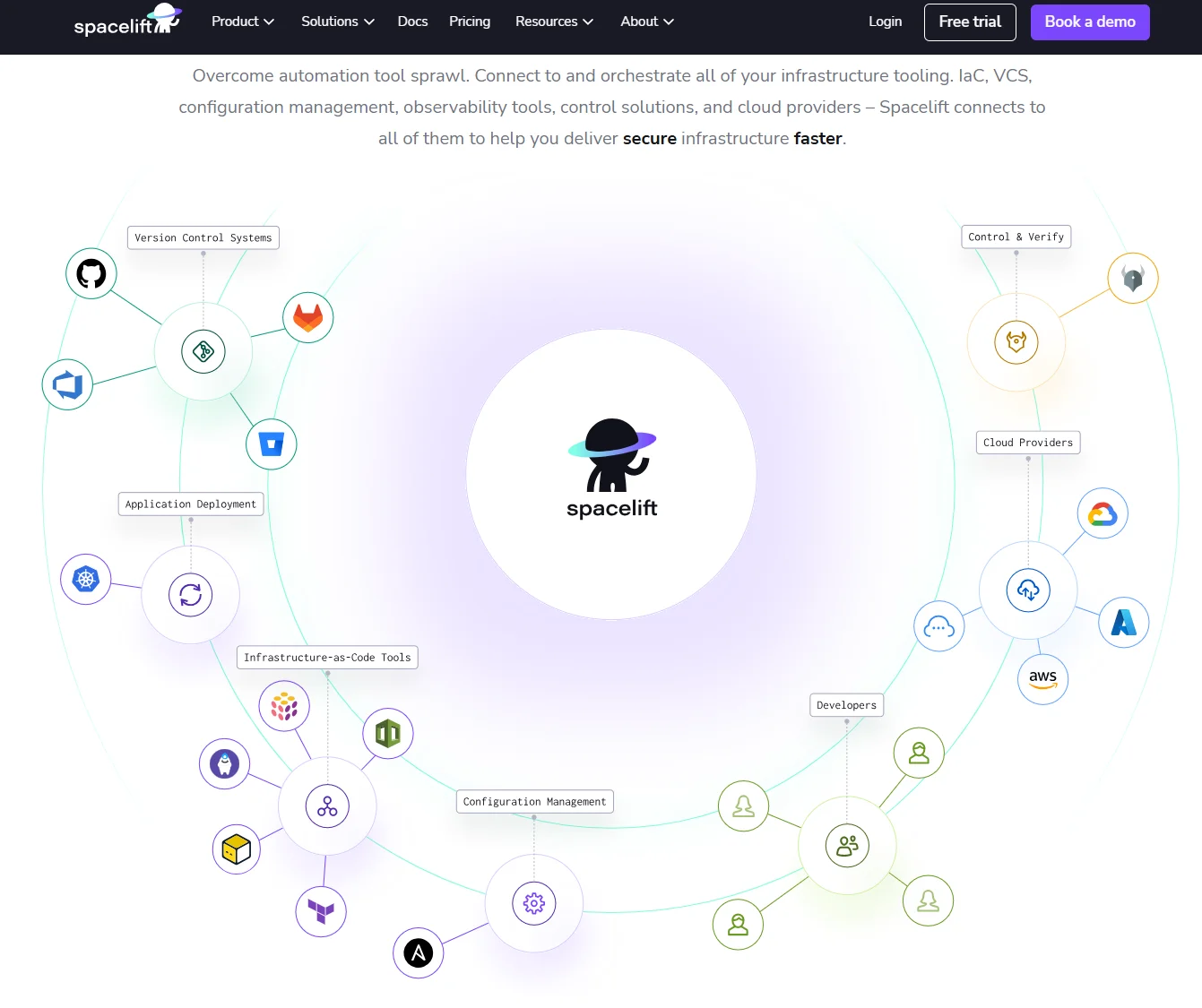
Spacelift isn’t a traditional continuous deployment tool. Instead, it acts as an orchestration layer that connects and manages your entire infrastructure stack. This includes infrastructure as code (IaC), version control systems, observability tools, governance frameworks, and cloud providers.
Spacelift CD capabilities:
- Supports Terraform, Pulumi, CloudFormation, and more
- Offers policy-as-code for governance and compliance
- Provides drift detection and automated remediation
- Integrates with major VCS providers like GitHub and GitLab
- Enable collaboration with approval workflows and notifications
Ideal for: Managing complex cloud infrastructure through code and requiring robust governance and automation.
18. DeployHQ
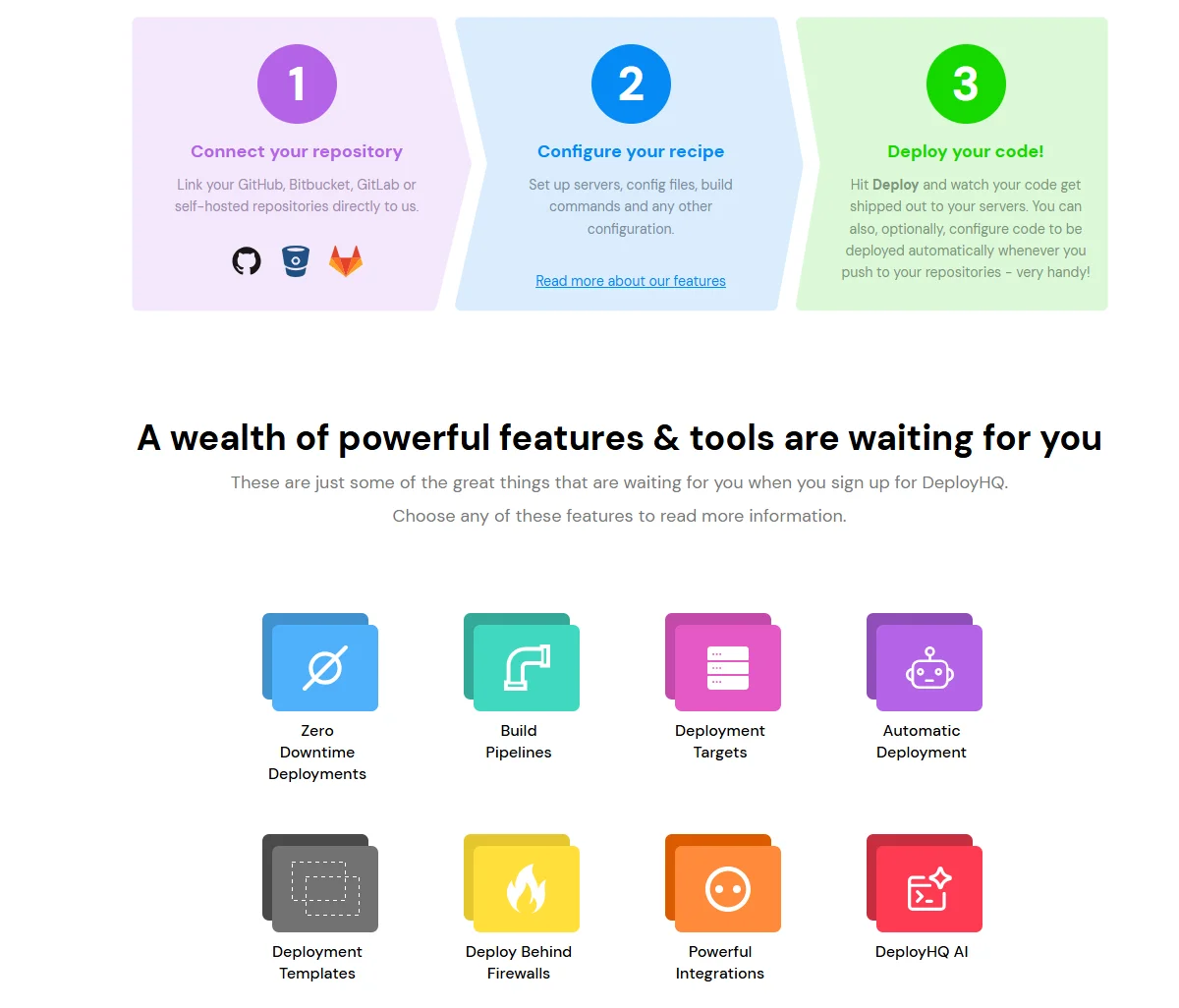
DeployHQ is a cloud-based deployment automation tool that simplifies deploying code from Git, SVN, and Mercurial repositories to various servers and hosting services.
DeployHQ CD capabilities:
- Ensures uninterrupted service by deploying updates without causing downtime
- Allows configuration of custom deployment workflows, including build commands and post-deployment scripts
- Integrates with version control systems to trigger deployments automatically upon code commits
- Supports deployments to various environments, including FTP/SFTP servers, cloud hosting platforms, and private networks
- Integrates with tools such as Slack, AWS, and Shopify to enhance deployment workflows
Ideal for: Organizations seeking a user-friendly, flexible, and efficient continuous deployment platform that also integrates well with existing tools and workflows.
19. PluralCD
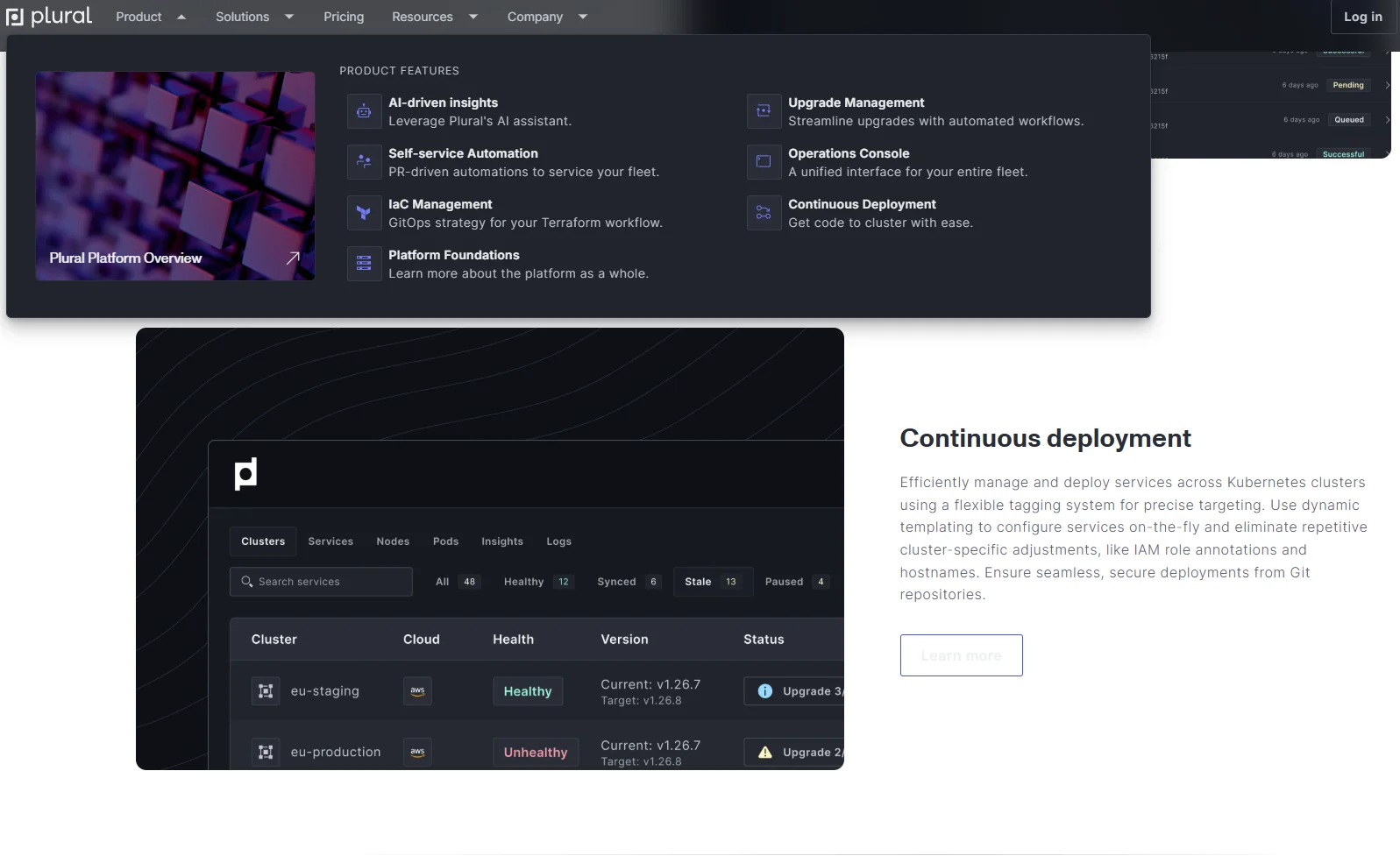
PluralCD is a Kubernetes-native continuous deployment platform that stands out for its instant, code-free cluster creation or import across multiple clouds. With its unified, GitOps-driven interface, PluralCD makes it easy to manage secure, scalable, multi-cluster application deployments.
Plural CD capabilities:
- It supports advanced deployment strategies (like blue/green and canary) without requiring custom scripts
- Supports zero-downtime upgrades
- Provides a marketplace of pre-configured applications
- Offers centralized management of clusters and applications
- Facilitates monitoring and logging integrations
- Enables role-based access control and audit logging
Ideal for: Teams deploying applications on Kubernetes seeking a streamlined and user-friendly platform.
Best Practices For Implementing Continuous Deployment
Implement these continuous deployment best practices to maximize effectiveness, boost efficiency, and keep your delivery pipeline cost-efficient.
1. Start with continuous delivery
Here’s the thing: Continuous deployment depends on a dependable, autonomous testing system. And that kind of system doesn’t appear overnight. It’s typically built and refined through trial and error during continuous delivery, where you have a manual approval step before the code reaches production.
2. Then automate everything you can
Once you’ve built your expertise in continuous delivery, start automating key processes. These include testing, security scans, deployments, rollbacks, and notifications. This ensures consistency, repeatability, and reliability across all environments.
3. Ensure robust test coverage
Include unit, integration, and end-to-end tests in your deployment pipeline. Catching bugs early (before they reach production) not only improves code quality but also helps you avoid costly rollbacks or last-minute emergency fixes.
Quick tip: Use parallel test execution to maintain speed without skipping quality.
4. Use feature flags strategically
Decouple deployment from release by hiding new features behind flags. Roll out incrementally to specific users, teams, or environments. Also, avoid deploying unfinished or risky code to all users. Try tools like LaunchDarkly, Flagsmith, or native flag features in tools like Harness.
5. Monitor performance and costs in real time
Integrate monitoring tools to track deployment metrics such as deployment frequency, error rates, rollback frequency, cost per deployment, and cost per feature.
CloudZero, for example, offers unit cost analysis like cost per deployment, per team, per environment, and more.
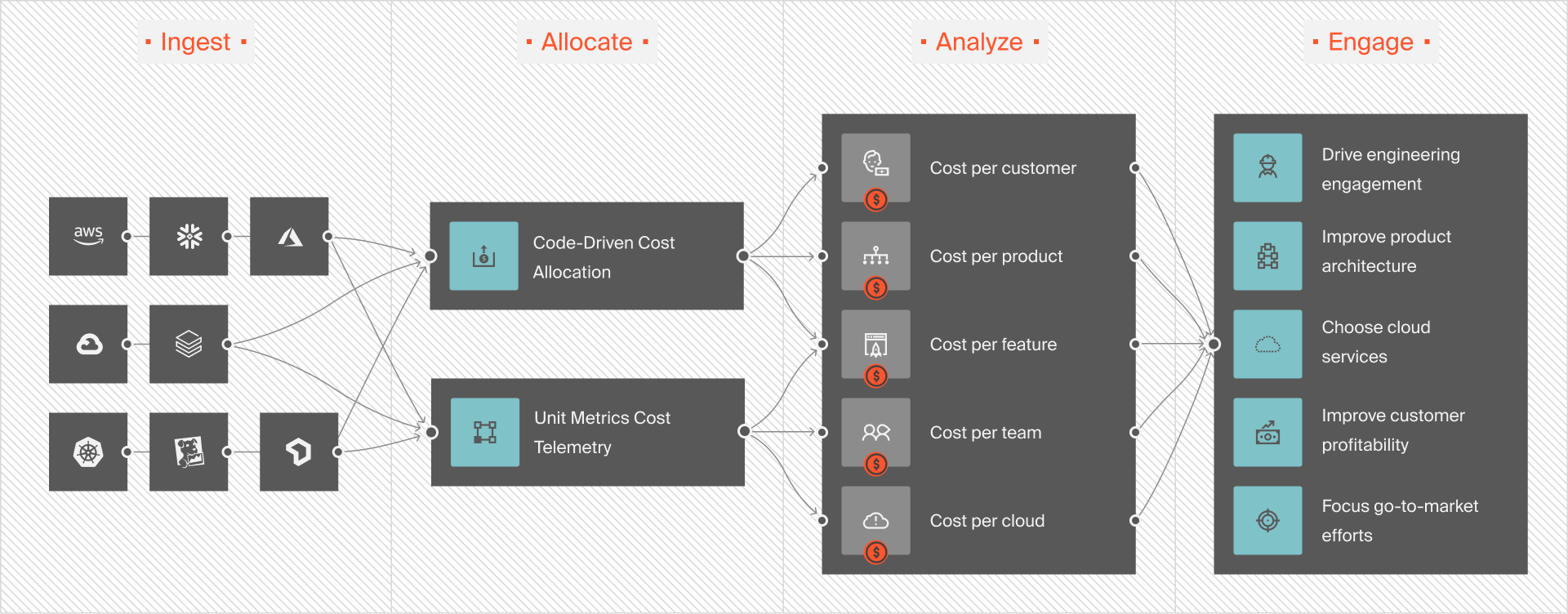
This precision enables you to pinpoint the root cause of cost spikes, so you can act quickly to prevent overspending. Curious about what you see here?  for a more hands-on experience of CloudZero.
for a more hands-on experience of CloudZero.
6. Enforce progressive delivery patterns
Use strategies like:
- Blue/Green deployments
- Canary releases
- Shadow deployments
Reduce the risk of widespread failure and test performance on subsets of traffic. Combine with monitoring to automatically roll back if KPIs drop.
7. Implement strict access controls
Use role-based access to limit who can trigger or modify deployments. This will help you prevent unauthorized changes that could disrupt production or cause unexpected costs.
8. Keep deployments small and frequent
Smaller changes are easier to test, deploy, and rollback. It also saves money; fixing small issues early is cheaper than untangling a large failure later.
9. Track metrics and continuously improve
Track and optimize for these DevOps metrics and KPIs:
- Lead time for changes
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR)
- Change failure rate
- Cost per deployment/service
Use these to identify bottlenecks and opportunities to cut waste in both time and cost.
10. Ensure immutable deployments
Package and deploy artifacts that don’t change post-deployment. This guarantees consistency between test/staging and production. It also minimizes unexpected bugs from config drift. Tools like Docker, Helm, or Spacelift help manage immutability.
You’ve Chosen A Tool. Now What? Monitor, Control, And Optimize Your Deployment Costs With Confidence
With the CD tools we’ve shared here, releasing verified builds to users is remarkably efficient. What most do not do is provide granular details about the costs of building, testing, and deploying those upgrades, updates, and patches. If you’re not monitoring how much you spend throughout your CI/CD pipeline, it’s easy to overshoot your cloud budget.
In Continuous Deployment, where every validated code change is automatically pushed to production, success depends on your ability to balance speed, stability, and cost.
That’s where CloudZero makes all the difference.
CloudZero delivers precise, real-time cost intelligence, down to the cost per customer, not just the average or total. You’ll see exactly which people, products, and processes are driving your cloud spend. That includes CD-related costs and data transfer charges between your tools.
With CloudZero, you get granular detail on:
- Cost per customer
- Cost per feature
- Cost per dev team
- Cost per environment
- Cost per project, and
- Cost per deployment
With this level of insight, you can make informed decisions about where to optimize, where to invest, and how to reduce waste — without slowing down engineering velocity or innovation.
Don’t just take our word for it.  and see why innovative teams at Duolingo, Drift, Skyscanner, and more trust CloudZero to monitor, control, and optimize their cloud spend (we just helped Drift save over $3 million).
and see why innovative teams at Duolingo, Drift, Skyscanner, and more trust CloudZero to monitor, control, and optimize their cloud spend (we just helped Drift save over $3 million).