More enterprises continue to adopt managed data integration services like AWS Glue. The global ETL tools market alone reached $7.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to soar beyond $22 billion by 2032. Likewise, the broader data integration market is on track to grow from $17.6 billion in 2025 to over $33 billion by 2030.
AWS Glue stands as one of the popular managed ETL services in the market today.
This article explains what AWS Glue is, when to use it, its strengths and limitations, as well as the best part, how to optimize its costs.
What Is AWS Glue?
AWS Glue provides a serverless solution that simplifies the entire process of discovering, preparing, and combining data for application development, machine learning, and analytics.
To adequately define what AWS Glue is, you’ll first need to understand how data integration works.
In essence, data integration is the process of setting up and combining data for analytics, application development, and machine learning.
It’s made up of multiple procedures – such as identifying and generating data from different sources, which is then followed by enriching, cleaning, normalizing, and merging data. In the end, the data is loaded and organized in data warehouses, databases, and data lakes.
AWS Glue streamlines all data integration procedures, enabling you to leverage your merged data quickly. That means you can analyze and leverage the data in minutes, rather than waiting forever.
Considering these capabilities, AWS Glue is technically described as a fully-managed ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) data integration solution.
Amazon even goes on to explain that the whole system is designed to provide an easy and cheap way to not only categorize your data, but also clean, enrich, and transfer it efficiently between different data streams and data stores.
It doesn’t run across one front, though. Rather, AWS Glue comes as a multi-faceted system that powers data integration through several components.
AWS Glue features: What can the AWS data integration service do?
AWS Glue provides the following capabilities:
- Run ETL jobs as newly collected data arrives – AWS Glue, for instance, lets you automatically run ETL jobs when new data comes into your Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets.
- Data Catalog – Use it to rapidly browse and search multiple AWS datasets without needing to move the data. The cataloged data is immediately searchable and queryable with Amazon Athena, Amazon Redshift Spectrum, and Amazon EMR.
- AWS Glue Studio -It supports no-code ETL jobs. AWS Glue Studio enables you to visually build, run, and monitor AWS Glue ETL jobs. Your ETL jobs can move and transform data with a drag-and-drop editor. AWS Glue auto-generates the code.
- Multi-method support – Supports a variety of data processing approaches and workloads, such as ETL, ELT, batch, and streaming. You can also use your favorite method, from drag and drop to writing code to connecting with your notebook.
- AWS Glue Data Quality – Creates, manages, and monitors data quality rules automatically. This ensures high-quality data throughout your data lakes and pipelines.
- AWS Glue DataBrew – This enables you to discover and interact with data directly from your data lake, data warehouses, and databases. You can do that with Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, AWS Lake Formation, Amazon Aurora, and Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS).
Also, DataBrew has over 250 prebuilt transformations to automate data preparation operations, including filtering anomalies, correcting invalid values, and standardizing formats.
What are the components of AWS Glue?
Under the hood, you’ll find these AWS Glue components:
- The console – The AWS Glue console is where you define and orchestrate your workflow. There are several API operations you can call from here to perform tasks, such as defining AWS Glue objects, editing transformation scripts, and defining events or job schedules for job triggers.
- AWS Glue Data Catalog – This is basically a central repository for your metadata, built to hold information in metadata tables — with each table pointing to a single data store. In other words, it acts as an index to your data schema, location, and runtime metrics, which are then used to identify the targets and sources of your ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) jobs.
- Job Scheduling System – The job scheduling system, on the other hand, is intended to help you automate and chain your ETL pipelines. It comes in the form of a flexible scheduler that’s capable of setting up event-based triggers and job execution schedules.
- Script – The AWS Glue service generates a script to transform your data. Alternatively, you can upload your script via the AWS Glue API or console. Scripts extract data from your data source, transform it, and load it into your data target. In AWS Glue, the scripts run in an Apache Spark environment.
- Connection – This refers to a Data Catalog object that comprises properties for connecting to a given data store.
- Data store – This is where your data is stored persistently, such as relational databases and Amazon S3.
- Data source – This refers to a data store that serves as input to a transform or process.
- Data target – This is the data store that a process writes to.
- Transform – Refers to the code logic used to change the format of your data.
- ETL Engine – AWS Glue’s ETL engine is the one component that handles ETL code generation. It automatically provides this in Python or Scala, and then gives you the option to customize the code.
- Crawler and Classifier – A crawler retrieves data from the source using integrated or custom classifiers. This AWS Glue component creates or uses metadata tables pre-defined in the data catalog.
- Job – This is the business logic that performs an ETL task in AWS Glue. Internally, Apache Spark with Python or Scala writes the business logic.
- Trigger – This starts ETL job execution at a specific time or on demand.
- Development endpoint – This creates a development environment in which your ETL job script can be developed, tested, and debugged.
- Database – It creates or accesses source and target databases.
- Table – You can create one or more tables in the database for use by the source and target.
- Notebook server – An online environment for running PySpark statements, a Python dialect for ETL programming. With AWS Glue extensions, you can run PySpark statements on a notebook server.
Together, these components enable you to streamline your ETL workflow. Here’s an image illustrating how AWS Glue components work:
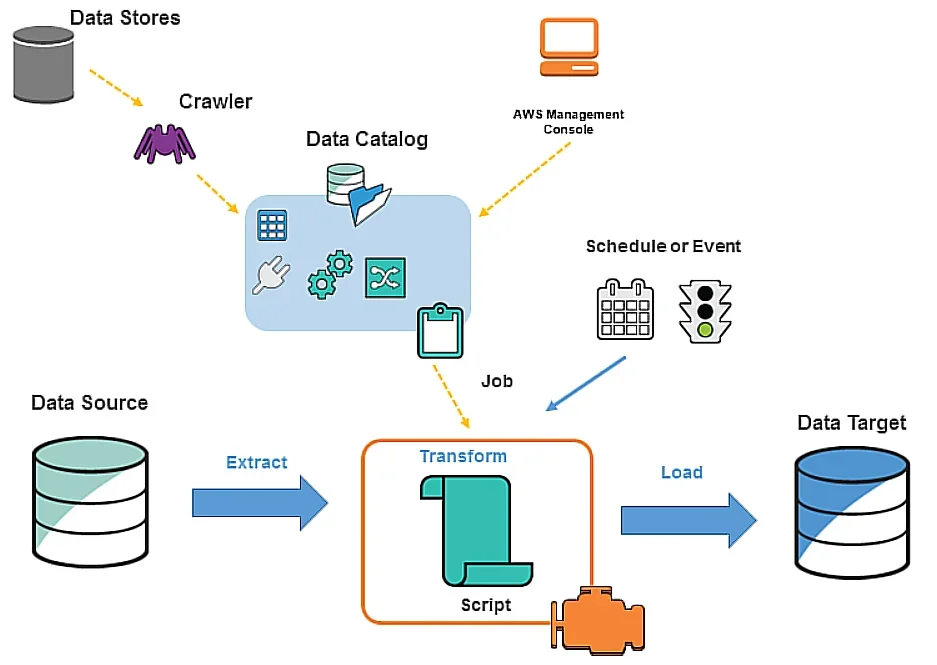
AWS Glue components
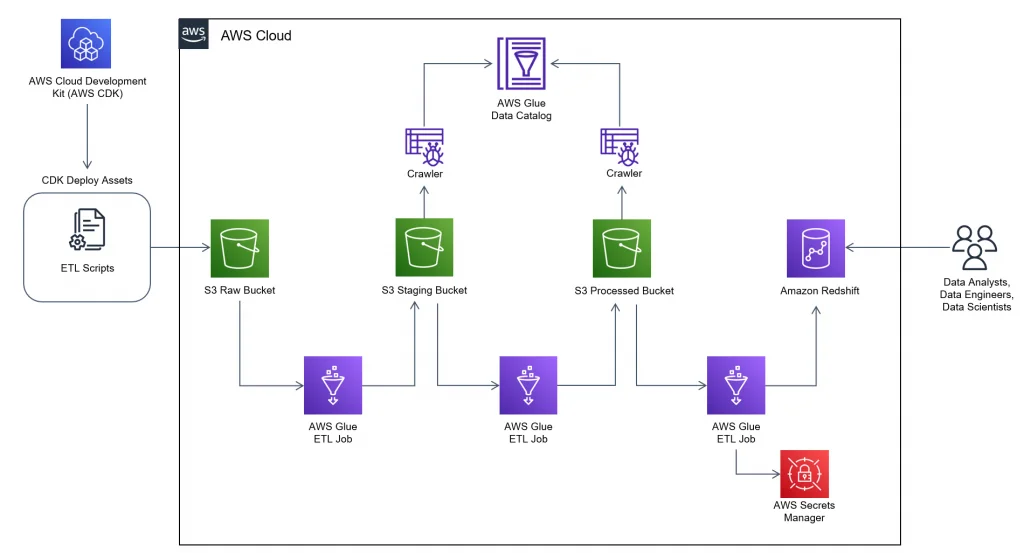
That’s one way to look at how AWS Glue works at the architectural level. Here’s a quick look at a reference architecture when building a data pipeline using the AWS Glue product family.
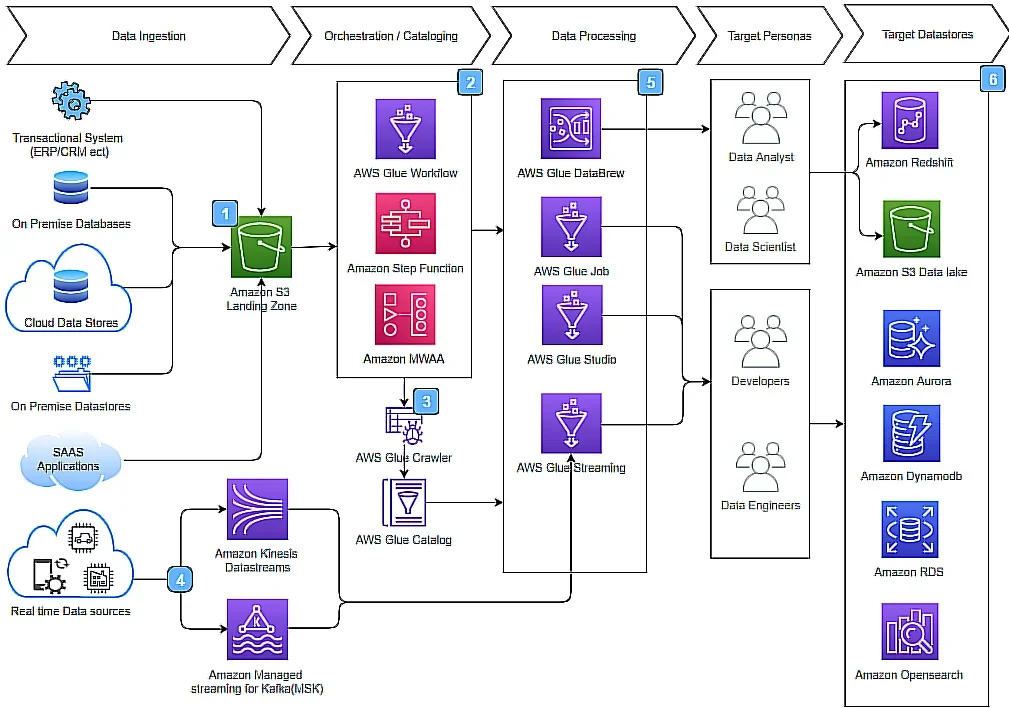
When Would You Want To Use AWS Glue?
While AWS Glue continues to serve different types of users, it’s particularly popular among organizations that are trying to put up an enterprise-class data warehouse.
They benefit from the fact that AWS Glue seamlessly facilitates the movement of data from various sources into their data warehouse.
The process itself is pretty simple — you use AWS Glue to validate, cleanse, organize, and format data, which is ultimately stored in a centrally accessible data warehouse. You’ll further notice that the platform enables you to load such data from both data streaming and static sources.
The key point of this approach is to gather critical data from various business areas and consolidate it into a central data warehouse.
As such, you should be able to conveniently access and compute all your business information from a common source. You can also:
- Automatically scaling resources to cover the current needs of your situation.
- Error handling and retrying to avoid stalling issues.
- Gathering KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), metrics, and logs of your ETL procedures for the sake of monitoring and reporting.
- Executing ETL jobs based on specific events, schedules, or triggers.
- Automatically recognizing database schema changes and subsequently tweaking the service to respond accordingly.
- Generating ETL scripts to enrich, denormalize, and transform data during its transfer from source to target.
- Identifying your data stores’ and databases’ metadata, and then proceeding to archive them in AWS Glue Data Catalog.
What Are The Benefits And Limitations Of Using AWS Glue?
As with everything else in the world of big data computing, AWS Glue has its strengths and weaknesses. Although Amazon has, admittedly, done a fairly good job on it, there are still a couple of things about it that you might find a bit limiting.
Here’s a breakdown of both sides:
Pros of AWS Glue
- Serverless – No need to manage infrastructure; AWS handles it
- Automatic ETL code – Generates Scala or Python code to speed up workflows
- Data visibility – Glue Data Catalog tracks and organizes data assets
- Developer endpoints – Lets engineers test and customize ETL scripts
- Job scheduling – Supports event-based, scheduled, or on-demand jobs
- Pay-as-you-go – Only pay when you use it, no long-term contracts
Cons of AWS Glue
- Technical barrier – Requires knowledge of Spark, Python, or Scala
- Limited languages – Only supports Python and Scala
- AWS-only – Doesn’t integrate well outside the Amazon ecosystem
AWS Glue Vs EMR (And Other Alternatives)
As it turns out, AWS Glue is not the only managed Amazon service that’s capable of handling big data. Other solutions include AWS Data Exchange, AWS Kinesis, AWS EMR, AWS Redshift, Amazon Athena, Apache Airflow, or AWS Step Functions. Here’s how they differ:
- AWS EMR (Elastic MapReduce): Ideal for heavy big data/ML workloads needing full Spark or Hadoop cluster control. Often cheaper than Glue at scale, but requires more configuration and ongoing ops.
- AWS Step Functions: AWS-native workflow orchestration. Great for coordinating Glue jobs, Lambdas, or other services in event-driven pipelines.
- Apache Airflow: Open-source orchestration, often used alongside Glue. Airflow excels at chaining tasks across multiple services, but it requires ongoing maintenance. Learn more about cloud orchestration here, and some of the best tools.
- Amazon Redshift: Best for real-time streaming pipelines and event-driven workloads. Redshift can replace Glue ETL in some scenarios, but it doesn’t offer the same level of flexibility in data preparation across varied sources.
- Amazon Athena: A serverless query service that lets you run SQL directly on S3. It’s simpler than Glue and cost-effective for ad hoc queries, but not a complete ETL solution.
- AWS Kinesis: Designed for real-time data streams, making it complementary to Glue rather than a direct replacement. Use it when your pipelines involve high-volume, low-latency streaming data.
Also, you should note that since AWS Glue is serverless, it tends to be a bit costlier than AWS EMR and AWS’s other services.
AWS Glue cost inefficiency at scale
AWS Glue is convenient, but it can become expensive at scale. At $0.44 per DPU-hour, large or long-running ETL jobs add up fast — especially if over-provisioned or left to reprocess data unnecessarily.
Ways to optimize costs:
- Right-size DPUs and enable auto-scaling.
- Use job bookmarks to avoid reprocessing data.
- Offload quick queries to Athena or Redshift Spectrum.
- Schedule batch jobs strategically.
You can also take advantage of CloudZero to track Glue spend down to the job, team, or feature.
How Can You Measure And Monitor Your AWS Glue Costs?
While Amazon Glue’s pay-as-you-go rate of $0.44 per DPU might seem reasonable at first, organizations commonly find themselves with bloated bills after prolonged use, which often run into thousands of dollars per month in extra or unnecessary costs.
Such cost overruns are mostly due to poor AWS cost management practices.
Something as simple as tracking your AWS Glue spend can be a challenge — since Amazon doesn’t readily provide comprehensive insights (like what you’re spending and why or how specific services drive your product and feature costs).
With CloudZero, however, you gain complete insight into your AWS cloud spend. CloudZero’s cloud cost intelligence maps costs to your products, features, dev teams, and more. The platform also automatically detects cost issues and alerts you before they run for days or weeks.
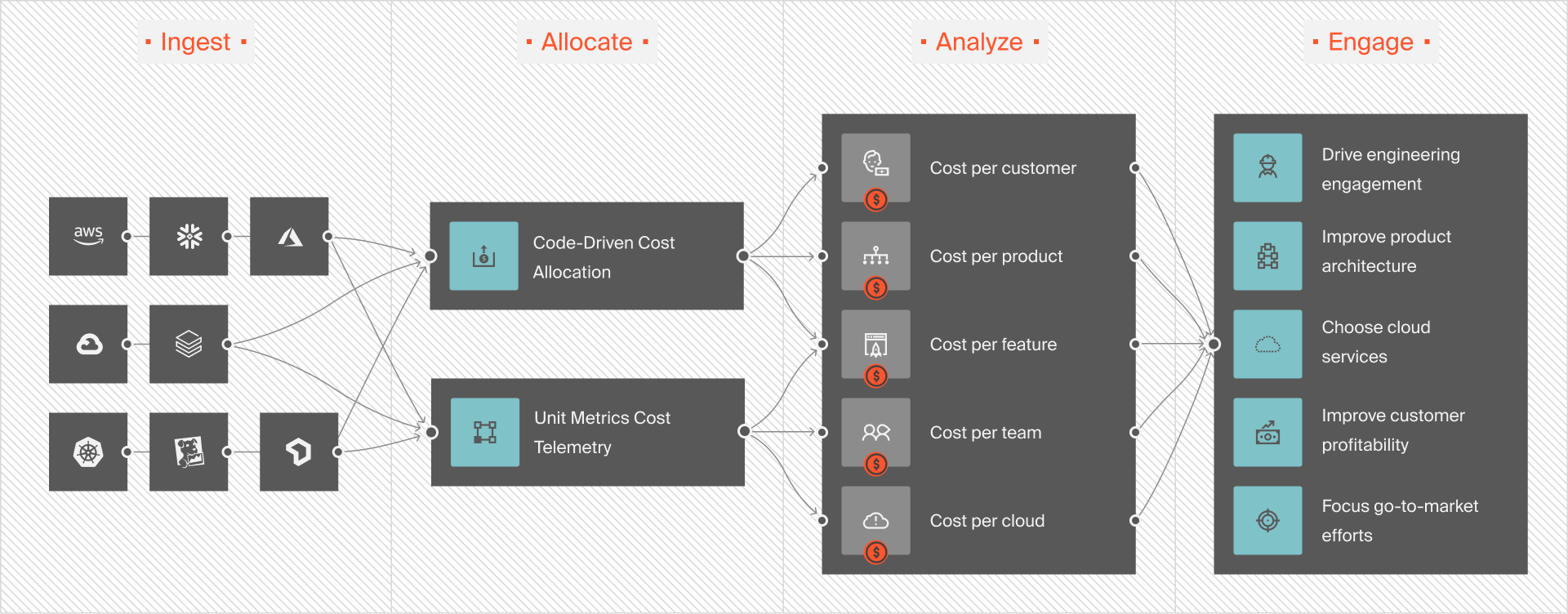
With cloud cost intelligence, you’ll be able to drill into cost data from a high level down to the individual components that drive your cloud spend — and see exactly how services drive your cloud costs and why.
Frequently Asked Questions About AWS Glue
This AWS Glue FAQs section answers common questions about the serverless data integration service.
Is AWS Glue good for ETL?
AWS Glue delivers a fully managed ETL service that simplifies data preparation and loading for analytics. AWS Management Console enables you to create and execute ETL jobs in a few clicks.
What is AWS Glue used for?
Using AWS Glue, you can discover, prepare, move, and integrate data from multiple sources for analytics, machine learning (ML), and application development.
Does AWS Glue use SQL?
The AWS Glue Data Catalog is compatible with the Apache Hive metastore. You can specify your development endpoints and AWS Glue jobs to access the Data Catalog as your external Apache Hive metastore. Then you can directly execute Apache Spark SQL queries against the tables you have stored in the Data Catalog.
Why use AWS Glue over Lambda?
Glue handles large workloads faster than Lambda by using parallel processing.
Also, Lambda requires more complexity or code to work with data sources (such as Amazon Redshift, Amazon RDS, Amazon S3, databases running on Amazon ECS instances, Amazon DynamoDB, and more). In addition, Lambda has a 15-minute timeout maximum, whereas you can configure AWS Glue to run for significantly longer.
What language does AWS Glue use?
The ETL scripts in AWS Glue are written in Python or Scala.
Can AWS Glue write to S3?
Yes. AWS Glue for Spark reads and writes to Amazon S3. By default, AWS Glue for Spark supports data formats such as CSV, Avro, JSON, ORC, and Parquet.
What database does AWS Glue use?
Various. AWS Glue automatically identifies structured and semi-structured data hosted on an Amazon S3 data lake, a data warehouse in Amazon Redshift, and a variety of databases running on the AWS cloud.
Can AWS Glue connect to Azure?
Yes, through the Azure Data Lake Storage Connector for AWS Glue. The connector facilitates the connection of AWS Glue jobs for data extraction from Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (ADLS). It also simplifies loading data into Azure ADLS.
Can AWS Glue replace Amazon EMR?
No. Both have a role to play and excel in different areas. See the AWS Glue vs Amazon EMR section to compare the two services — and decide which one is right for you and when.
When should you not use AWS Glue?
AWS Glue does not support job bookmarks and grouping small files, among other limitations.