In 2024, global data volumes reached an estimated 149 ZB, and new data generation is expected to jump to 181 ZB by 2025. According to estimates, that’s roughly 402.7 million terabytes created per day.
A large portion of this data is likely to be significant to your business. It can provide you with new insights that help you improve your product, communicate with consumers, and perform risk analysis. However, you’ll need the right tools to extract, sort, process, and analyze it.
That’s where tools like Amazon’s Elastic MapReduce (EMR) come in. In this guide, we’ll discuss what EMR is, how it works, and how it may benefit you. You’ll then be able to decide if it’s worth integrating as part of your big data strategy.
What Is Amazon EMR?
Amazon Elastic MapReduce offers tools and workflows for managing big data in the cloud. With Amazon EMR, your data scientists gain access to a web-based big data platform that can process massive amounts of data using a variety of open-source tools, including Presto, Apache Spark, and Apache Hive.
EMR also enables you to build, scale, and optimize your cloud data environment more easily compared to building and maintaining one on-premises. Here’s the thing:
Companies seeking to gain more insight and value from their data often struggle to capture, store, and analyze all of it. As data grows, it comes from more sources and becomes increasingly diverse. Thus, it needs to be securely accessed to be analyzed by different applications and lines of business.
AWS EMR can help solve these issues. EMR is a managed cluster platform that enables organizations to run Big Data frameworks on AWS, analyzing and processing large datasets more efficiently.
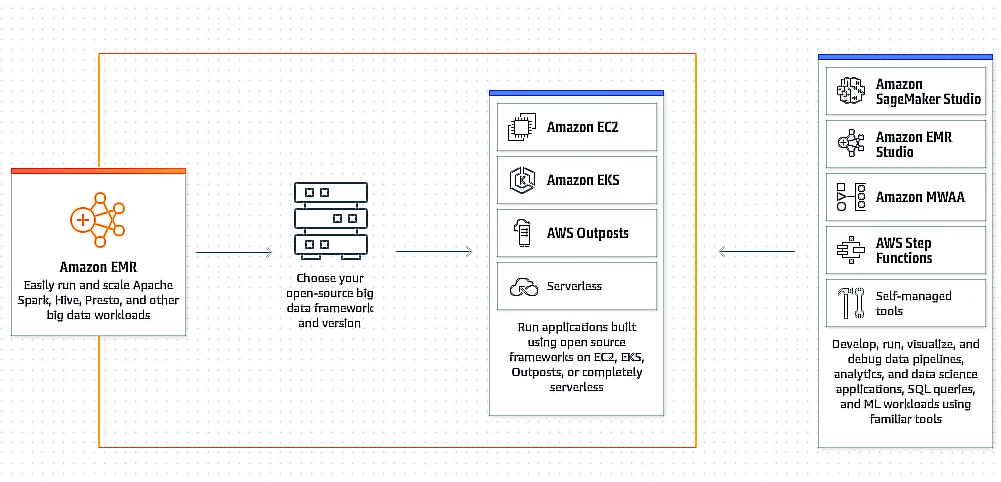
By utilizing these frameworks in conjunction with related open-source projects, such as Apache Flink and Apache Pig, you can process and analyze data for business intelligence and analytics purposes.
In addition, you can use AWS EMR to transform and move large sets of data into and out of other AWS data stores and databases, such as Amazon Simple Storage Services (Amazon S3) and Amazon DynamoDB.
Amazon EMR Features: What Can EMR Do?
AWS designed EMR to be an easy-to-use, highly scalable, and reliable platform for big data. It does that by enabling certain capabilities, such as:
- Managed big data platform – Provision, configure, and launch your clusters in minutes by eliminating a lot of the manual work it would otherwise take.
- Automated elasticity – Use custom policies to continuously scale your clusters so you can meet your workload requirements.
- Optimize big data processing costs – Deploy multiple clusters or resize a running one to handle an increase in workload or reduce capacity if there’s less work to do, thereby reducing your costs.
- Leverage a variety of flexible data stores – Use data stores like the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon RedShift, and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS).
- Take advantage of your favorite big data solutions – Select and use the latest version of your choicest open-source platform, such as Apache Spark or Hadoop applications.
- Manage your data with Amazon S3 – Use Apache Hudi to manage incremental data processing and pipeline development.
- Processing large data sets fast – EMR uses in-memory, fault-tolerant, resilient distributed datasets (RDDs) along with directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to specify how the data transformations happen.
- Secure your data with access controls – Amazon EMR application processes call other AWS services using the EC2 instance profile by default. There are three ways Amazon EMR manages access to Amazon S3 data in multi-tenant clusters: by integrating with AWS Lake Formation, integrating natively with Apache Ranger, or with User Role Mapper.
These features make Amazon EMR ideal for performing big data analytics, building scalable data pipelines, and processing streaming data in real-time. Yet, those are only a few highlighted Amazon EMR features; there are other ways to use the managed big data platform.
What Does The Amazon EMR Architecture Consist Of?
The Amazon EMR architecture comprises several layers. Each layer provides a particular set of features and functions to the cluster:
Storage layer
This is the layer that contains the cluster’s file systems. Amazon EMR lets you use several file systems with your cluster, such as:
- The location file system – A locally connected storage on which data persists only as long as an Amazon EC2 instance is running.
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) – The ephemeral, scalable, and distributed file system for Hadoop distributes data in its storage across clusters, retaining multiple copies of the data on different instances as a backup in case any instance fails.
- Elastic MapReduce File System – EMRFS extends Hadoop’s ability to access data directly in Amazon S3 as you would in HDFS. S3 stores the input and output data while HDFS stores intermediate results.
About the next layer.
Cluster resource management layer
This is where cluster resources are managed. The EMR service uses Yet Another Resource Negotiator (YARN) to centrally manage resources for multiple data processing frameworks. The layer also schedules jobs for processing.
Data processing frameworks layer
This is where data processing and analysis occur using a variety of supported frameworks. You can pick a framework based on your processing requirement, such as batch, streaming, interactive, or in-memory. The two main supported frameworks are Hadoop MapReduce and Apache Spark.
App and programs layer
This is where your apps are hosted, including Apache Hive and Pig. The applications enable the addition of capabilities such as building data warehouses, utilizing ML algorithms, and creating stream processing applications.
As for how the Amazon EMR architecture works in practice, consider Amazon EMR on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), as an example.
EMR on EKS loosely couples workloads to the infrastructure on which they run. Each infrastructure layer supports orchestration for the following layer.
You first set up Amazon EMR on EKS. Then you assign a job to Amazon EMR through a job definition. A job run is a unit of work, such as a Spark SQL query. The job’s definition includes all of the parameters specific to the application. EKS uses these parameters to determine which pods and containers to deploy.
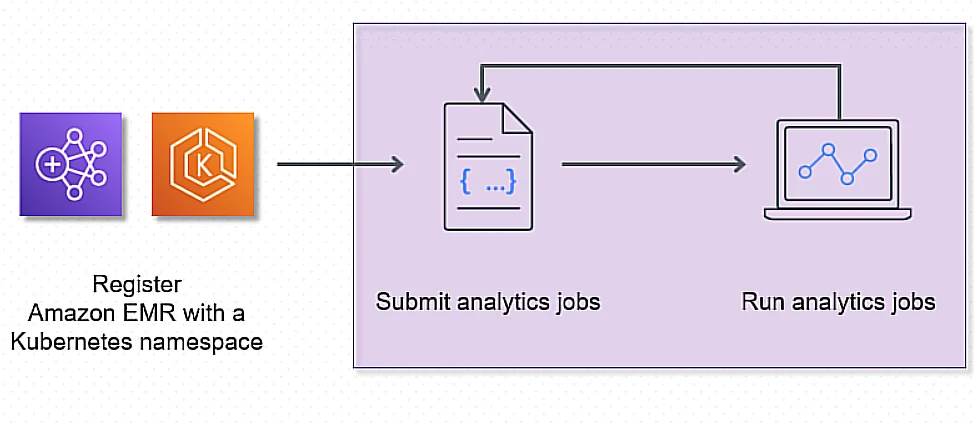
Credit: Amazon EMR at work
After that, Amazon EKS brings up the required Amazon EC2 and AWS Fargate resources to run the job.
This means:
- You can perform multiple isolated jobs concurrently thanks to this loose coupling.
- You can also use different backends to benchmark the same job.
- Or, you can also spread your job across multiple Amazon Availability Zones (AZ) to maximize availability.
Related read: AWS EKS 101: When To Use And Tips To Optimize
Here is an illustration of how Amazon EMR on EKS interacts with other AWS services.
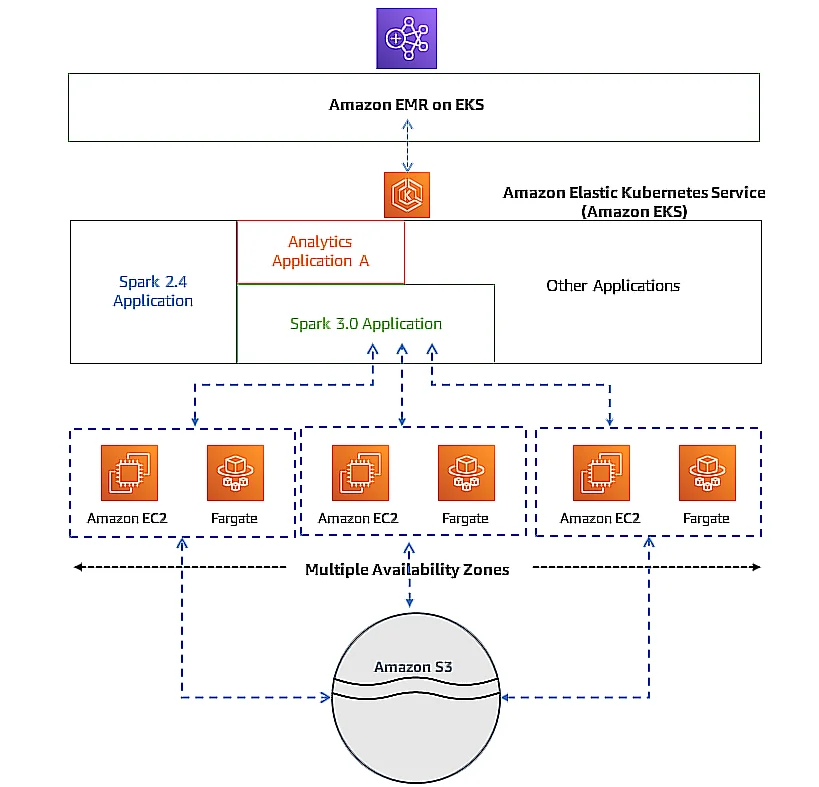
Credit: How Amazon EMR on the Elastic Kubernetes Service works with other AWS services.
How Does Amazon EMR Actually Work?
The Amazon EMR service processes your data using Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, along with open-source tools such as Apache Spark, Apache Flink, Apache HBase, and Apache Presto.
You get to pull all data into a data lake and analyze it with your choice of open-source distributed processing frameworks, such as:
- Apache Spark
- Apache Hadoop
- Apache Storm
- Presto
By far, Amazon S3 is the most popular storage infrastructure for a data lake. EMR allows you to store data in Amazon S3 and run compute tasks as needed to process that data. EMR clusters can be launched in minutes. You don’t have to worry about node provisioning, cluster setup, Hadoop configuration, or cluster tuning.
Once the processing is done, you can switch off your clusters. You can also automatically resize clusters to accommodate peaks and scale them down without impacting your Amazon S3 data lake storage.
Additionally, you can run multiple clusters in parallel, allowing them to share the same data set. EMR will monitor your clusters, retry failed tasks, and automatically replace poorly performing instances.
If you use Amazon CloudWatch along with EMR, you can collect and track metrics, logs, and audits. This approach also allows you to set alarms and automatically react to changes.
Amazon EMR Pricing
Pricing for Amazon EMR is based on several factors, including the duration of use, the method of deployment for EMR apps, and the deployment type.
Check this out:
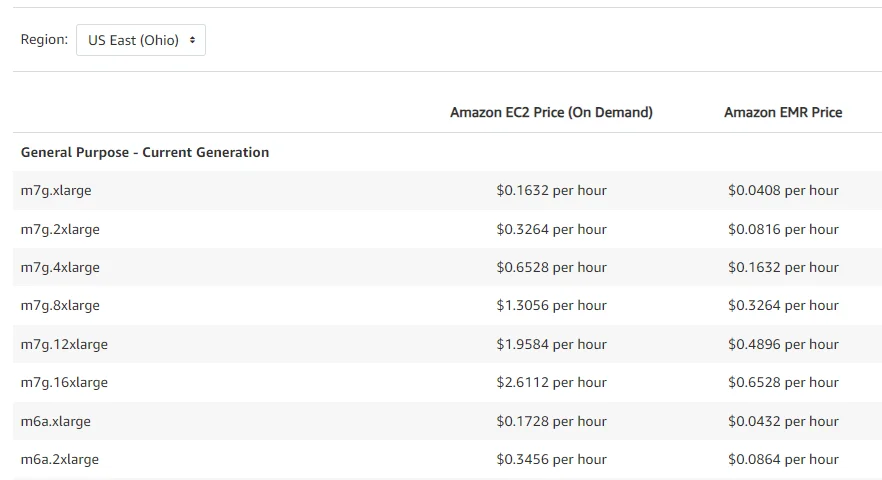
How pricing for Amazon EMR on EC2 works
Now we explain. In terms of duration, Amazon EMR billing is based on the time you use it, with a minimum requirement of 60 seconds. You’ll likely pay per hour, though.
In terms of how you deploy your EMR apps, you can either run Amazon EMR with EC2 instances or AWS Fargate. That means you pay a separate fee for the underlying EC2 or Fargate servers in addition to the EMR rate per hour.
As for deployment type, you can choose from four options:
Pricing for Amazon EMR on EC2 instances
Pricing is based on the AWS Region, instance type, duration, and purchase option (On-Demand, Reserved Instances, or Spot Instances). For example, it costs $0.1728/hour plus $0.0432/hour to run EMR on an m6a.xlarge EC2 instance in the US East (Ohio) Region.
Pricing for Amazon EMR on EKS clusters
The service charges you based on the memory and vCPU resources you request to run a Pod or a Task (from the time the image download begins to when it completes, to the nearest second). There’s a 60-second minimum requirement. For example, pricing in the US East (Ohio) Region is $0.01012/vCPU/hour and $0.00111125/GB/hour.
Pricing for Amazon EMR on AWS Outposts
Amazon EMR charges similarly to cloud-based instances of EMR.
Pricing for Amazon EMR serverless
As a serverless service, pricing is based on the amount of compute (vCPU and memory) and storage resources your apps consume, aggregated across all your worker nodes. It is also based on the operating system you run them on.
For example, it costs $0.052624/vCPU/hour and $0.0057785/GB/hour for compute and memory, as well as $0.000111/GB/hour for any extra ephemeral storage you add to the default 20 GB.
Of course, you can find the latest pricing updates for Amazon EMR on the relevant AWS pricing pages.
When To Use AWS EMR
AWS EMR makes deploying distributed data processing frameworks easy and cost-effective. By decoupling compute and storage, both can grow independently for better resource utilization.
In the past, frameworks like Apache Spark and Hadoop were difficult to operate on-premises. They required costly hardware, constant upgrades, and complex management. Centralized clusters were often underutilized during idle periods and overloaded during peak demand.
EMR solves these challenges with flexible, on-demand clusters. You pay a per-second rate only for the resources you use, with 24/7 AWS support. Using spot pricing, you can cut costs by up to 90%. IDC also found EMR delivers a 342% ROI over five years compared to on-premises systems.
Real-World Applications Of Amazon EMR
Here are some real-world applications where organizations rely on EMR for scale, speed, and flexibility:
Log processing and operational analytics
Enterprises often funnel logs from applications, servers, and IoT devices into S3. EMR can parse and enrich these logs at scale, then feed results into tools like Amazon OpenSearch or SIEM systems. This supports real-time monitoring, compliance reporting, and incident response.
Machine learning at scale
Data science teams use EMR to prepare massive datasets for machine learning. EMR integrates with frameworks such as Apache Spark MLlib and TensorFlow to train predictive models on a wide range of applications, including churn prediction and supply chain optimization. Its ability to scale clusters on demand means training jobs run faster and at lower cost.
Clickstream and customer behavior analytics
E-commerce and streaming platforms generate massive clickstream data from websites and apps. EMR processes terabytes of raw logs to build customer profiles, segment audiences, and run recommendation models. For example, online retailers can combine EMR with S3 and Redshift to deliver personalized shopping experiences.
Fraud detection and real-time analytics
EMR Serverless supports near-real-time data processing to detect anomalies or suspicious patterns.
What Are The Benefits And Limitations Of Amazon EMR?
Amazon EMR is nearly unbeatable, especially when coupled with some of Amazon’s other web-based services. Nevertheless, while its benefits may be self-evident and many, it does have its limitations. In this section of the guide, we’ll summarize some of Amazon EMR’s pros and cons.
Amazon EMR Pros:
- Lower costs – No physical servers; pay only per second for what you use.
- Time-saving – No manual setup; EMR handles provisioning and scaling.
- Better resource use – Decouples compute and storage, scales up or down automatically.
- 24/7 support – Round-the-clock AWS customer service included.
Other benefits include fast spin-up times for EC2 instances. Essentially, this is an EMR service that can be run on AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). This allows for increased data security.
Amazon EMR Cons:
- Complex interface – Steep learning curve; often requires training or certified experts.
- AWS-only storage – Works only with Amazon storage, so data from other clouds must be migrated.
AWS EMR’s other limitations are service-based. For instance, Amazon EMR Studio is only available in specific regions, including East US, West US, Asia-Pacific, Canada, and EU. You can only set a single Amazon VPC with a maximum of five subnets for an EMR studio. However, you can create multiple EMR studios and associate them with different VPCs and subnets.
How To Really Understand Amazon EMR Costs
AWS EMR can help you change your rigid in-house cluster infrastructure and provide you with hassle-free Hadoop management. It can also significantly reduce the time required for data processing. However, as with most AWS products, its pricing can be a little incomprehensible.
Amazon charges you a per-second rate that is also tied to the number of clusters you are running. Additionally, you’ll need to pay for the EC2 server and Amazon’s Elastic Block Store (EBS). If you’re running a large relational database, you’ll need to consider the cost of using the AWS Database Migration Service to move and host your data.
This is only just the tip of the iceberg. To get the most out of EMR, you’ll likely need to employ a host of other AWS tools, such as CloudWatch and S3 (for logs). Tracking and managing these costs can be quite daunting. It’s different when you use ClouZero.
How CloudZero Can Help You
With CloudZero, however, you gain complete insight into your AWS cloud spend. CloudZero’s cost intelligence platform maps costs to your products, features, services, dev teams, and more. For example, you’ll see your cost per individual customer, per product feature, per service, per environment, and more.
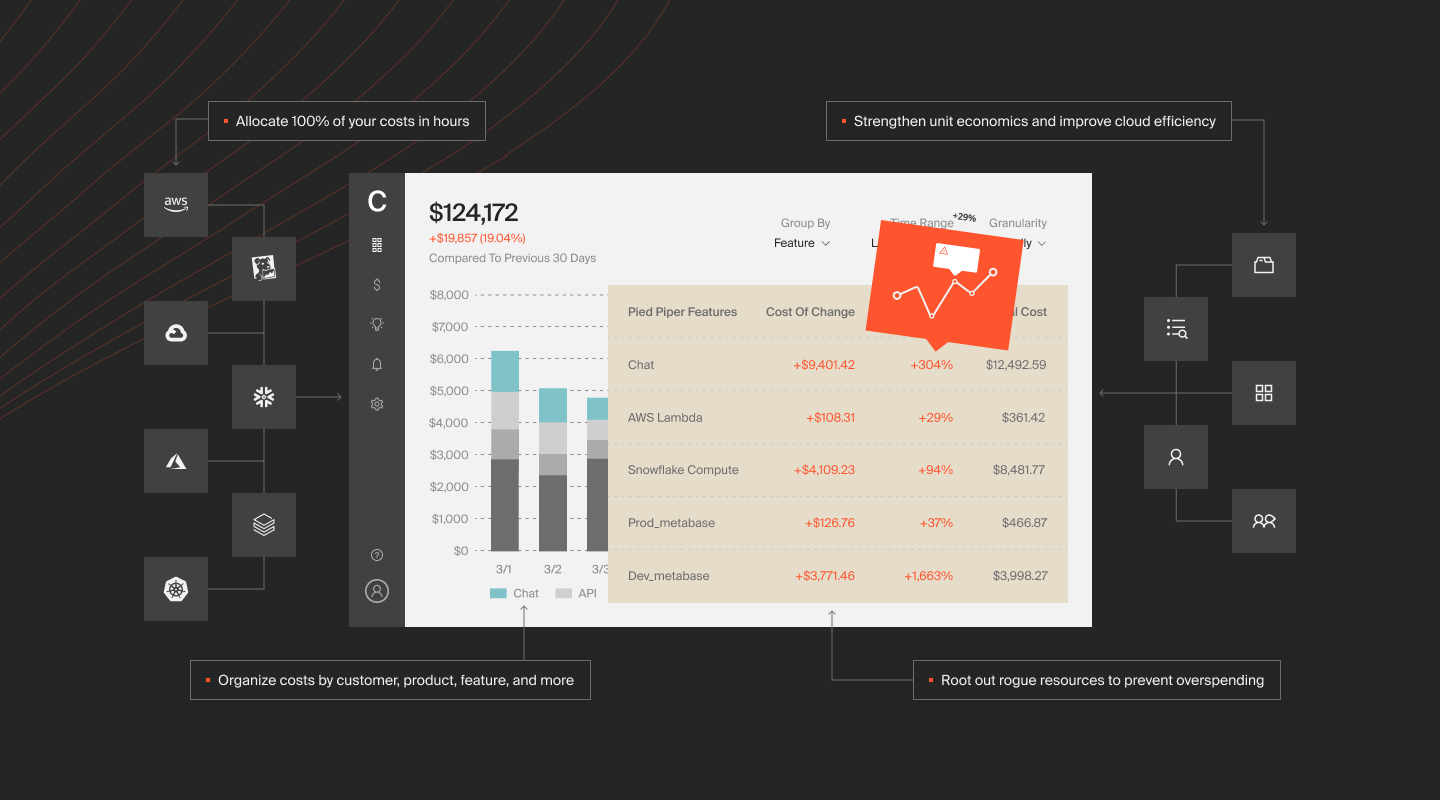
CloudZero also automatically detects cost issues in real time. You’ll then receive context-rich alerts via Slack so you can stop the bleeding before it runs for days or weeks. This ensures you catch potential overspending before it hurts your COGS and margins.
With cloud cost intelligence, you’ll be able to drill into cost data from a high level down to the individual components that drive your cloud spend — and see exactly how services drive your cloud costs and why.
That means you’ll know exactly who, what, and why your cloud costs are changing across AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, Snowflake, Datadog, etc — right from one platform.
Drift has saved over $4 million using CloudZero. Upstart was able to reduce cloud costs by $20 million with the help of CloudZero. Here’s your chance to control your Amazon EMR costs.  to see CloudZero in action for yourself. It’s on us — at no risk to you.
to see CloudZero in action for yourself. It’s on us — at no risk to you.